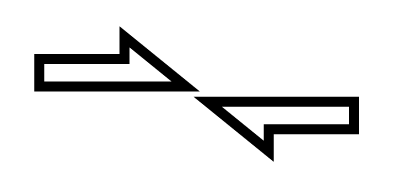
A force is an action which can set a body in motion, modify its motion, or deform it.
Modifying the resting state of a body means setting it in motion.
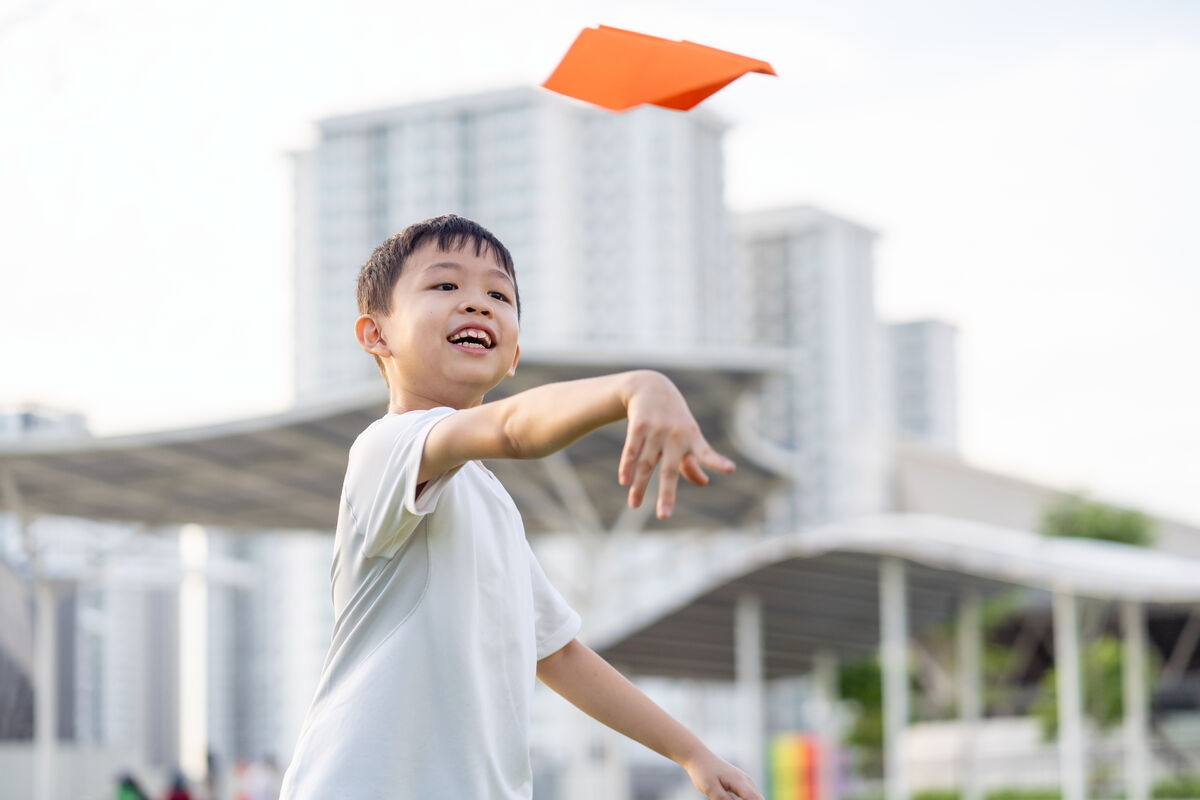
To launch a paper plane in the air, a force must be applied to it.

