The simple future verb tense is used to express actions or states that begin and end in the future.
It is formed with will or going to.
For:
- Promises ⇒ will
- Spontaneous actions or decisions ⇒ will
- Future facts ⇒ will
- Predictions⇒ will or going to
- Plans ⇒ going to
To learn more on using will or going to, visit Verb Tense vs. Verb Tense.
-
Promises

Benita will give a present to her best friend Sarah next week.
-
Future facts

Italy will host the 2026 Winter Olympic Games.
-
Spontaneous actions or decisions

As soon as Sarah sees it, she will jump with joy.
-
Predictions

They think Sarah will become a ski champion!
-
Plans
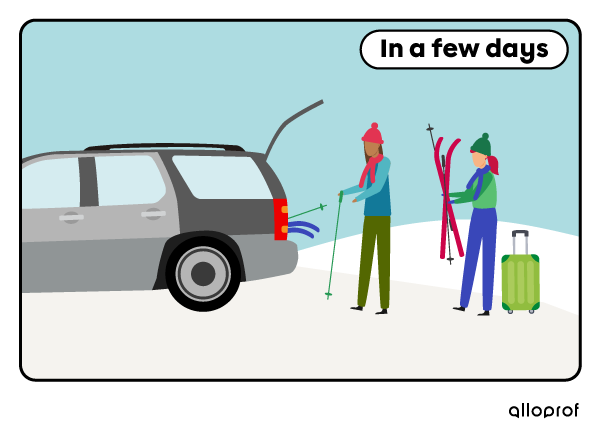
Benita and Sarah are going to try their new equipment in a few days.
Many keywords can help you recognize the future.
| A word | A word combination | |||
| next... | in... | this... | within... | |
|
|
|
|
|
Possibilities and Consequences
The simple future can also be used in conditional sentences. If a condition is met, the future action will happen.

If Sarah trains well, she will make the national team.

If Sarah is careful, she will ski down the slope without falling.

She will only make it to the Olympics if she gets financial help.
When an event is scheduled, the simple present can be used to express the future.

"Don't be late, training starts at 4:15 p.m.!"
When you plan an activity in advance, the present continuous can be used to express the future.

Sarah is visiting Banff on Saturday.
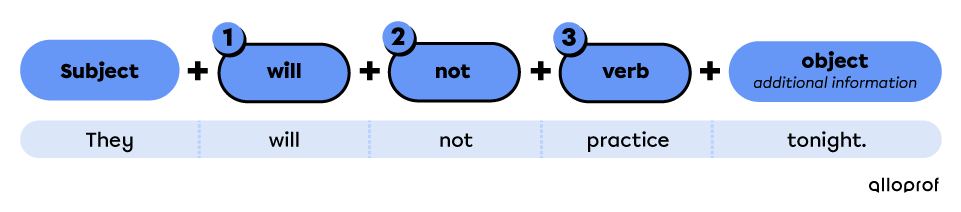
Points to remember when forming affirmative sentences:
With will
-
Place the auxiliary verb will in front of the verb.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
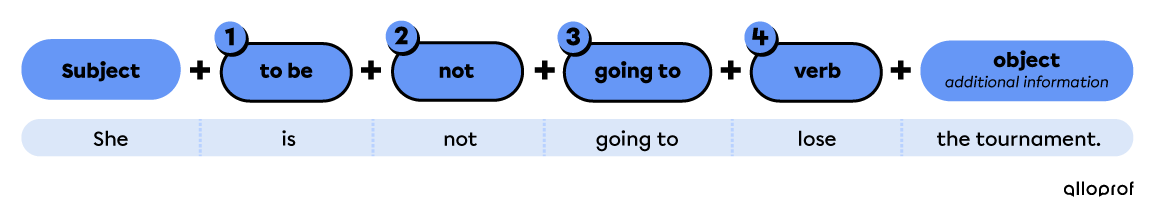
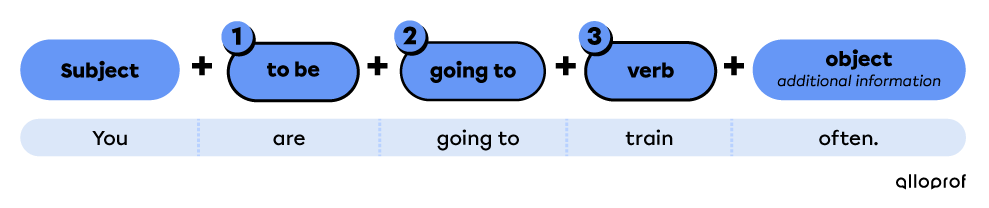
With to be going to
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be in front of the verb.
-
Use going to.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
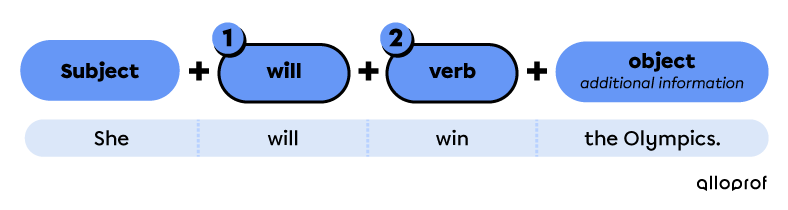
With will

