A season is a time of year characterized by a relatively constant climate and temperature. In astronomy, a season is defined as the time interval during which the Earth travels a portion of its orbit during its revolution around the Sun.
The cycle of the seasons is caused by the combination of 2 phenomena:
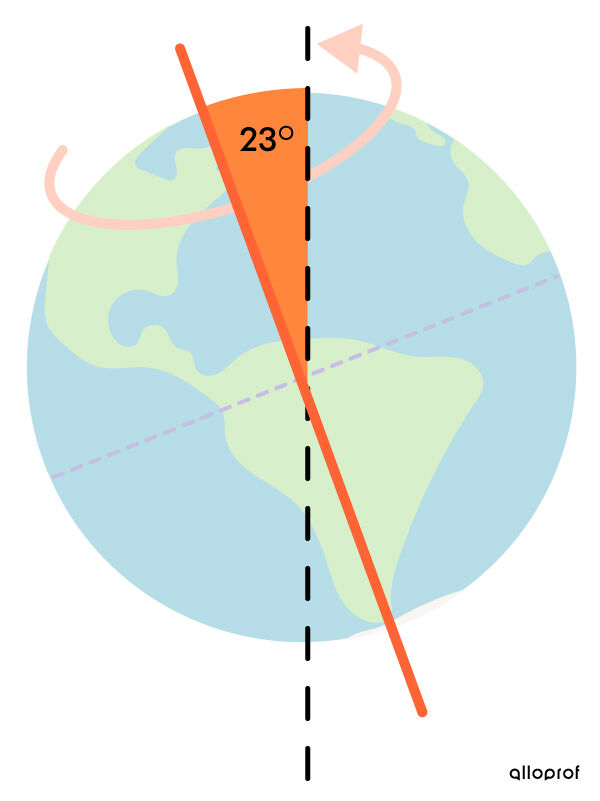
The Earth spins on its axis in a day. This phenomenon is called rotation. Its axis of rotation is slightly tilted.
Earth’s tilted axis is approximately 23° compared to the vertical.
The Earth's revolution is the Earth’s trajectory around the Sun in one year or 365.25 days.
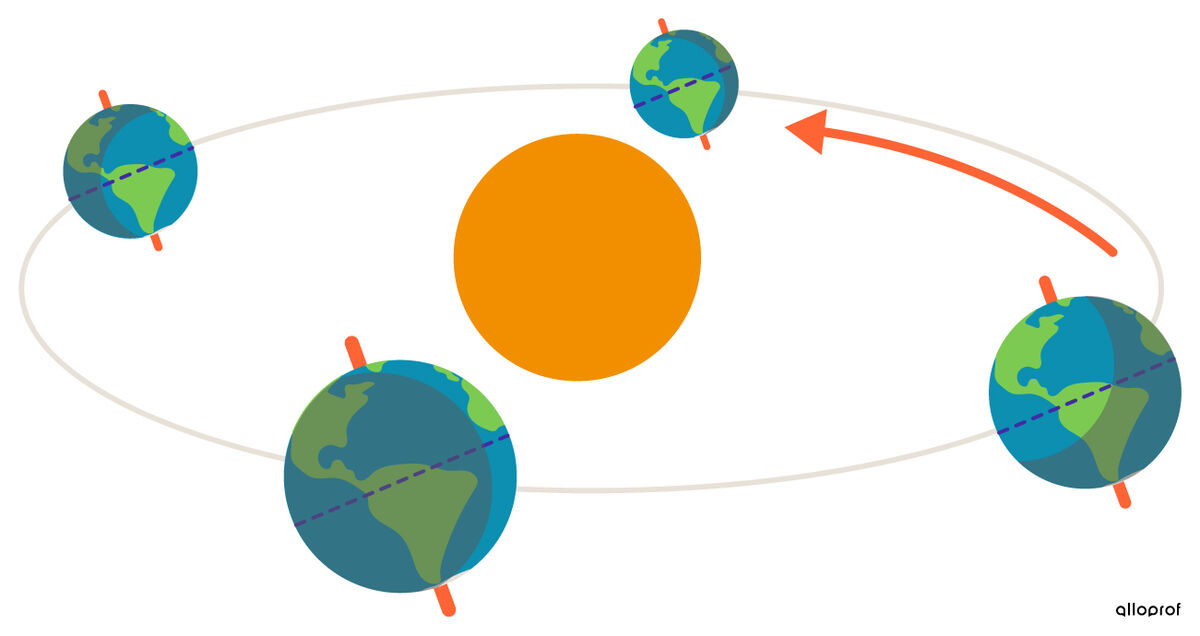
The duration of the Earth's revolution is 365.25 days. Since a year lasts 365 days, a delay of 0.25 days per year accumulates. It is caught up every 4 years by adding a 366th day: this is a leap year.