MH-Lee, Shutterstock.com
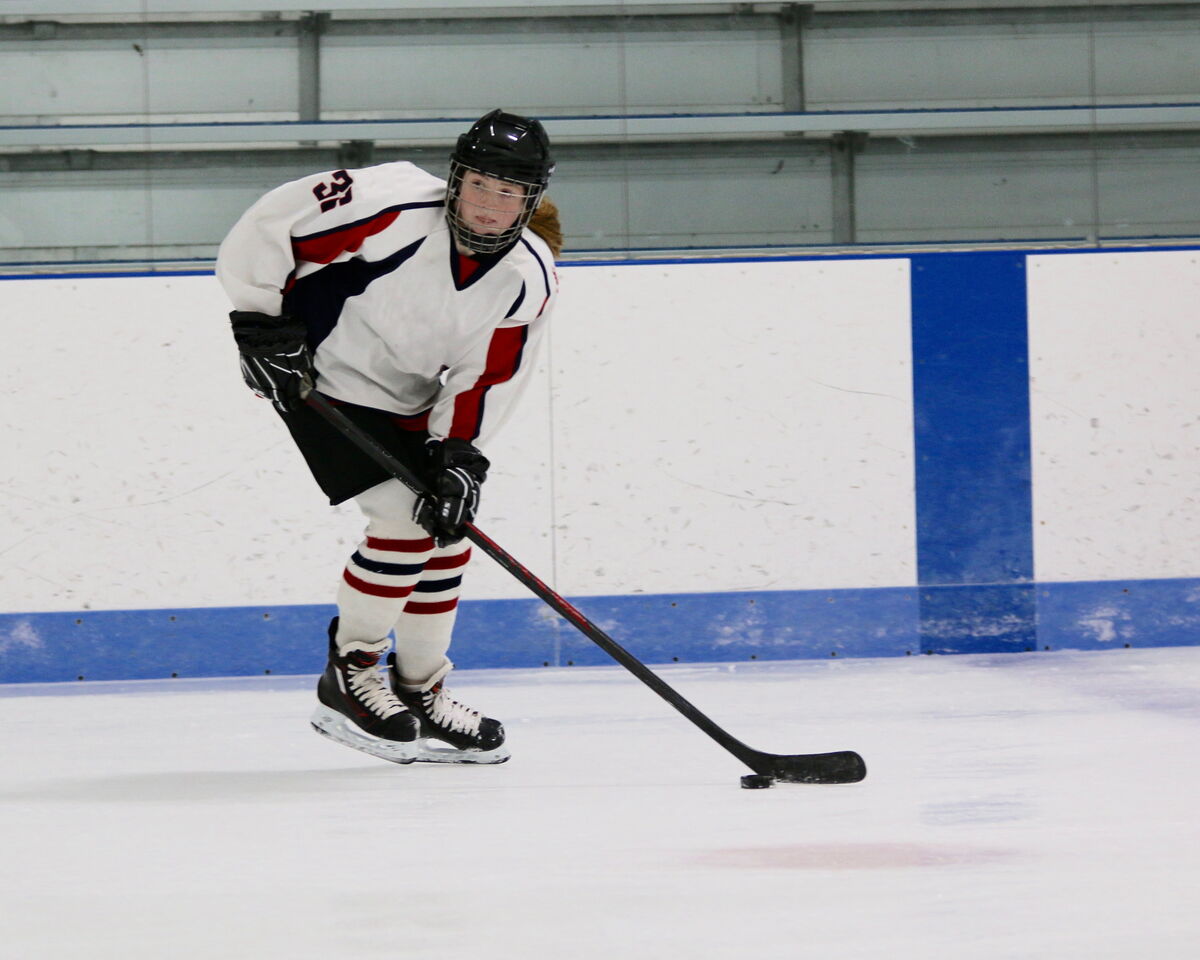
Modifying the motion of a body means slowing it down, accelerating it, or modifying its trajectory.
To change the speed and trajectory of a puck, you have to act on it by applying a force with the stick.

Steve Gilbert, Shutterstock.com
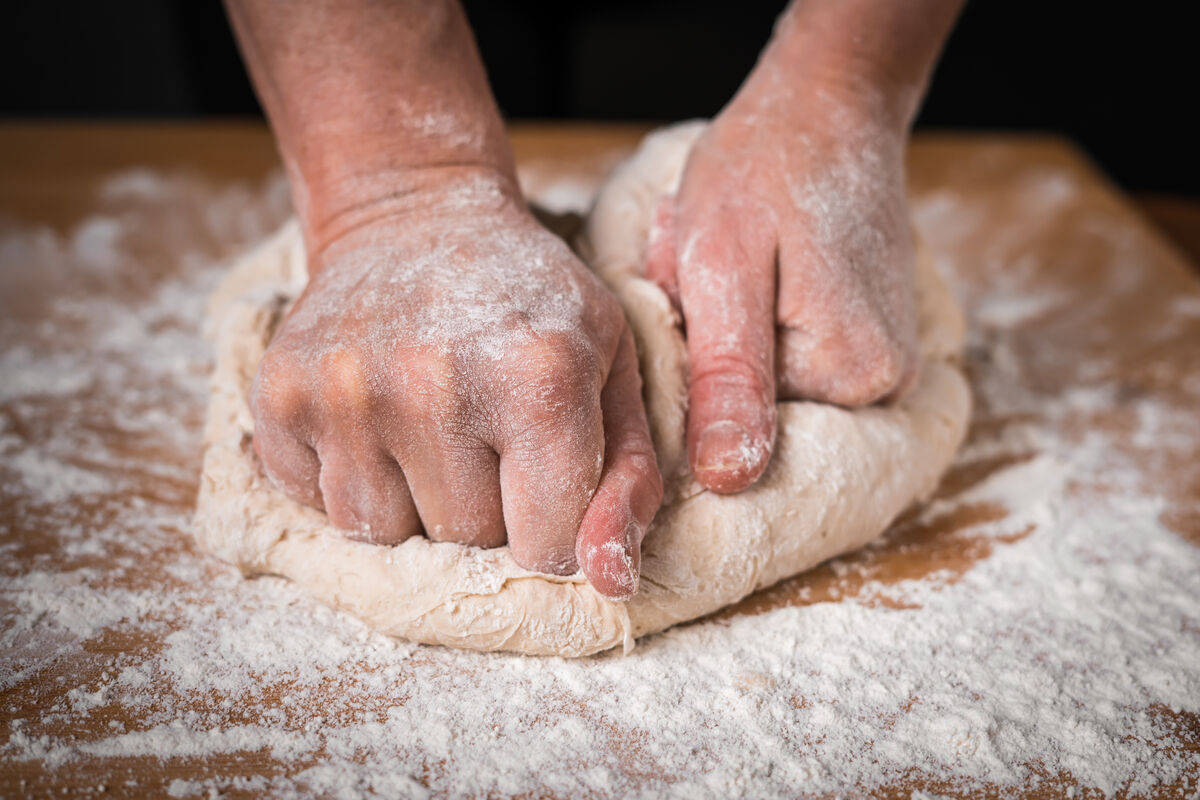
To deform an object means to modify its shape.
A ball of dough is crushed by applying a force of compression.

