Each state is sovereign on its own territory and can therefore decide on its own economic development. However, on its own, a state has limited human and financial resources. For this reason, several economic groupings and organizations have been established over the years. This allows countries to work together on a larger scale.
Sovereignty is the absolute power of a state to govern itself by making its own laws and enforcing them within its territory. A sovereign state is independent, meaning that it cannot be controlled by any other state or institution.
Economic groupings allow states to increase their trade. This contributes to their economic development.
Both international and non-governmental organizations help countries around the world develop and reduce disparity.
Disparity is inequality between two things.
Economic groupings are formed between countries with very strong economic relationships. By forming these economic groupings, the member countries contribute to the economic development of all the members. Large economic groupings play a big role in global trade, which benefits the member countries of these groupings. However, these groupings also reduce the opportunities for non-members since they control almost all of the global market.
Many economic groupings exist around the world, including the European Union and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.

The European Union flag has 12 yellow stars in a circle on a blue background, representing solidarity and union among the peoples of Europe.
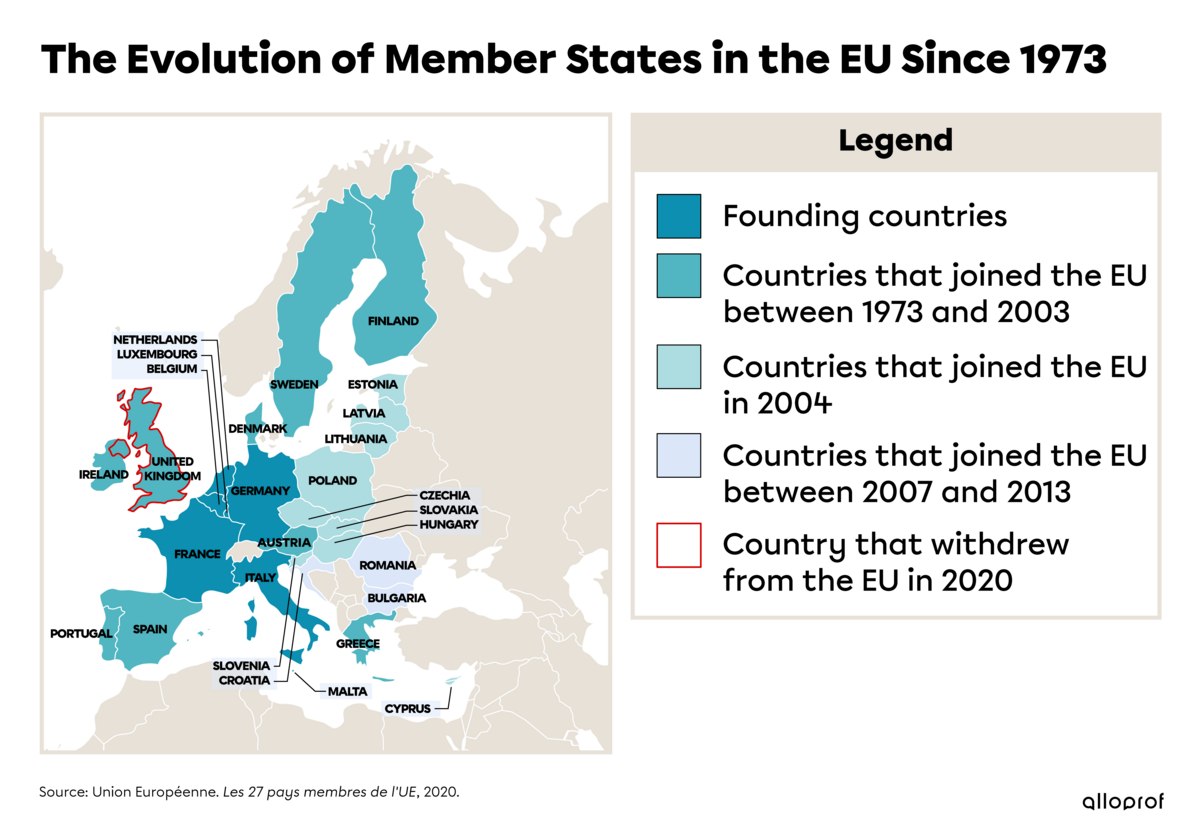
The European Union (EU) aims to strengthen economic cooperation between member countries. The European Economic Community (EEC) was created in 1958 and changed its name to the European Union (EU) in 1993. Originally, it was an economic cooperation, but it has evolved to encompass several policy areas such as the environment and health. The EU countries, which are grouped together in a common market and use a common currency, accounted for 16% of the world’s GDP in 2020, just behind China and the United States.
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is another major economic grouping. It was founded in 1967, with the aim of accelerating economic growth and improving the living conditions of people in Southeast Asian countries. Members include Cambodia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam, among others.

International organizations (IO) give states the opportunity to share their views on a wide range of issues. In doing so, they help establish trade and financial regulations between different countries around the world.
An international organization (IO) is an organization that brings together representatives of different states to achieve common objectives on global issues.

The World Trade Organization (WTO) was founded in 1995. It now brings together 164 states, accounting for almost all international trade. The WTO creates international trade regulations in collaboration with member states around the world.
Its aim is to facilitate international trade by limiting trade barriers. One of its aims is also to help countries in their development.
The WTO provides the framework for multilateral agreements between several different states. These agreements serve to reduce trade barriers, but also to guarantee equality for all countries. These agreements contribute to the economic growth and development of the individual states. They regulate the trade of goods and services as well as intellectual property. Intellectual property refers to the rights to intellectual innovations, such as patents, trademarks and copyrights. Examples of intellectual property are a soft drink recipe, the colour of a logo and the lyrics to a famous song. Each country that signs an agreement must comply with its terms.
The Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) was created to arbitrate economic disputes between member states, when one country believes that another country has violated an agreement.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank (WB), established in 1944, are specialized agencies under the United Nations. They have a joint mission to promote global economic growth.
An institution is an organization governed by rules and laws that plays a specific role in society. Its role may be political, social, economic, religious, etc.
To better understand what an institution is, you can watch the video What is… an institution?.