The path of the Earth around the Sun is not a perfect circle, but rather a slightly flattened circle, called an ellipse. The Earth is not always at exactly the same distance from the Sun.
One might think that when the Earth is closest to the Sun, it is summer. However, it is not the distance between the Earth and the Sun that determines the seasons. On the contrary, the time when the Earth is closest to the Sun corresponds to winter in the Northern Hemisphere. Seasons are determined by the amount of light received. This factor varies depending on the revolution of the Earth and also the tilt of its axis of rotation.
As it revolves around the Sun, the Earth covers a distance of approximately 936 million kilometers at an average orbital speed of approximately |106\ 700\ \text{km/h.}|
Solstices and equinoxes, which correspond to the start of each season, are influenced by the revolution and tilt of the Earth.
The revolution and tilt of the Earth influence the angle at which the Sun's rays strike the surface of the ground and the amount of daily sunshine in a given territory. This is what determines the seasons.
The summer solstice is the name given to the first day of summer. It is the longest day of the year.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the summer solstice occurs around June 21st.
At this time, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted as much as possible towards the Sun. It receives a greater amount of solar energy because the solar rays strike it almost perpendicularly. The rays are therefore more concentrated there.
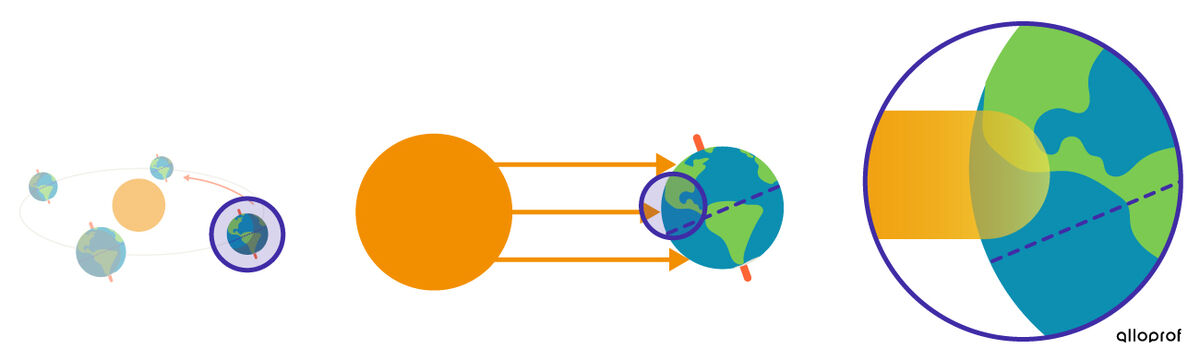
The tilt of the Earth at this time of year also causes the length of day to be longer than the length of night.
The fall equinox is the name given to the first day of fall. The length of day and night is equal.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the fall equinox occurs around September 21st.
At this time, the Northern Hemisphere receives as much solar energy as the Southern Hemisphere. The length of day and night are the same.
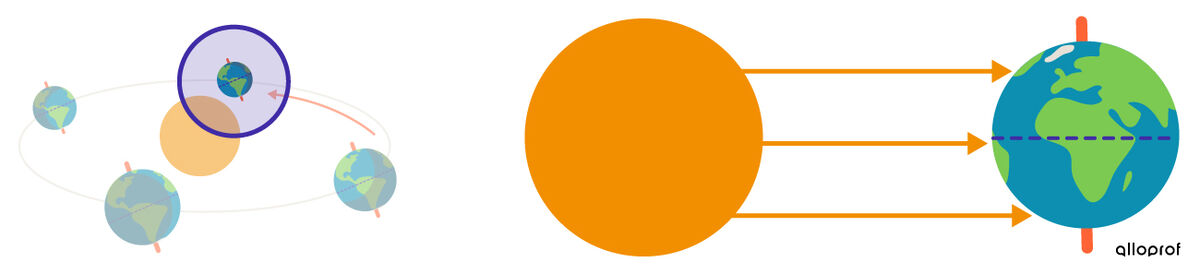
The winter solstice is the name given to the first day of winter. It is the shortest day of the year.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the winter solstice takes place around December 21st.