Johnny Bravoo, Shutterstock.com
If several forces are exerted simultaneously on a material, it can tend to deform in different ways. The effect of these forces on the material is called a constraint.
There are different constraints depending on the number and orientation of the forces exerted.
|
Application of forces |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
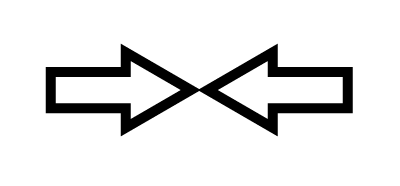
Two forces applied towards each other |
|
|
Effect |
|
|
Tendency to crush materials |

DaniiD, Shutterstock.com
|
Application of forces |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
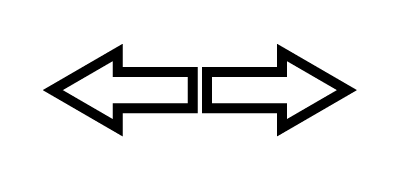
Two forces applied in opposite directions |
|
|
Effect |
|
|
Tendency to stretch materials |

Dmytro Balkhovitin, Shutterstock.com
|
Application of forces |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
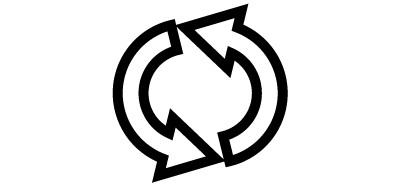
One or two parallel forces in opposite directions applied to an object so that it rotates around an axis |
|
|
Effect |
|
|
Tendency to twist materials |
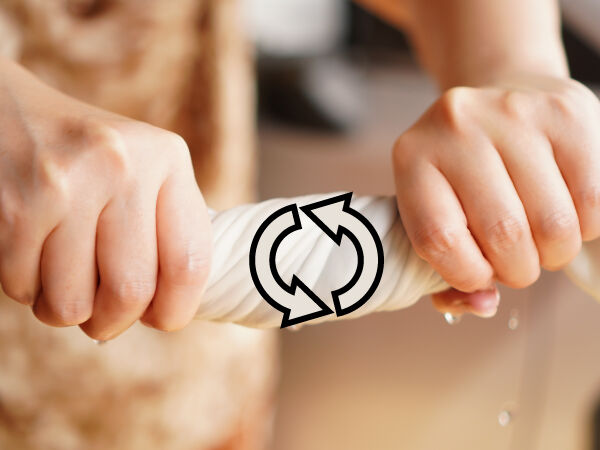

Lek in a BIG WORLD, Shutterstock.com
|
Application of forces |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
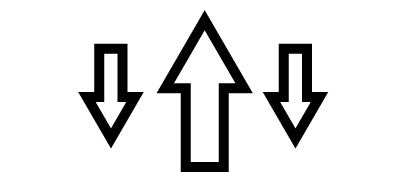
One or more parallel forces in opposite directions, applied at different places on an object |
|
|
Effect |
|
|
Tendency to fold or bend materials |

Vaclav P3k, Shutterstock.com
|
Application of forces |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
Two parallel and opposing forces applied slightly apart from each other |
|
|
Effect |
|
|
Tendency to tear or split materials |
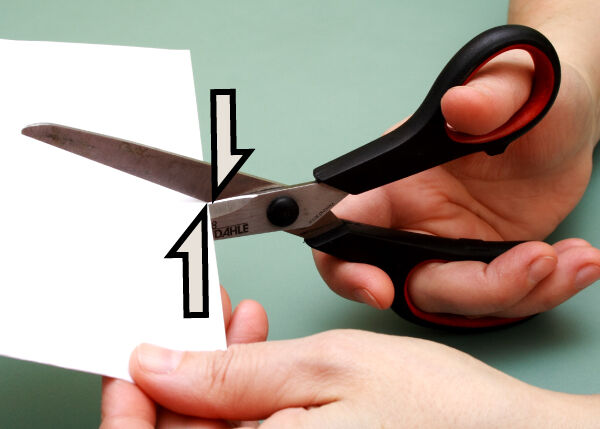

Einar Muoni, Shutterstock.com
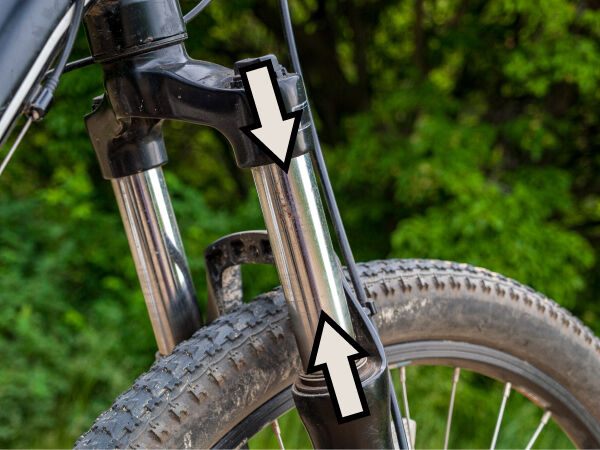
The weight of the upper part of the bicycle fork applies a downward force while the lower part of the fork applies an upward force. The suspension is subjected to a compression constraint.
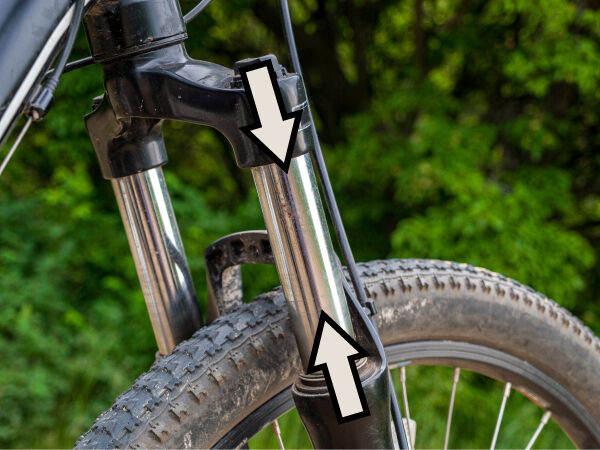

