An eclipse is the total or partial disappearance of a celestial body which ceases to be visible when another celestial body is positioned between it and an observer.
The word “eclipse” comes from the Greek word ekleipsis which means “to leave, to abandon.” On Earth, it is common to be able to observe four to seven eclipses per year. At these times, the Sun, Earth, and Moon are perfectly aligned. Depending on the respective positions of these different celestial bodies, two types of eclipses can be observed:
An eclipse of the Sun, also called a solar eclipse, results from the passage of the Moon between the Earth and the Sun.
The Moon then blocks sunlight from reaching a certain portion of Earth and instead casts a shadow in that area. The region of the Earth that is in the umbra of the Moon is plunged into complete darkness: this is a total eclipse (the Sun is entirely hidden by the Moon). The region of the Earth that is in the penumbra still receives some light: a partial eclipse can then be observed in this region (only part of the Sun becomes hidden to the observer).
The shadowy area on the Earth's surface, where an observer can see a total solar eclipse, is never more than 270 km in diameter. This is why a total eclipse can rarely be observed. Partial eclipses are more common and easier to observe since the penumbra region on the Earth's surface can measure up to 6 000 km in diameter.
The total duration of a solar eclipse is about two hours. During this time, the light gradually disappears. Total darkness lasts about 8 minutes. Solar eclipses always take place during the day, at the time of the new Moon. On average, they occur every 18 months.
Direct observation of a solar eclipse can severely damage eyesight and even cause blindness. Solar eclipses should NEVER be viewed directly. Even if the light is hidden by the Moon, other invisible rays continue to reach the ground. However, indirect observation (by projecting the image of the eclipse on a cardboard for example) or the use of filters can provide a safe observation.
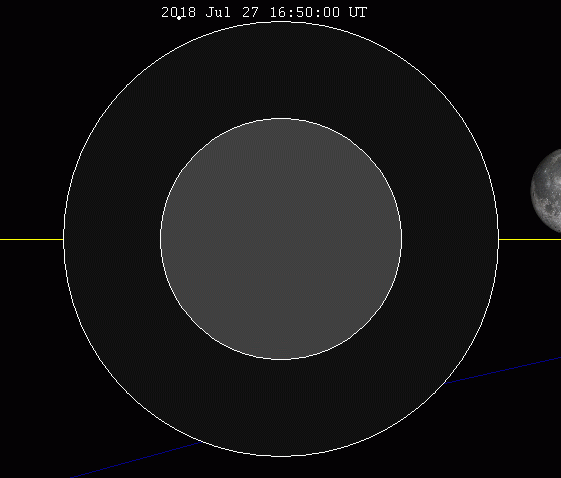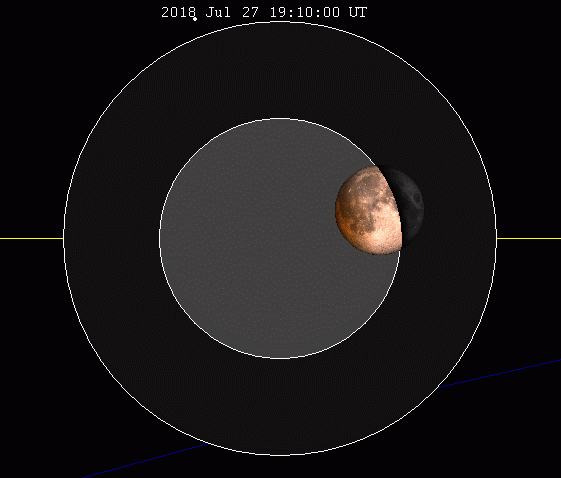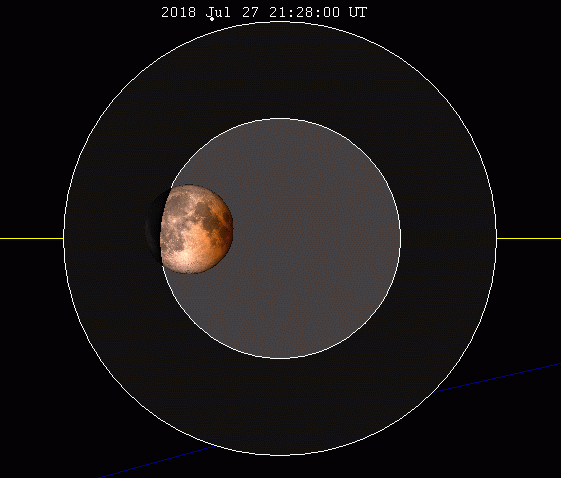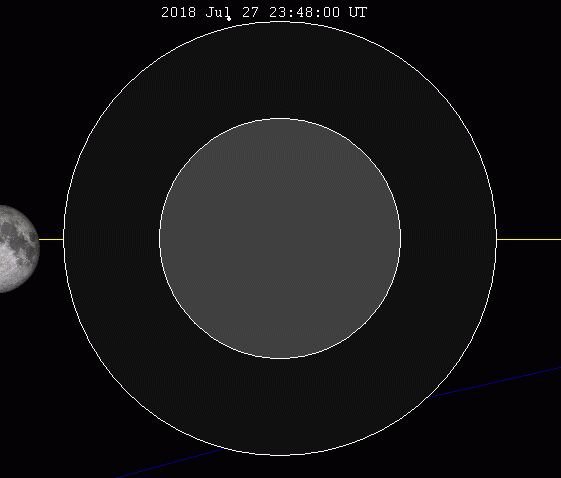
An eclipse of the Moon, also called a lunar eclipse, is the result of the Earth passing between the Moon and the Sun.
The Earth then hides the sunlight and the Moon is no longer directly illuminated. When the Moon is completely in the Earth's shadow, it is referred to as a total lunar eclipse. If the Moon is rather more in the penumbra or partially in the Earth's shadow, it is a partial lunar eclipse.
This phenomenon always takes place at night, when the Moon is full. It can safely be observed with the naked eye anywhere on the part of the Earth that is not exposed to the Sun. This type of eclipse is not as spectacular as the solar eclipse, but it is more frequent. A lunar eclipse takes place over about two to three hours.
During the eclipse, the Moon takes on a reddish hue. This is due to the phenomenon of diffusion. When the Moon is behind the Earth, the Sun's rays must pass through our atmosphere to reach the Moon. However, the majority of the rays will be deflected from the Moon by diffusion. Infrared rays, on the other hand, are less deflected and will therefore pass through our atmosphere to finally reach the Moon.