Characteristics of Images Obtained from Convex (Converging) Lenses
| | Image Characteristics | |||
| Position of the object | Image Type | Orientation | Image size | Image position |
| Infinity | Real | Punctual (point) | At F | |
| Greater than 2F | Real | Inverted | Smaller | Between F and 2F |
| At 2F | Real | Inverted | Same size | At 2F |
| Between 2F and F | Real | Inverted | Larger | Greater than 2F |
| At F | No image | |||
| Between F and O | Virtual | Upright | Larger | Further than the object |
To represent images in convex (or converging) lenses, it is essential to draw at least two of the three principal rays coming from the endpoint of the object. The intersection point of these refracted rays are then be connected perpendicularly to the principal axis to form the image.
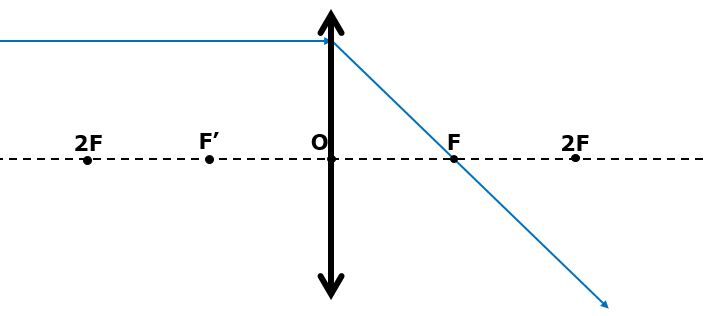
Since the object is very far away, only the parallel rays will be considered. The resulting image is a point (the size of a dot) at the principal focal point of a lens. It is a real image.
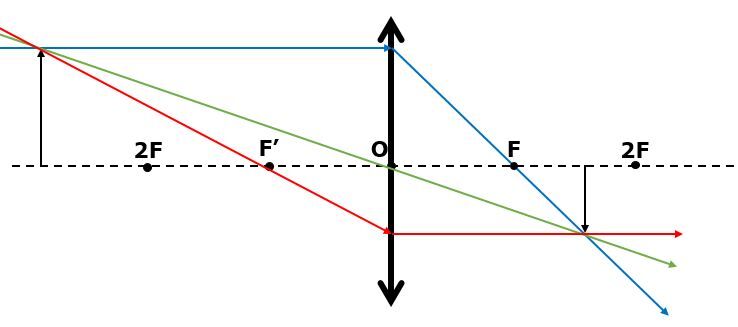
The characteristics of the image obtained are as follows: the image is smaller than the object, real (since it can be projected on a screen), inverted (since it is not upright like the object) and located between the focal point and twice the focal length.
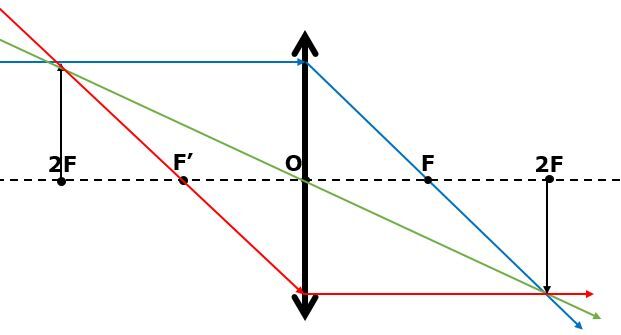
The characteristics of the image obtained are as follows: the image is the same size as the object, real (since it can be viewed on a screen), inverted (since it is not upright like the object) and located at the same distance from the lens, at a distance that is twice the focal length.

The characteristics of the image obtained are as follows: the image is larger than the object, real (since it can be viewed on a screen), inverted (since it is not upright like the object) and located beyond twice the focal length.
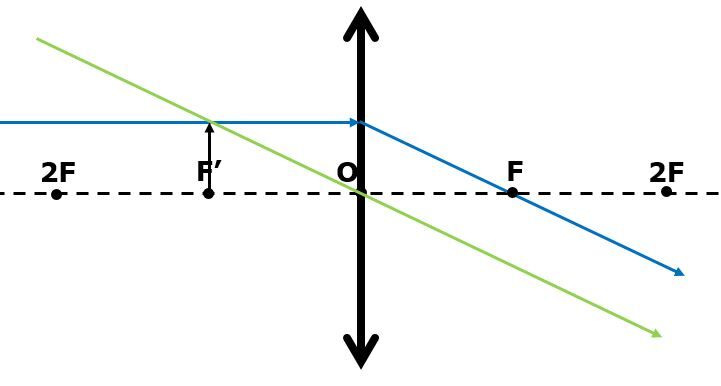
No image is obtained in this situation, because the refracted rays are parallel and therefore cannot intersect.
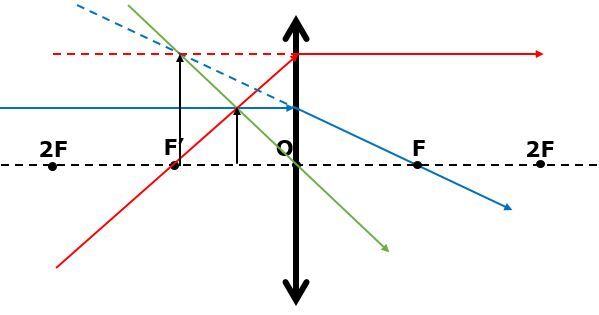
The characteristics of the image obtained are as follows: the image is larger than the object, virtual (since it cannot be projected on a screen), upright (since its orientation is the same as the object) and located further away from the lens than the object.