DaniiD, Shutterstock.com
The hull of the boat is pushed towards the dock by the waves. The hull applies a force towards the dock, while the dock applies a force towards the boat’s hull. The boat's fenders are under a compression constraint.
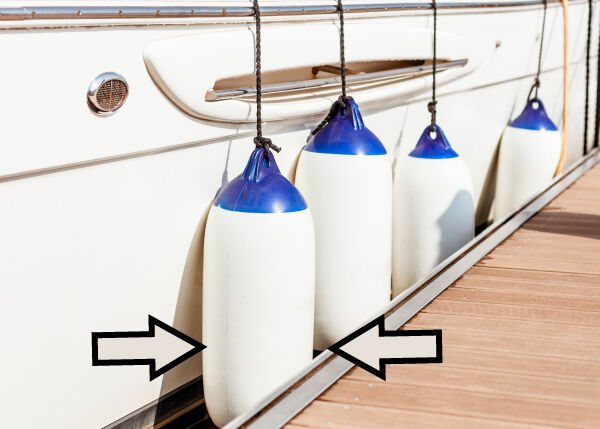

I’M PHOTOGRAPHER, Shutterstock.com
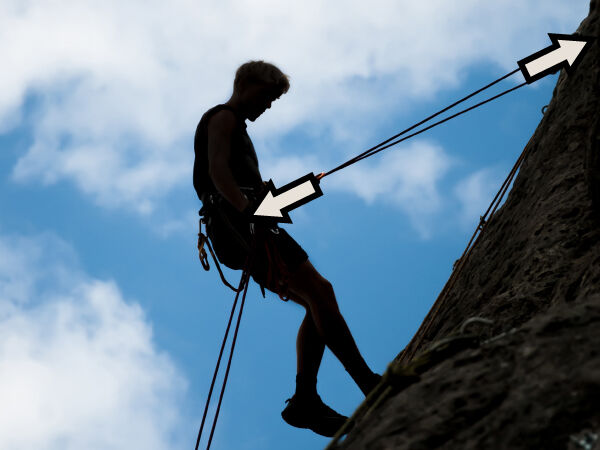
The climber's weight applies a downward force, while the anchor holding the rope to the top of the wall applies an upward force. The rope is under a tension constraint.

Dmytro Balkhovitin, Shutterstock.com
The small dog applies a force to the left, while the large one applies a force to the right. The toy is subjected to a tension constraint.
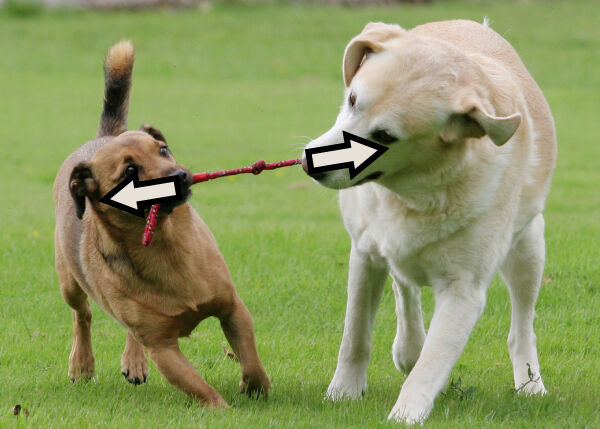

Sue McDonald, Shutterstock.com
The right hand applies a force to rotate one end of the dishcloth in one direction, while the left hand applies a force to rotate the other end of the dishcloth in the other direction. The dishcloth is subjected to a torsion constraint.
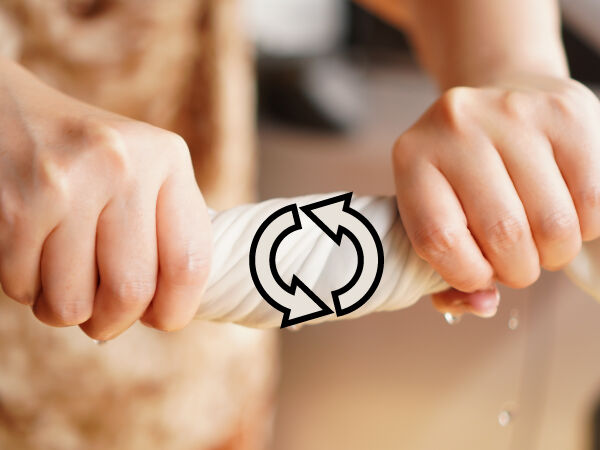

