-
Genetics is the science that studies the transmission of hereditary traits through genes.
-
Heredity is the transmission of hereditary traits from one generation to the next.
-
A hereditary trait is a physical, morphological, or physiological trait transmitted from parents to their descendants.
Eye colour, nose shape, blood type, sex, and genetic diseases are examples of hereditary traits.
-
Genes are fragments of DNA stored in the nucleus of cells. They contain instructions for producing specialized proteins. All of an individual's cells (except gametes) contain the same set of genes.
-
Alleles are the different forms that a gene can take. They occupy a specific place in a chromosome.
In a species that reproduces sexually, an individual's chromosomes are found as pairs in the nucleus of its cells. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes.
One chromosome of each pair comes from the female gamete (ovum) and the other comes from the male gamete (spermatozoon). The male and female gametes form the zygote during fertilization. The chromosomes in a pair are called homologous because they contain the same genes.
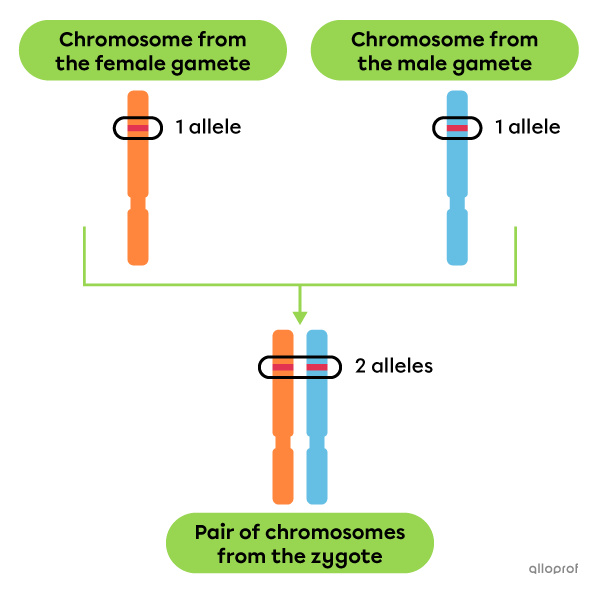
