Gerunds are verb forms that end in -ing and function as nouns in a sentence.
Infinitives are verb forms in their base form and function as nouns, adjectives or adverbs in a sentence.
|
Gerund in a sentence |
Conjugated verb |
Infinitive in a sentence |
|
Reading is one of my favourite hobbies. |
I am reading a good book right now. |
Thriller stories are great to read. |
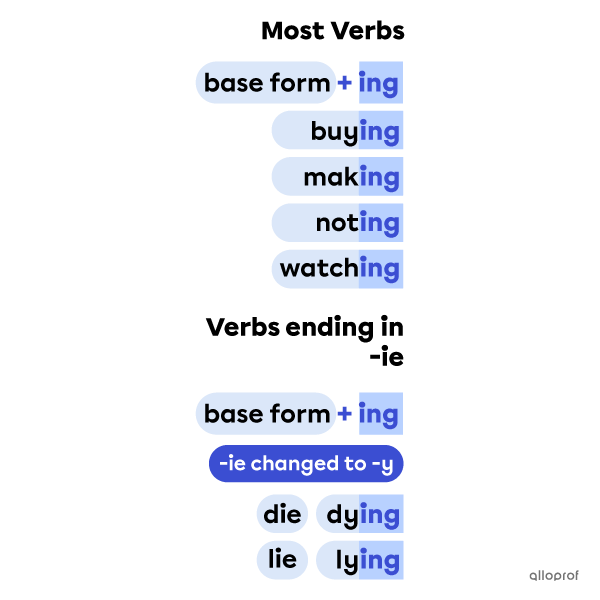
Forming Gerunds
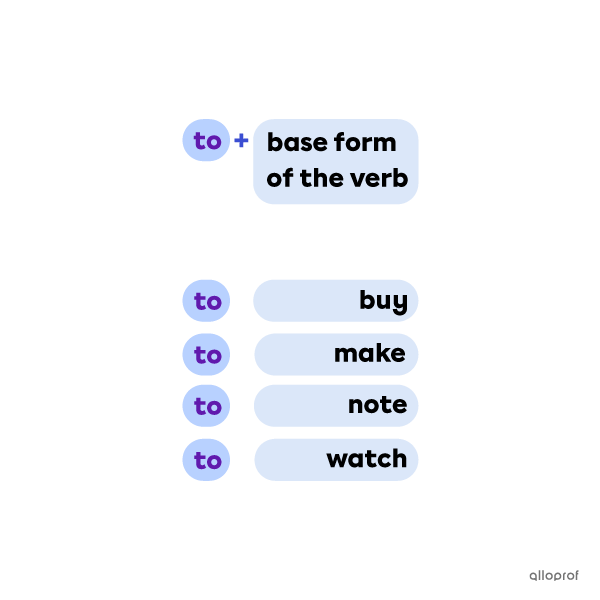