Lek in a BIG WORLD, Shutterstock.com
The hands apply a force to turn the cross wrench in one direction, while the nut applies a force to rotate the cross wrench in the other direction. The cross wrench is subjected to a torsion constraint.
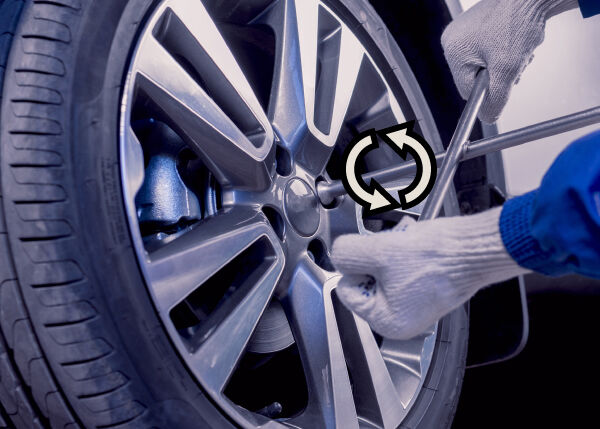

63ru78, Shutterstock.com
The man's weight applies a downward force to the middle of the slackline, while the anchors holding the ends of the slackline apply upward forces to each end. The slackline undergoes a bending constraint.

Vaclav P3k, Shutterstock.com
The weight of the basket applies a downward force to one end of the wooden rod, the person's shoulder applies an upward force to the middle of the rod, and the person's hands apply a downward force to the other end of the rod. The wooden rod undergoes a bending constraint.
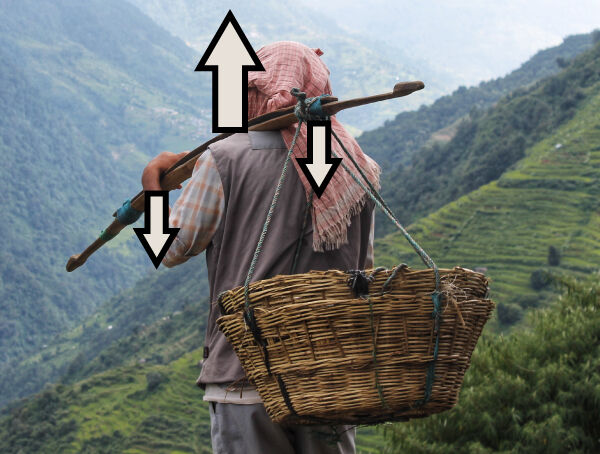

Omri Eliyahu, Shutterstock.com
The top scissor blade applies a downward force to one point on the sheet, while the bottom blade applies an upward force to another point on the sheet, slightly offset from the first.
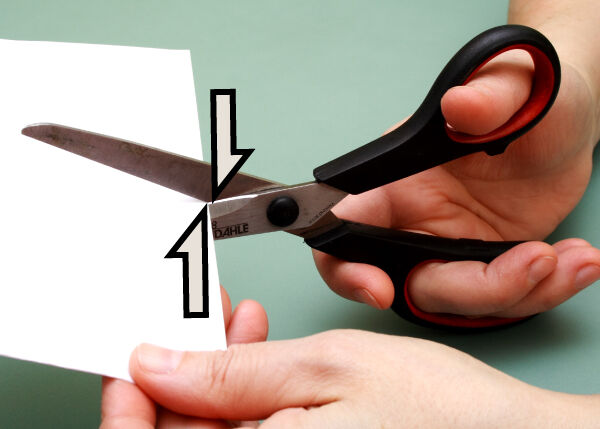

Einar Muoni, Shutterstock.com
The San Andreas fault in California is under a shearing constraint. The part to the right of the fault moves very slowly in one direction, while the part to the left of the fault moves in the other direction.
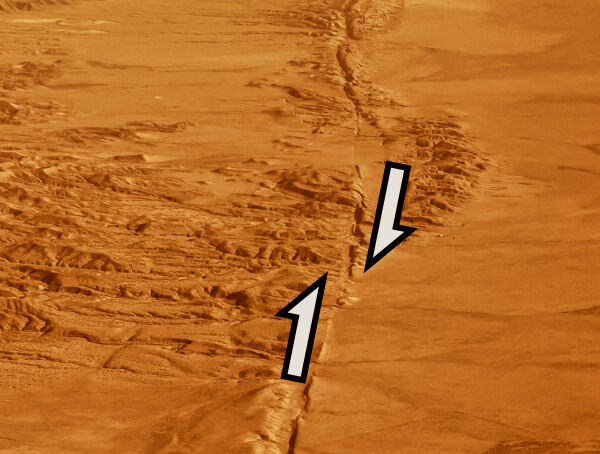

Mike Chappazo, Shutterstock.com
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des contraintes de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :

Depending on the nature of the material and on the magnitude of the force applied, the deformation may be invisible or apparent.
If a tension constraint is applied to a non-elastic rope, the rope retains its shape and does not stretch. The deformation is not apparent.