A gene encoding a hereditary trait always comprises two alleles: one allele per chromosome of a homologous pair.
-
A dominant allele imposes its instructions as soon as it is present and prevents the other allele from expressing its own instructions. A single copy of a dominant allele is needed for the allele to express itself.
-
A recessive allele must absolutely be present in two copies so that it can express its instructions.
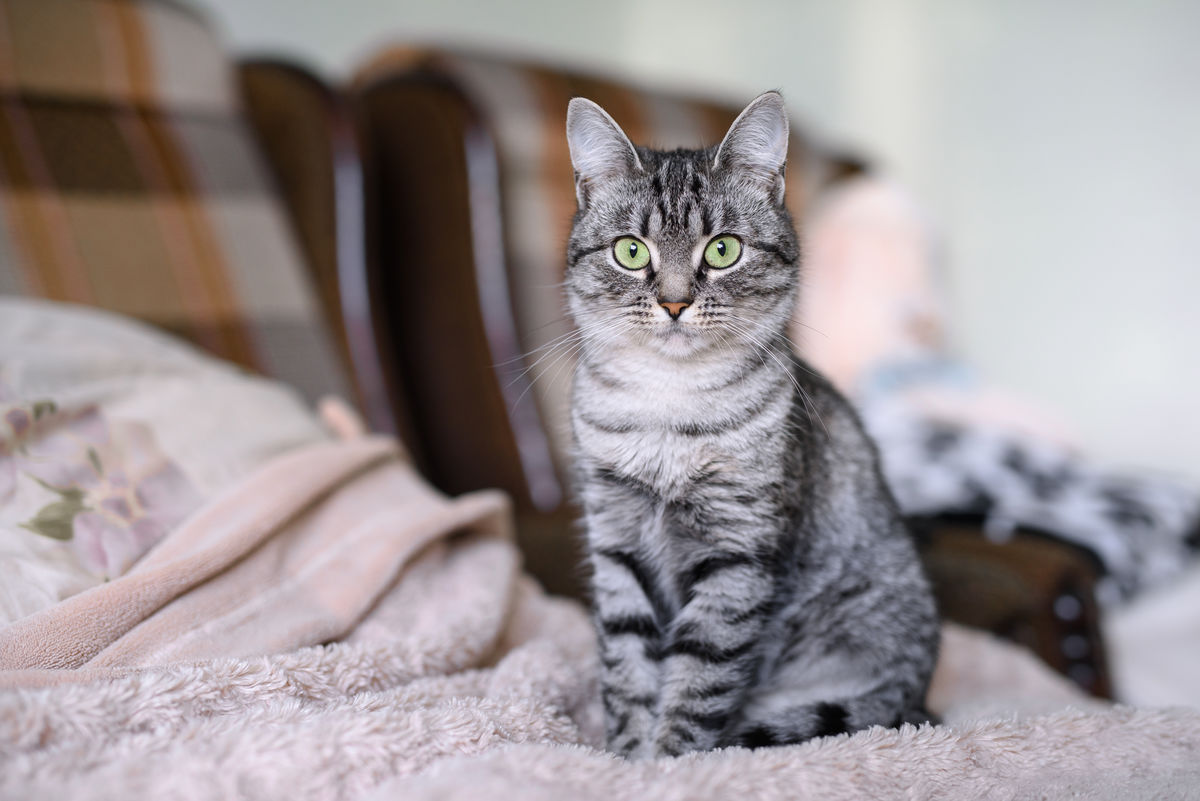
In cats, one main gene is responsible for fur length. The alleles for the gene are short and long.
For this trait, the short allele is dominant and the long allele is recessive.
During fertilization, a kitten receives two alleles, one allele from its biological mother and one allele from its biological father, for the gene responsible for fur length. The combination of the two alleles determines whether this kitten will be short-haired or long-haired.
We can see that this kitten has short hair.

Lalandrew, Shutterstock.com
Since the short allele is dominant, there may be one or two copies of this allele so that it can be expressed. The kitten therefore has one or two short allele(s) transmitted by its parents.
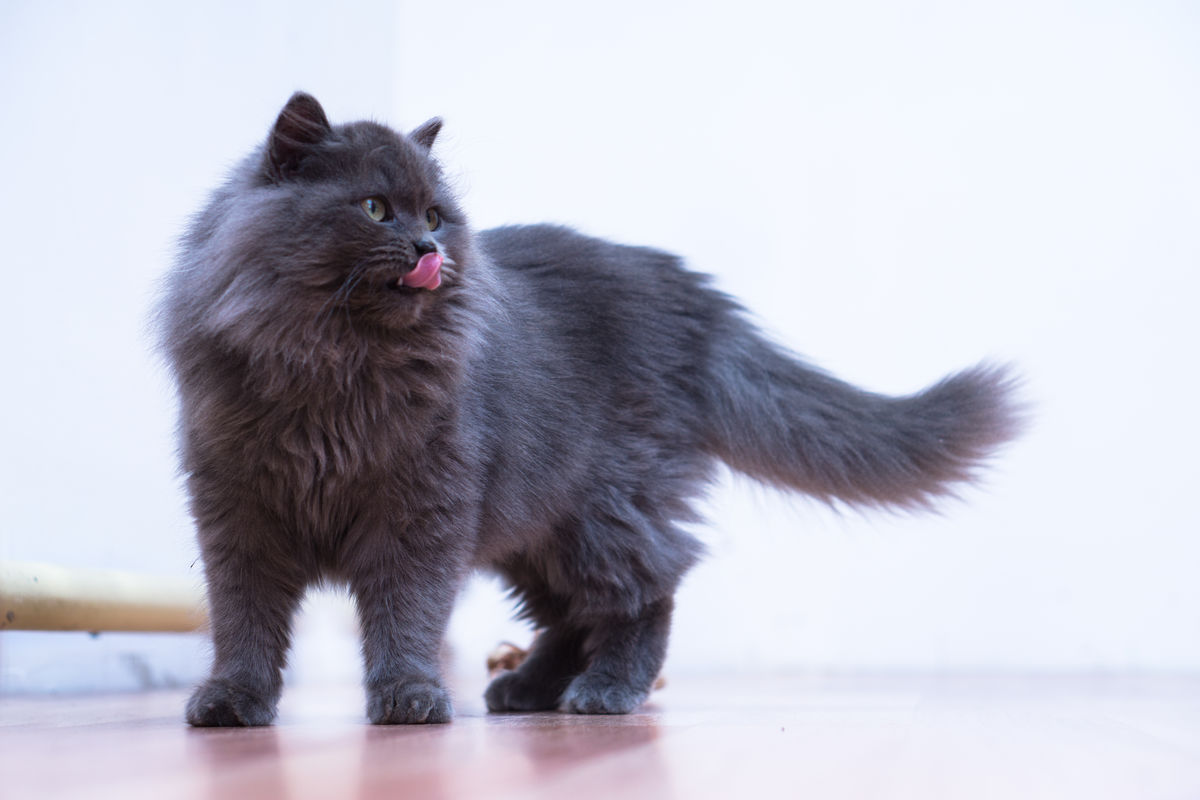
We can see that this kitten has long hair.