Forming Infinitives
Gerunds and infinitives can be used as:
-
the subject of the sentence
-
the object of the sentence
-
Subject of the sentence
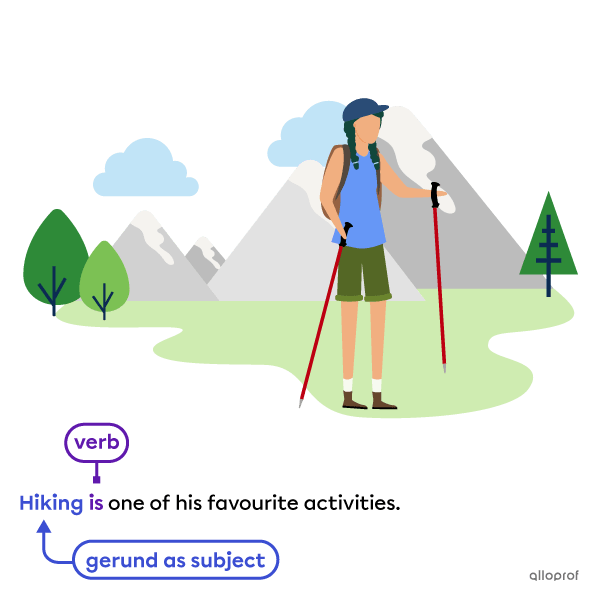
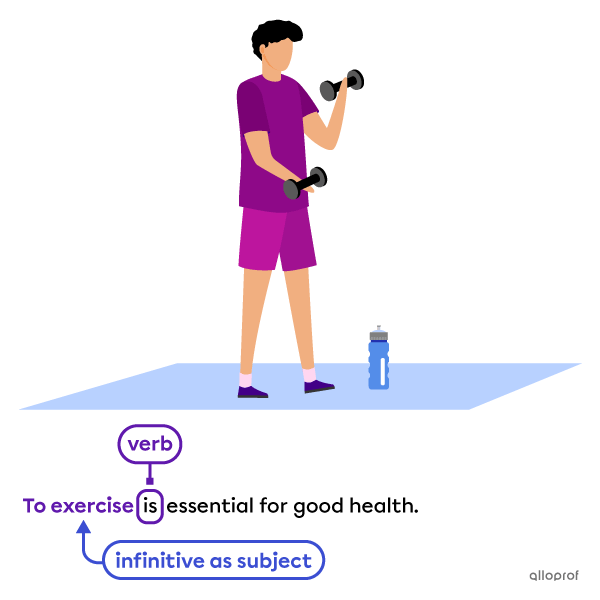
-
Object of the sentence
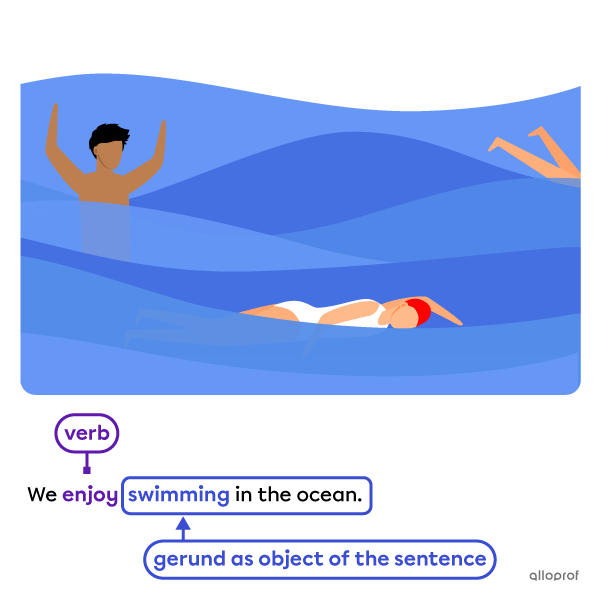
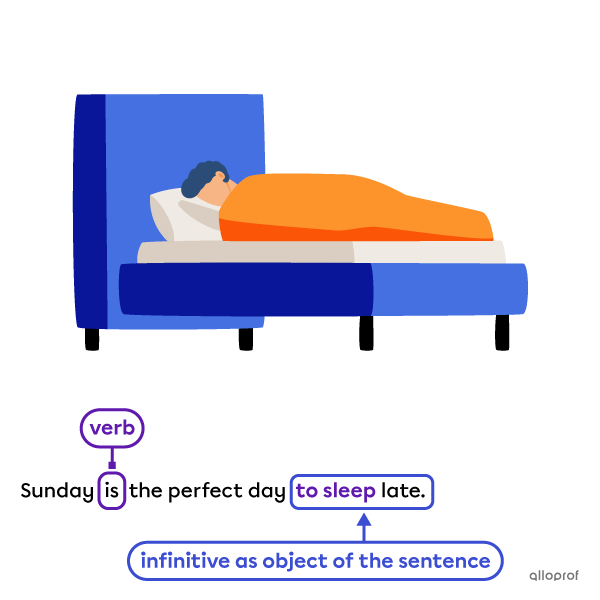
Both gerunds and infinitives can be the object of a sentence.
When the object follows a preposition, a gerund is generally used.