Marc Dietrich, Shutterstock.com
If a tension constraint is applied to a rubber band, it deforms while stretching. The deformation is apparent.
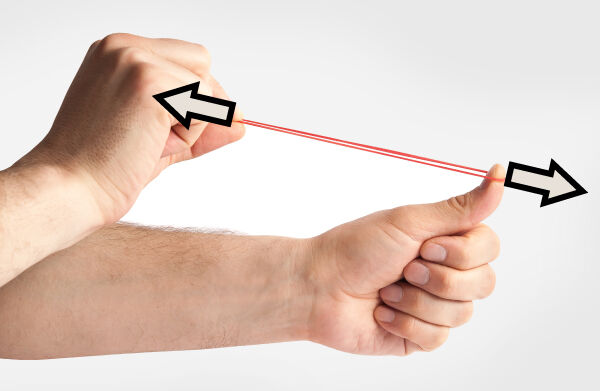
Sharomka, Shutterstock.com
Constraints can cause two types of deformation, temporary deformation and permanent deformation.
|
Type of deformation |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Temporary (or elastic) deformation |
The material is deformed when the constraint is applied; it then returns to its original shape when the constraint ceases to be applied. |
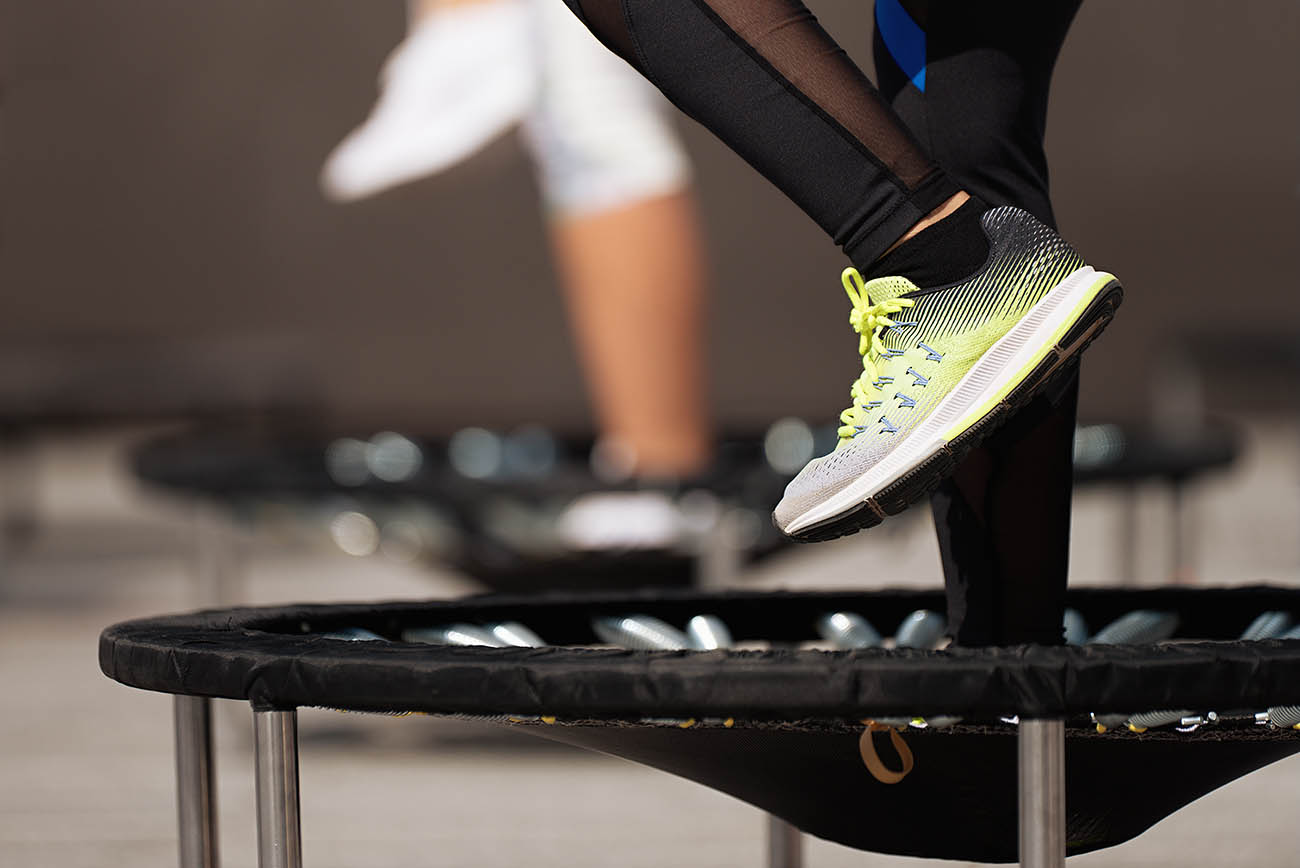
A trampoline that deforms when subjected to the weight of a person
Pavel1964, Shutterstock.com |
|
Permanent (or plastic) deformation |