Alexandr Korolev, Shutterstock.com
Since the long allele is recessive, it must be present in two copies so that it can be expressed. This cat definitely has two long alleles inherited from each parent.
The combination of the two alleles of a gene forms an individual's genotype for that gene.
The genotype describes an individual's alleles for one or more genes.
The genotype of an individual for a given gene is generally represented by a combination of two letters: a capital letter and/or a lower case letter (AA, Aa, or aa). A capital letter represents a dominant allele and a lowercase letter represents a recessive allele. The choice of letter is usually the first letter of the dominant allele depending on the trait studied.
-
A homozygous individual for a gene carries two identical alleles for the gene.
-
A heterozygous individual for a gene carries two different alleles for the gene.
It is also possible to qualify the genotype of an individual with the following terms: dominant homozygous (AA), recessive homozygous (aa), or heterozygous (Aa).

Lalandrew, Shutterstock.com

Alexandr Korolev, Shutterstock.com
For fur length in cats, the possible alleles are short and long where the short allele is dominant and the long allele is recessive.
To represent the genotype of an individual for the trait, we use the capital letter S to represent the short allele and the lowercase s to represent the long allele.
The possible genotypes are as follows.
-
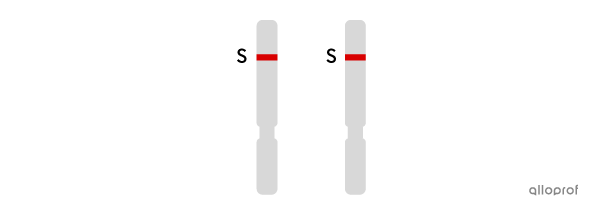
SS or dominant homozygous: presence of the dominant allele in two copies (short - short). Each parent passed on a short allele.
-
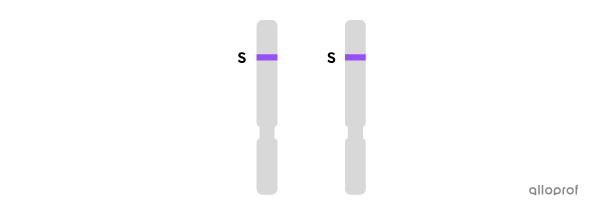
ss or recessive homozygous: presence of the recessive allele in two copies (long - long). Each parent passed on a long allele.
-
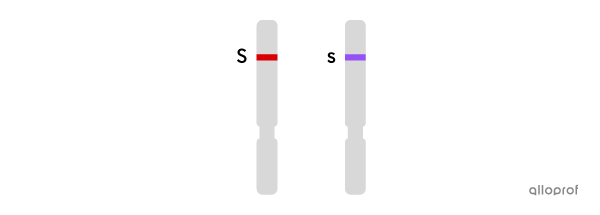
Ss or heterozygous: presence of a dominant allele and a recessive allele (short - long). One parent passed on a short allele and the other parent passed on a long allele.
In peas, the pea colour gene has two possible alleles: yellow and green, where yellow is the dominant allele and green is the recessive allele.
