Two glands in particular have a big impact on the male reproductive system: the pituitary gland and the testicles. These glands have essential functions in triggering puberty as well as maintaining male fertility.
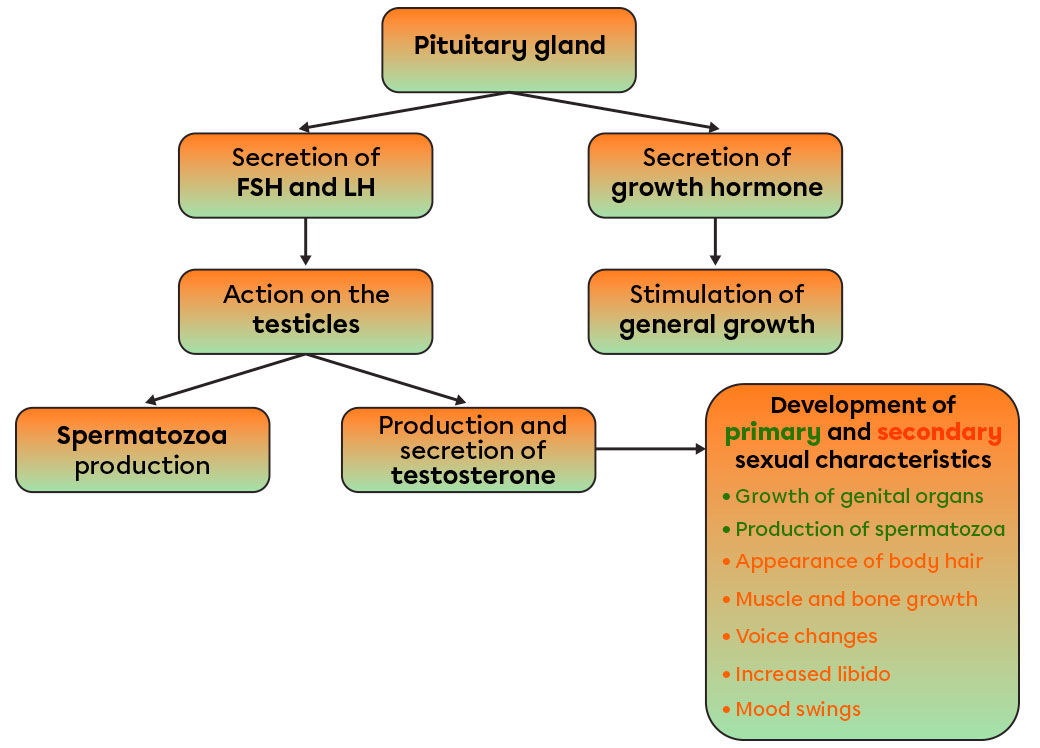
The testicles produce the male reproductive cells, the spermatozoa. In addition, they produce and secrete hormones, including testosterone. As for the pituitary gland, it is a small gland located under the cerebrum, in front of the brain stem. This tiny gland produces more than eight hormones that interact with the different systems of the human body. Three of them are directly related to the human reproductive system: the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), the luteinizing hormone (LH) and the growth hormone. All three are involved in the maturation and functioning of the reproductive system, as well as in the general growth of the human body.
The age at which puberty begins and the course of puberty varies according to heredity, ethnic group, diet, geographical location, socio-cultural environment and stress level. On average, puberty begins in boys around the age of 12. All the changes that occur are due to the influence of the pituitary gland. In general, the pituitary gland increases the secretion of growth hormone, which results in a growth spurt. Also, two other hormones are secreted in greater quantities: FSH and LH. FSH increases the testicles’ production of spermatozoa, while LH stimulates their secretion of testosterone.
Testosterone is responsible for the development of genital organs and male secondary sexual characteristics. This hormone triggers the appearance of pubic, underarm and facial hair. Muscles and bones in the body also develop under the effect of this hormone. In addition, the larynx increases in volume and consequently, the voice becomes deeper. Then, the skin thickens and becomes more oily, which in turn leads to the appearance of acne. This hormone has more than just physiological effects on the male body. Mood and behaviour are also affected by testosterone production. The libido (sexual desire) increases during puberty as well.
Testosterone is responsible for sexual impulses in both males and females.
Libido increases during adolescence, regardless of sexual orientation.
The ability to ejaculate appears at the beginning of puberty. When ejaculation occurs during sleep, it is called nocturnal emission. Although the ability to ejaculate appears early in puberty, the amount of spermatozoa in semen only becomes significant after a few years.