In early prehistory, humans fed on plants and game. They had to move constantly to follow the herds of animals or to exploit the resources of a new territory. They were therefore nomadic, as they were required to move to meet their needs. Gradually, humans grouped together and settled in a given territory in order to carry out livestock farming and agriculture. In other words, they became sedentary.
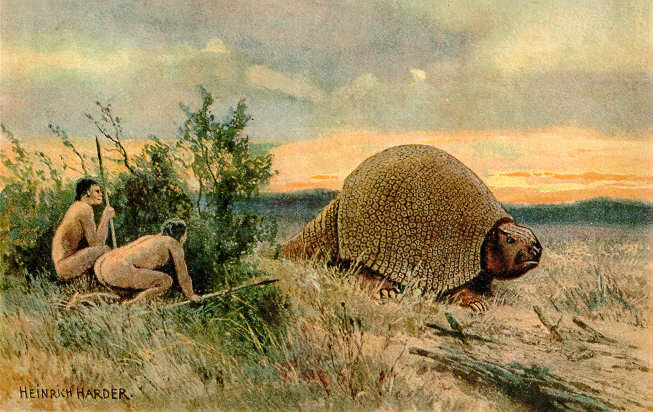

Artwork representing nomadism
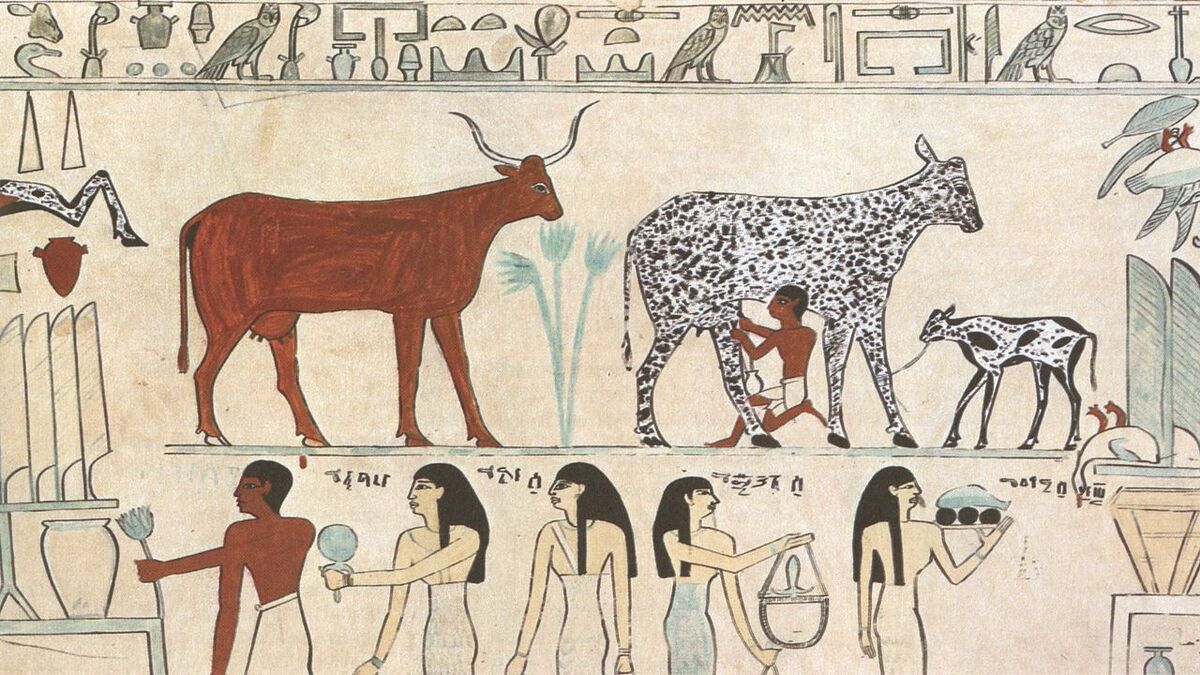

Artwork representing the sedentary revolution.
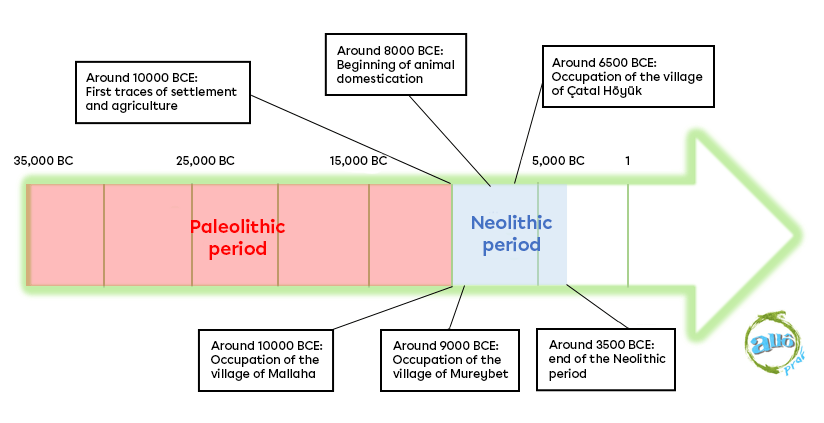
Early humans gathered in small fortified villages to protect themselves and their crops. Groups could number in the thousands. The villages of Mallaha, Mureybet and Çatal Höyuk are known to archaeologists as the most important of their time.