The main objective of the International Monetary Fund is to ensure the stability of the international monetary system. To do this, the IMF analyzes the economic policies of its 189 member states. If a member state is experiencing severe financial difficulties, the IMF can provide financing to help its economy recover and avoid a crisis in the international monetary system.
The international monetary system refers to anything that affects how the currencies of different countries interact, such as currency exchange rates. It also covers the movement of capital (the movement of money) between states and the elements that enable credit (the borrowing of money). In short, this term broadly includes financial transactions between states.
When Greece borrowed money from the International Monetary Fund in 2010, it had to manage its economy very strictly, which resulted in a recession (reduced economic growth) and a massive increase in unemployment.
Fortunately, this strict financial management paid off: from 2013 to 2019, the unemployment rate in Greece has improved, falling from 27.7% to 16.8%.

The World Bank’s (WB) mission is to reduce poverty and raise the income of less wealthy people in developing countries. The WB provides financial support to countries facing poverty. Funding can take the form of low-interest or interest-free loans, or even donations. The World Bank also provides governments with policy advice and technical assistance to help them better manage their economies.
However, IMF and WB loans come with several conditions. When a country borrows money from these institutions, its economic policies must be adjusted to address the problems that led its request for financial assistance.
The World Bank provides advice to borrowing countries, which must comply with the WB’s policies and guidelines. For example, the WB recognizes that natural disasters have long-lasting and far-reaching effects on poverty. To reduce these effects, it provides financial and technical support for risk assessment, risk reduction and sustainable reconstruction. This financial assistance is only provided if borrowing countries respect and implement the World Bank’s policies and guidelines.

Leaders of the G7 countries attend a meeting at the G7 summit in Biarritz, France.
Source: Kilpatrick, Sean. « Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, right, takes part in a working session with G7 leaders during the G7 Summit in Biarritz, France, on Sunday, Aug 25, 2019. », The Canadian Press, August 25, 2019.
The Group of Seven (or G7) consists of leaders of the seven major industrialized countries (France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States, Canada and Japan). The group was formed in 1975 with the aim of facilitating trade to resolve economic problems. The G7 has no formal charter governing its mission and actions and its bureaucratic structure is limited. Most importantly, it is a space for member states to discuss global issues in meetings and working sessions.
Along the same lines, the G20 is a forum for leaders from developed and developing countries to discuss economic and social issues. G20 countries include the G7 members as well as China, India, Brazil and other members.
From 1998 to 2014, Russia was a member of the G7, making it the G8. Russia was then expelled from the group in 2014 because of tensions over the annexation of Crimea.

The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has 37 member countries worldwide. It focuses on the economy, education and development. Its mission is to pool knowledge from different economic and social players, including public authorities or civil society representatives, to promote better public policy practices around the world.
The United Nations has created several development and economic organizations. Like other organizations, UN organizations have the ability to collect statistical data from around the world on a variety of topics. These data are then used to develop policies and programs specific to people’s needs. Below are examples of UN Specialized Agencies:
-
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development and the United Nations Industrial Development Organization assist countries in their economic and industrial development to reduce poverty.
-
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) is an international financial institution and a specialized agency of the United Nations that fights poverty and hunger in the rural areas of developing countries.
-
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) aims to make healthy and sufficient food available to all populations.
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are organizations formed independently from the states. At an international level, they seek to reduce poverty in a variety of ways. For example, some provide assistance to low-income people to help them start their own small local businesses. This allows them not only to create wealth for their communities, but also to be independent of large international companies. Some NGOs have major influence over states. They bring attention to the needs of poor communities to try to improve their situation or change the way things are done. In general, NGOs aim to ensure that everyone in the world has equal opportunities.
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is a non-profit organization made up of citizens who defend a cause and act independently from the government.

The International Movement ATD Fourth World (also known as ATD Fourth World) is an NGO that seeks to eradicate extreme poverty in the world. To achieve this, its members and volunteers focus on long-term projects with people living in poverty. Its main priorities are education, building a more equitable economy and defending human rights.

Oxfam, which is short for Oxford Committee for Famine Relief, was founded in 1942. Its main objectives are to end poverty and defend human rights. To do this, the NGO advocates for climate action, gender equality, access to land and access to education.

Amnesty International focuses on defending rights, including economic and social rights. It also works to protect the dignity of everyone around the world. One of its many priorities is the abolition of modern slavery. As an NGO, it is independent of any government or political ideology.
The World Social Forum (WSF) is an open space for discussion and debate that brings together NGOs from around the world. It was founded in 2001 and supports the search for ideas and projects to defend human rights and promote sustainable development. It is held annually at different locations around the world.

Doctors Without Borders (MSF) is a humanitarian aid organization that provides medical care in areas affected by conflict, natural disasters or epidemics. Founded in 1971, the NGO aims to ensure that everyone has access to medical care, wherever they may be. It achieves this by sending medical equipment (medicine, hospital tents, etc.) and medical staff (doctors, nurses) to the people most in need. This is done at the request of a country or the United Nations (UN).
By improving people's health, this organisation helps them to be active in society and therefore, indirectly, to contribute to a state's economy.
Ladouceur, Maude and Alain Parent. Globe. Cahier d’apprentissage, 2014, p.173-175.