To represent a plant's genotype for pea colour, the capital letter Y is used to represent the yellow allele and the lowercase y is used to represent the green allele.
The possible genotypes are as follows.

-
YY or dominant homozygous: presence of the dominant allele in two copies (yellow - yellow). Each parent passed on the yellow allele.
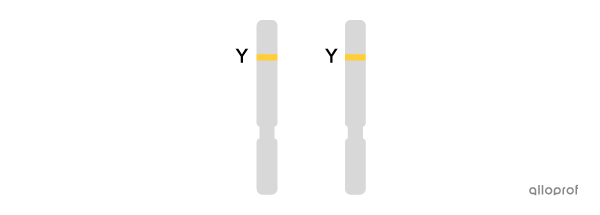
-
yy or recessive homozygous: presence of the recessive allele in two copies (green - green). Each parent passed on the green allele.
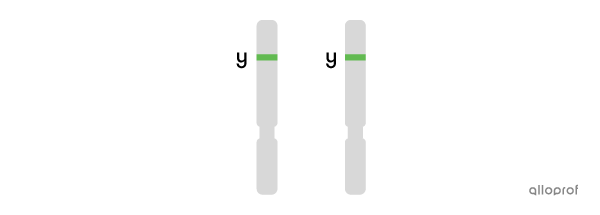
-
Yy or heterozygous: presence of a dominant allele and a recessive allele (yellow - green). One parent passed on the yellow allele and the other parent passed on the green allele.
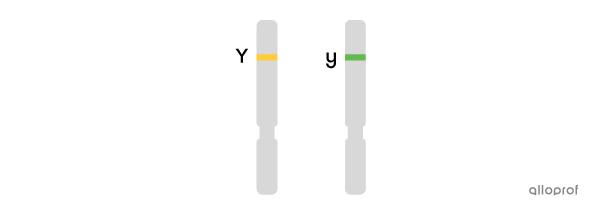
Phenotype is the trait that can be observed in an individual or the expression of the genotype.
The phenotype observed in an individual depends on its genotype for the trait studied. If a dominant allele is present in one or two copies in the genotype, the dominant trait is expressed. On the other hand, if a recessive allele is present in two copies in the genotype, the recessive trait is expressed.
Here are the phenotypes observed depending on the genotype for the fur length gene in cats.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| SS: dominant homozygous | Short hair |
| Ss: heterozygous | Short hair |
| ss: recessive homozygous | Long hair |
Here are the phenotypes observed according to the genotype for the gene responsible for the colour of the peas.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| YY: dominant homozygous | Yellow peas |
| Yy heterozygous | Yellow peas |
| yy: recessive homozygous | Green peas |
In peas, the pea texture gene has two possible alleles: smooth and wrinkled, where smooth is the dominant allele and wrinkled is the recessive allele.
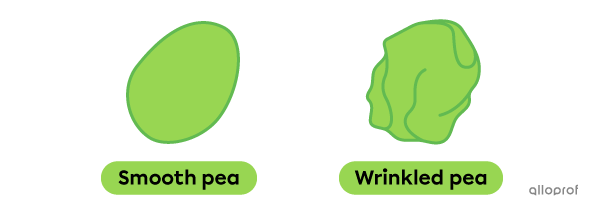
-
What is the genotype representation of a dominant homozygous pea plant and what is its phenotype?
-
What is the genotype representation of a heterozygous pea plant and what is its phenotype?
-
What is the genotype representation of a recessive homozygous pea plant and what is its phenotype?
To represent the genotype of a plant for the pea texture gene, the capital letter S is used for the smooth allele, because it is the dominant allele. We use the lowercase letter s to represent the wrinkled allele because it is recessive.
-
The genotype of the dominant homozygous pea plant is SS (smooth - smooth) and its phenotype is the presence of smooth peas.
-
The genotype of the heterozygous pea plant is Ss (smooth - wrinkled) and its phenotype is the presence of smooth peas.
-
The genotype of the recessive homozygous pea plant is ss (wrinkled - wrinkled) and its phenotype is the presence of wrinkled peas.