The prehistoric period is divided into two sections: the Paleolithic (3,000,000 BC to 10,000 BC) and the Neolithic period (10,000 BC to 3,500 BC). It is the sedentarization of human beings that separates these two periods. Nomadic in the Paleolithic period, humans became sedentary in the Neolithic period.
The first sedentary villages were formed in a region known as the Fertile Crescent. This region was conducive to the establishment of the first villages because of its agricultural potential. The Fertile Crescent is located in the region of the world currently known as the Middle East.
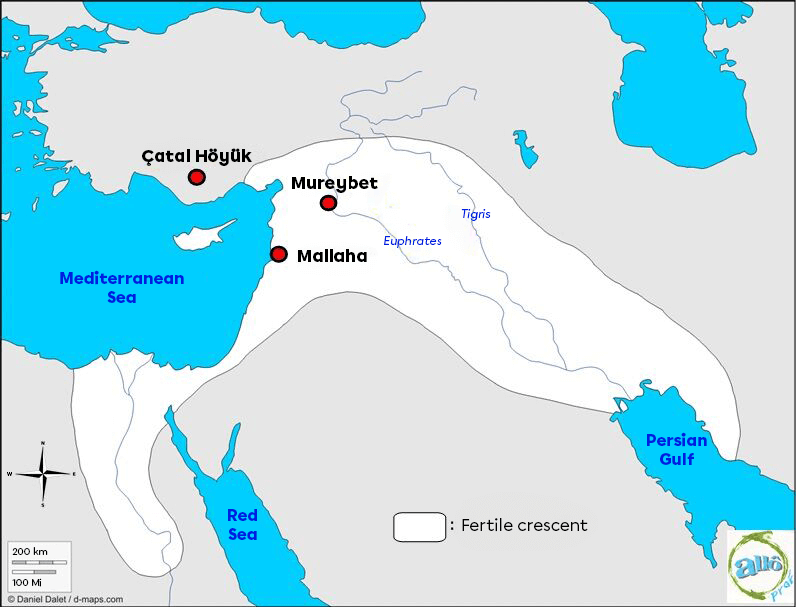
Map of the Fertile Crescent, showing the Tigris River and the Euphrates River
First of all, the Earth's warming climate has contributed to this phenomenon. Little by little, humans are settling in regions of the world where the weather is warmer and resources are more plentiful. They also settled near rivers, because the land there was fertile and made it easier to transport goods.