At this time, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun. It receives a smaller amount of solar energy because the solar rays hit it obliquely. The rays are, therefore, less concentrated.
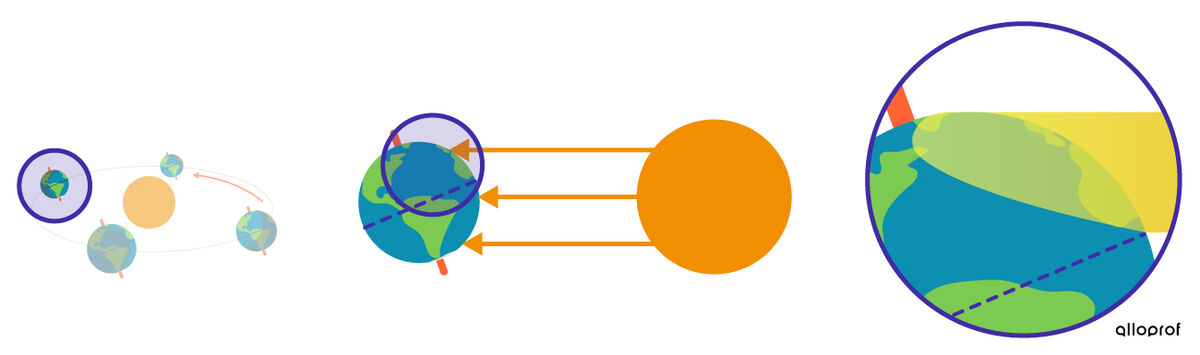
The tilt of the Earth at this time of year also causes the duration of night to be longer than the duration of day.
The spring equinox is the name given to the first day of spring. The length of day and night is equal.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the spring equinox takes place around March 21st.
At this time, the Northern Hemisphere receives as much solar energy as the Southern Hemisphere. The length of day and night is the same.
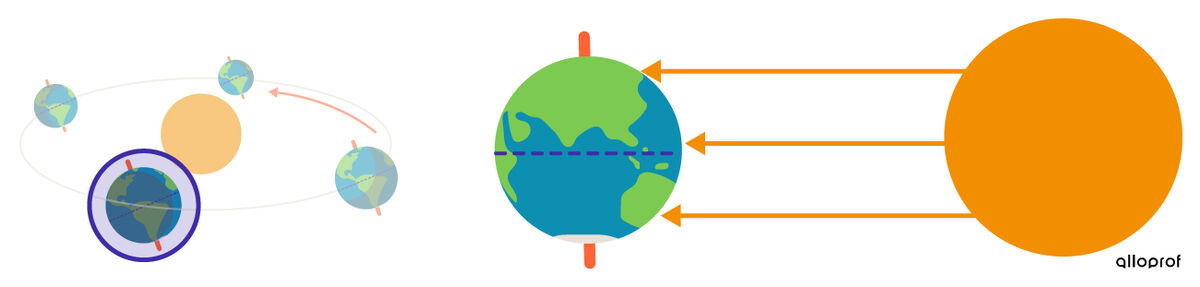
The seasons are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere compared to the Northern Hemisphere. For example, around June 21st, summer begins in the Northern Hemisphere, while winter begins in the Southern Hemisphere.
The seasons in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
| June 21st | September 21st | December 21st | March 21st | |
| Northern Hemisphere | summer | autumn | winter | spring |
| Southern Hemisphere | winter | spring | summer | autumn |
Since it takes time to store heat, the atmosphere lags behind the seasons. As a result, temperatures in fall are often warmer than spring temperatures. Indeed, the atmosphere warms up during the summer. So, even though the Earth receives the same amount of energy during these two seasons, it is usually warmer during the fall because the heat had built up during the previous season.