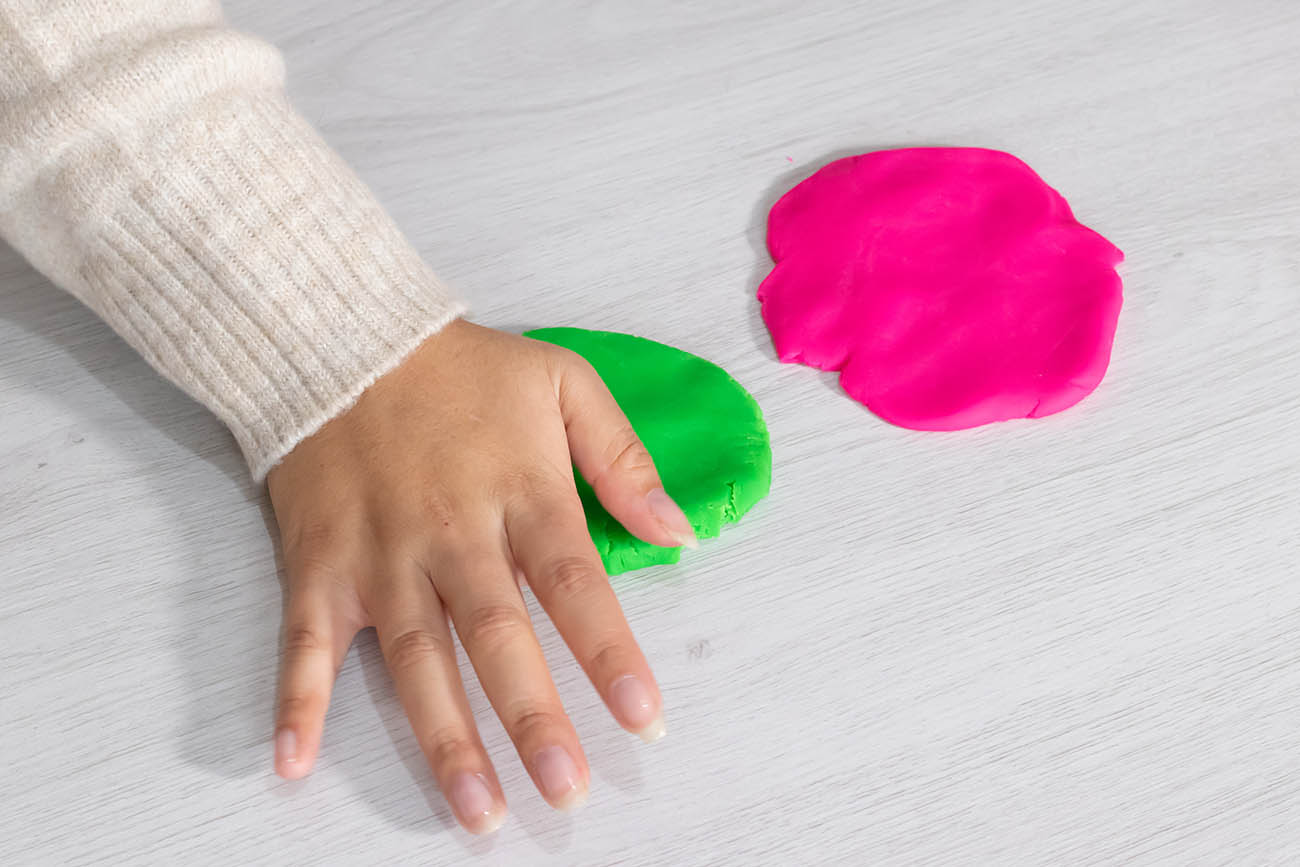
The material deforms when the constraint is applied, but does not recover its original shape when the constraint ceases to be applied. It retains its new form. |
Plasticine that deforms when crushed
DanitzaPulgarM, Shutterstock.com |
Materials have a strength threshold, that is, a maximum force that they can withstand. If the constraint exceeds the strength threshold of the material, the material breaks. This effect is called a fracture.
When inflating a balloon, the rubber undergoes a tension constraint and deforms. If the constraint exceeds the strength threshold of the material, the balloon bursts. This is what is known as a fracture.
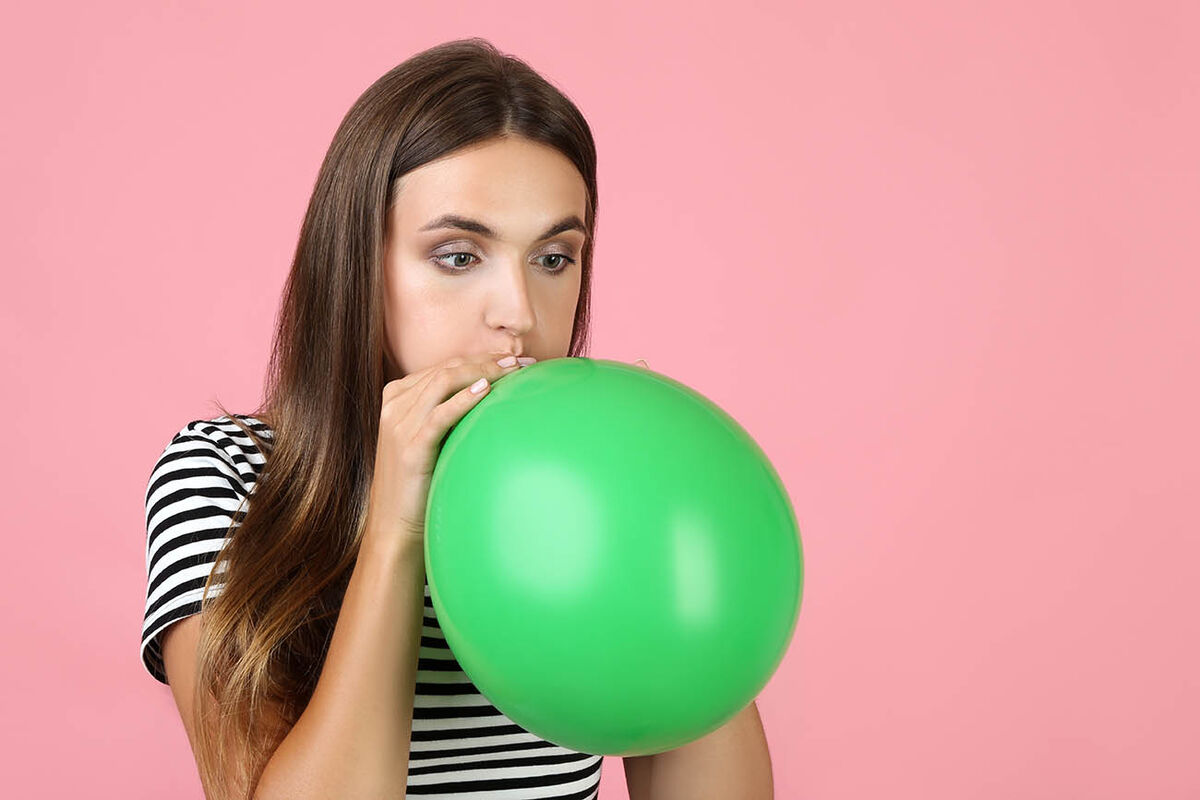

