Factoring allows us to know more about the composition of a number. In addition, prime factorization is essential for finding the GCF and the LCM of two or more numbers.
Factoring a number is the process of writing that number as a product of two or more factors.
A factor is one of the terms in a multiplication.
Express |56| as a product of its factors.
Here are two possibilities. ||56=2\times 28\ \text{or}\ 56=4\times 2\times 7|| In the first example, the factors of |56| are |2| and |28|. In the second example, the factors are |4|, |2|, and |7|.
The prime factorization of a number is the expression of a natural number greater than |1| as a product of its prime factors.
A prime factor is a factor that is a prime number.
The prime factorization of a number is unique to that number (the order in which the factors are written does not matter).
Consider the number |30|.
It is possible to factor the number like so.
||30=5\times 6||Notice that the factor |5| is prime, but that |6| is not. To find the prime factorization of |30,| the number |6| must be factored further.
||30=5\times \color{blue}{6}\Rightarrow 30=5\times \color{blue}{2\times 3}||This is the prime factorization of |30|, since all the factors are prime.
The prime factorization of |30| is therefore written: |30=2\times3\times5| (The factors are normally written in ascending order).
As mentioned in the Important section above, this factorization is unique; in other words, no matter the order in which the factors are written, the prime factorization of the number |30| above is the only possible factorization.
It is helpful to use a factor tree when finding the prime factorization of a number in order to not forget any factors.
-
Write the number to be factored at the top of the tree and decompose it into two factors, then write those numbers at the end of two branches.
-
If one or both factors are not prime, continue factoring until all the factors at the ends of the branches are prime.
-
Write the number as a product of its prime factors using the factors at the ends of each of the branches of the tree.
Decompose the number |120| into prime factors.
-
Write the number to be factored at the top of the tree and decompose it into two factors, then write those numbers at the end of two branches
There are several possible factors for this first step. No matter which ones are chosen, the final prime factorization will be the same. Take |120=30\times4.|
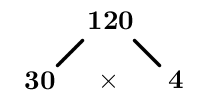
-
If one or both factors are not prime, continue factoring until all the factors at the ends of the branches are prime
Notice that |30| and |4| are not prime, so keep factoring in the same way.
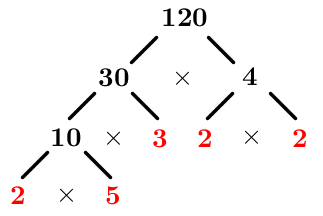
The prime factorization is complete when all the numbers at the ends of the branches are prime.
-
Write the number as a product of its prime factors using the factors at the ends of each of the branches of the tree
The prime factorization of |120| is the following. ||120=\color{red}{2}\times\color{red}{2}\times\color{red}{2}\times\color{red}{3}\times\color{red}{5}||
It is possible to use exponential notation to express the prime factorization of a number.
For the example above, |120| would be written: |120=2^3\times 3\times 5.|
This form of notation is called the prime factorization in exponential form.