Village located near a river
|
Lifestyle |
Nomadic |
Sedentary |
|
Period |
Paleolithic |
Neolithic |
|
Livelihood activities |
hunting, fishing, foraging or gathering |
farming, livestock farming, hunting, fishing, foraging or gathering |
|
Type d'habitation |
temporary (caves or small huts) |
permanent (rectangular houses) |
|
Innovations techniques |
cut stone, knowledge of fire |
polished stone, pottery, metalwork |

Representation of a nomadic home
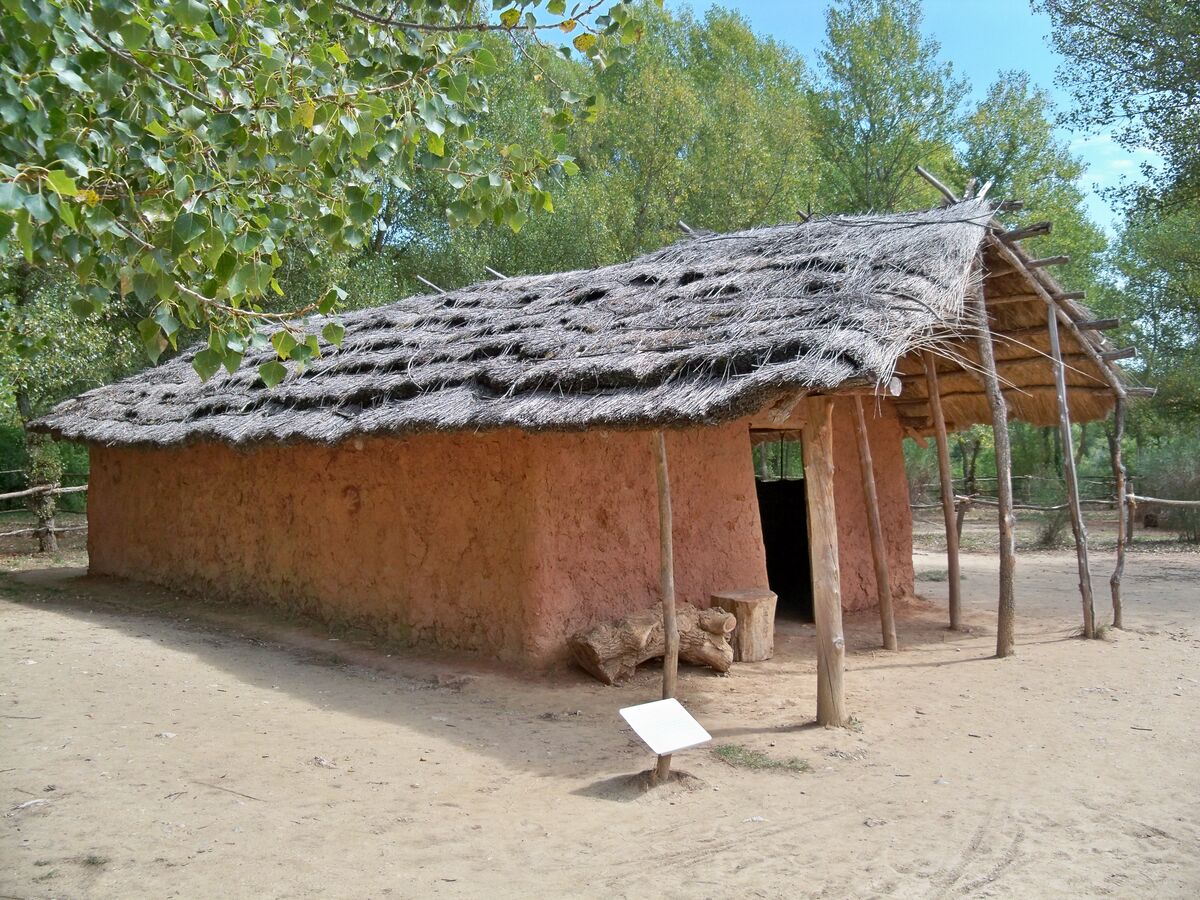

Representation of a sedentary home