Here are some examples:
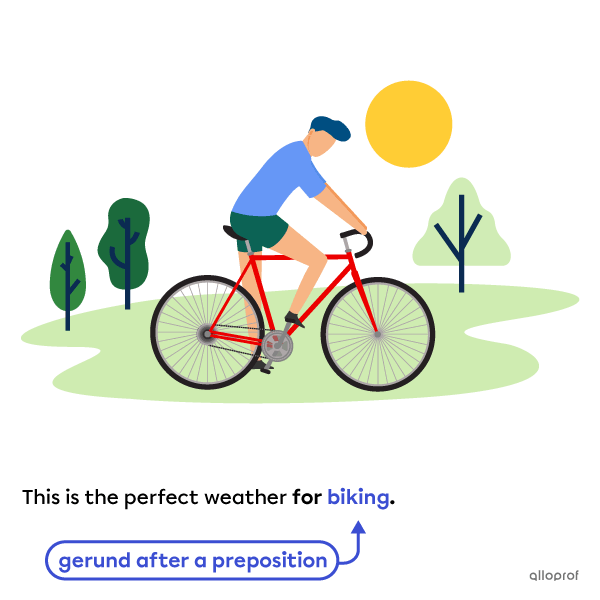
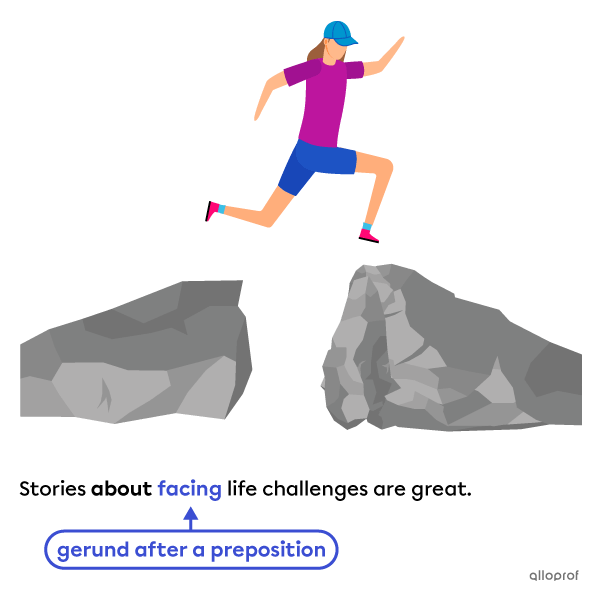
Here are some more examples:
|
Incorrect use of infinitives |
Correct use of gerunds |
|
We’re looking forward to to see you again. X |
We’re looking forward to seeing you again. ✔ |
|
She’s afraid of to fly. X |
She’s afraid of flying. ✔ |
|
I’m interested in to learn new things X |
I’m interested in learning new things. ✔ |
|
She apologized for to interrupt the meeting. X |
She apologized for interrupting the meeting. ✔ |
Gerunds are used after prepositions except the prepositions but and except.
For these two prepositions, we use an infinitive after.
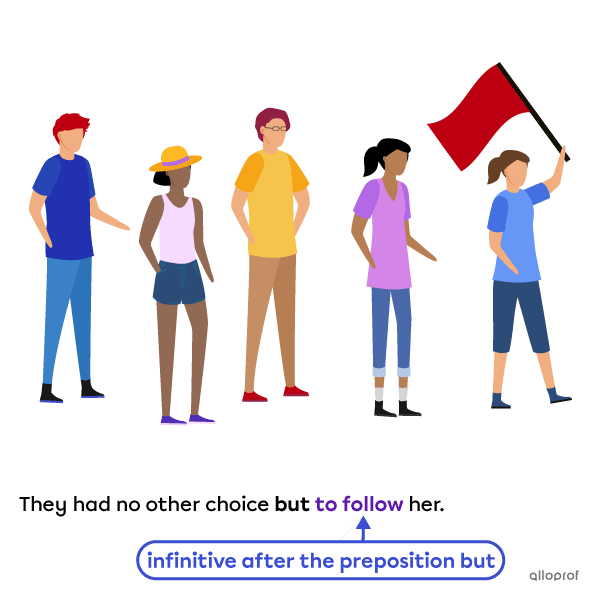
Infinitives can also be used as:
-
Adjectives
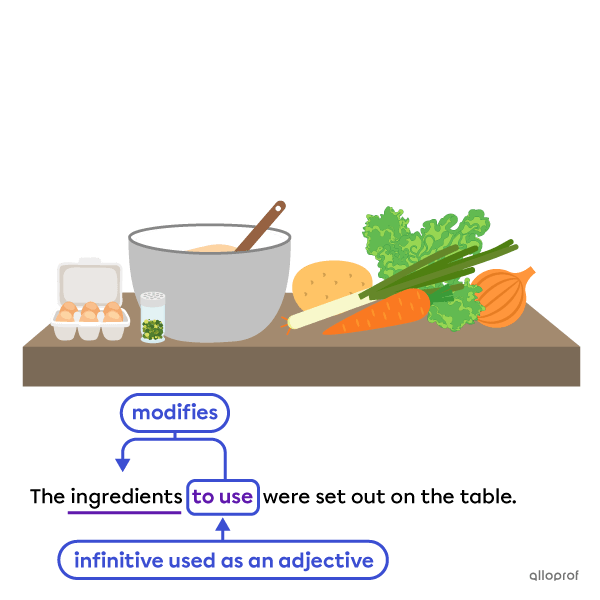
The infinitive to use modifies the noun ingredients, acting as an adjective.
-
Adverbs
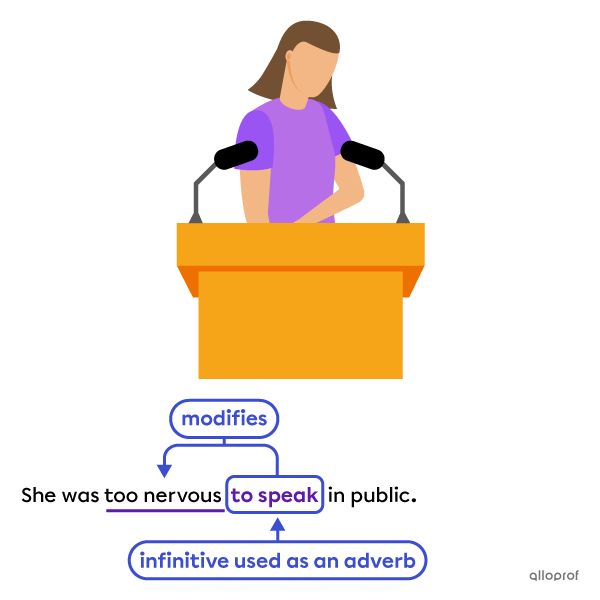
The infinitive to speak modifies the adjective nervous, acting as an adverb.
In most cases, gerunds and infinitives can be interchanged since the meaning is similar.
|
Gerund in a sentence |
Infinitive in a sentence |
|
He started collecting scissors. |
He started to collect scissors. |
However, some verbs should be followed by gerunds, and other verbs by infinitives.
Here are some examples of verbs that should be followed by a gerund:
|
Main verb |
Example with a gerund in a sentence |
|
admit |
They admitted committing the crime. |
|
advise |
He advised returning to the entrance gate. |
|
avoid |
You should avoid transmitting private information to random people online. |
|
consider |
They considered moving away, but they decided to stay. |
|
deny |
I deny knowing anything about this situation. |
|
involve |
The project involved developing three new apps. |
|
mention |
You mentioned meeting my father earlier for a job interview. |
|
recommend |
Teachers recommend using gerunds and infinitives. |
|
risk |
“Don’t risk injuring yourself!” |
|
suggest |
They suggest exploring the area. |
Here are some examples of verbs that should be followed by an infinitive:
|
Main verb |
Example with an infinitive in a sentence |
|
agree |
I agreed to buy new equipment for my friend. |
|
decide |
I decided to go to the party tonight. |
|
deserve |
Everyone deserves to be respected. |
|
expect |
You should expect to hear from the coach today. |
|
hope |
We were hoping to see progress this week. |
|
learn |
They learned to trust their teammates. |
|
need |
We need to search for a new research subject. |
|
offer |
I offered to pay for the meal. |
|
plan |
They are planning to travel to Norway in June. |
|
promise |
She promised to help me with my science homework. |
|
seem |
It seems to be a problem. |
|
wait |
I can’t wait to participate in the next competition. |
|
want |
We don’t want to make any mistakes. |
Try to follow these guidelines to use them correctly:
-
Use a gerund when discussing something specific, real or that has already happened.
-
Use infinitives when discussing something abstract, not real or that only might happen.
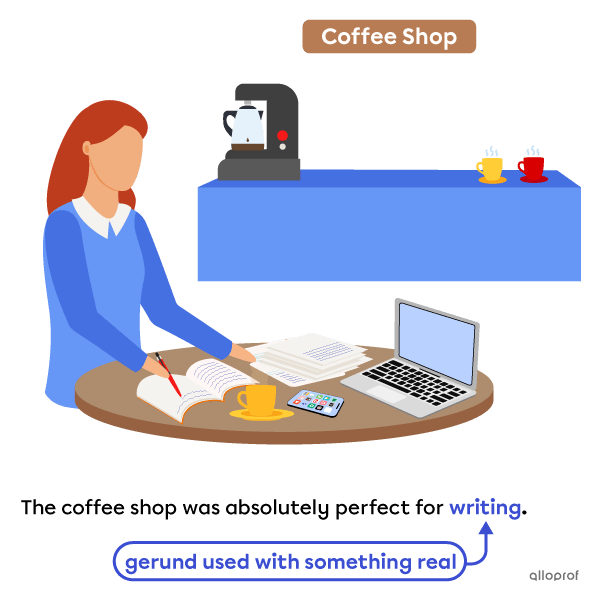
The coffee shop is real and offers a specific place to write.
The location is abstract and the proposal only might happen.