Sarah will win a gold medal.
With to be going to

They are going to stay in a hotel during the Olympics.
The modal shall isn’t commonly used anymore as an alternative to will.
It’s still used in formal writing or classic literature, legal documents and court orders.

Sarah shall climb this mountain to conquer its slopes.

The athlete shall avoid drug use during the competition.
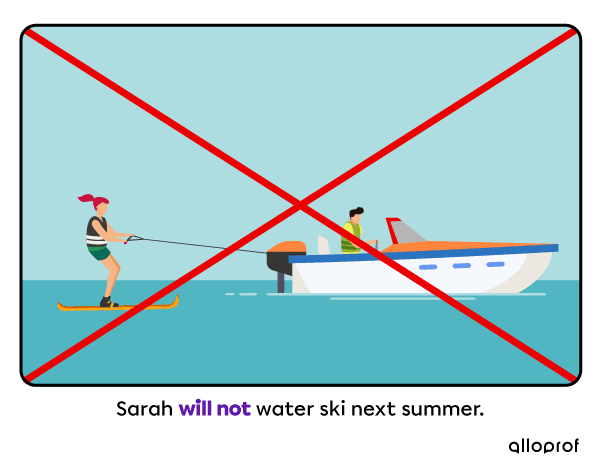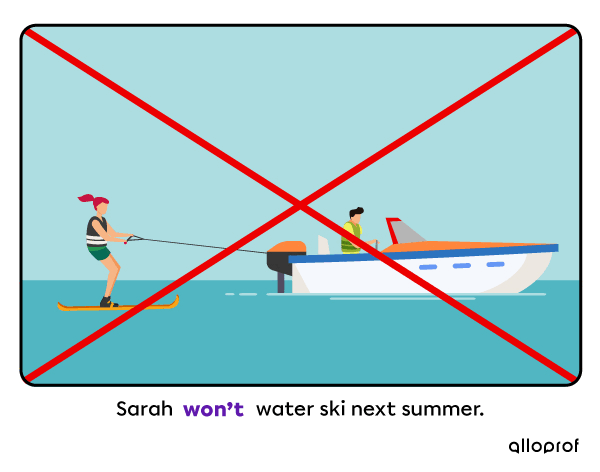
1. With will
2. With to be going to
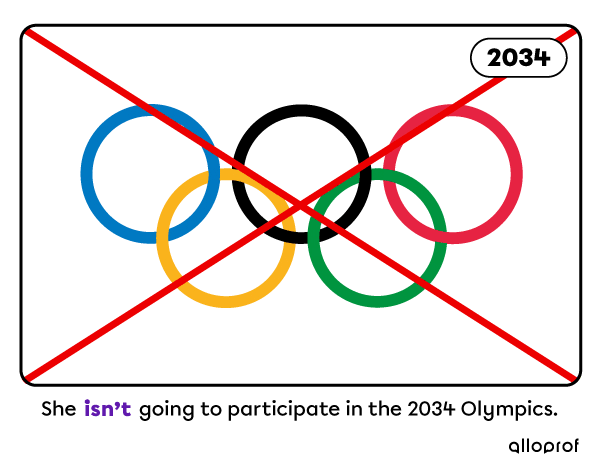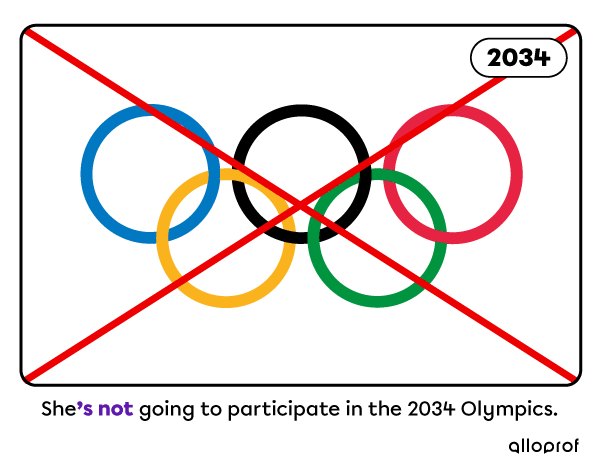
-
answered by yes or no
-
answered with information
-
never answered by yes or no
-
use question words
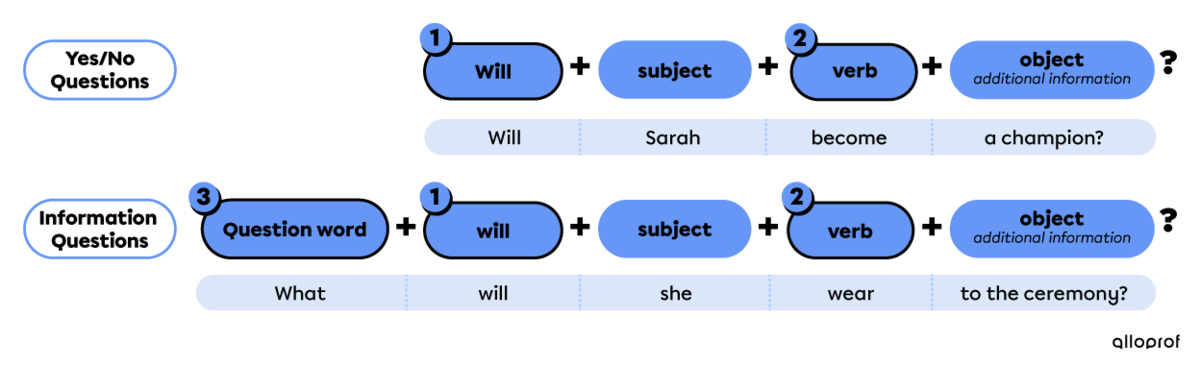
Points to remember when forming questions in the simple future:
With will
-
Place the auxiliary will before the subject for yes/no questions.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
For information questions only: -
Place a question word at the beginning.
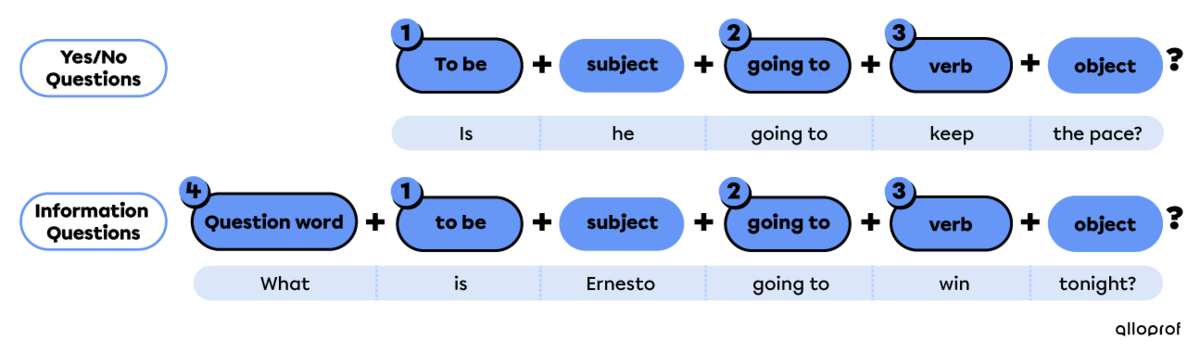
With going to
-
Place the auxiliary to be at the beginning for yes/no questions.
-
Use going to after the auxiliary to be.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
For information questions only: -
Place a question word at the beginning.
1. Yes/no questions with will
| Will | subject | verb | object? |
| Will | she | sign | a contract? |
| Will | they | pack | their equipment? |
1. Yes/no questions with to be going to
| To be | subject | going to | verb | object? |
| Are | they | going to | visit | Beijing? |
| Is | she | going to | be | careful? |
2. Information questions with will
| Question word |
will | subject | verb | object? |
| What | will | Sarah | win | at the Olympics? |
| Why | will | Sarah | stay | healthy? |
2. Information question with to be going to
| Question word |
to be | subject | going to | verb | object? |
| What | is | she | going to | carry | to the mountain? |
| Where | are | they | going to | compete | during the Olympics? |