5 second Studio, Shutterstock.com
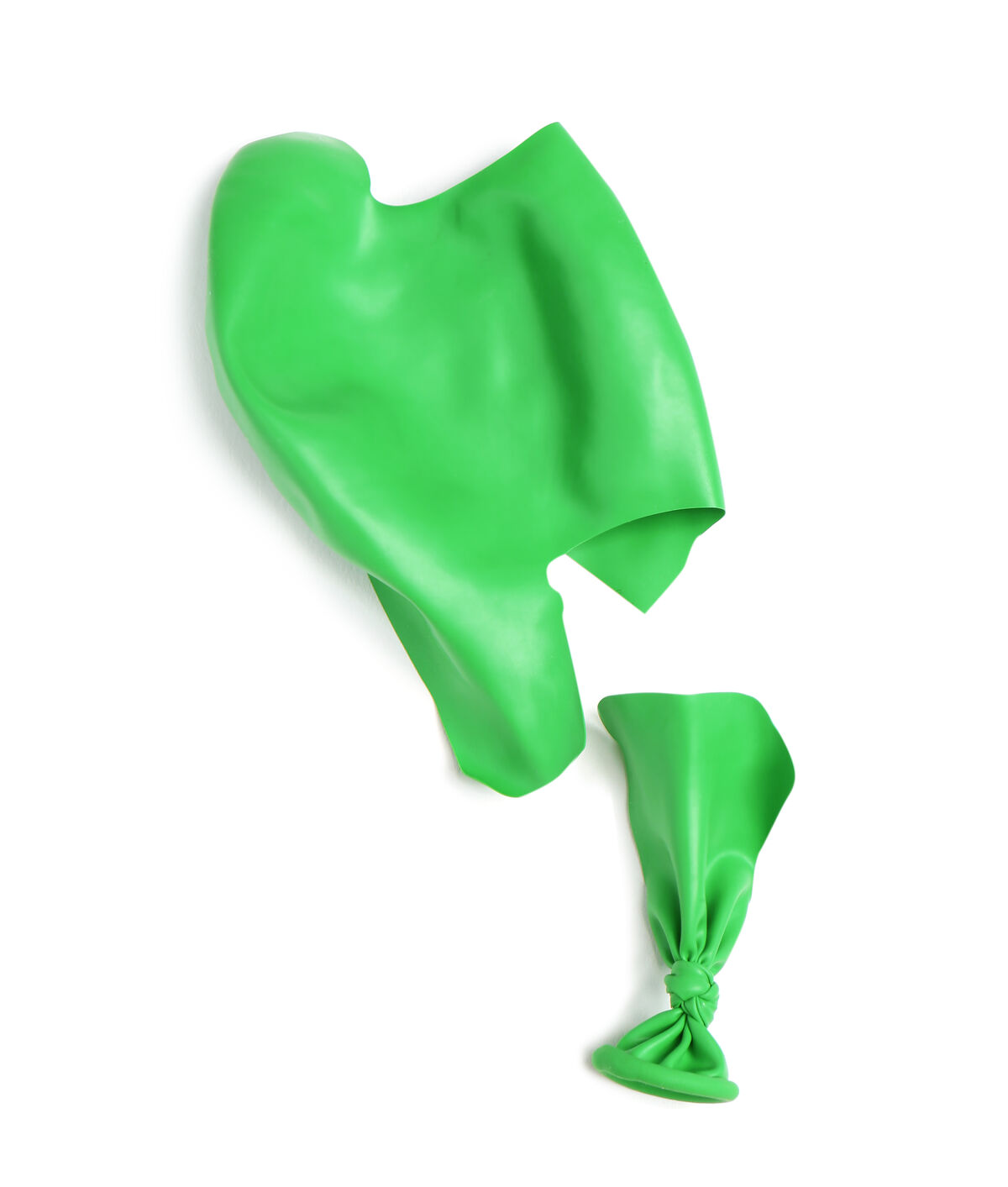

New Africa, Shutterstock.com
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des contraintes de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :