Governments adopt economic policies to help them manage the exchange of commodities, control the financial market and create laws to avoid serious economic crises. Generally speaking, economists aim for profitability. To achieve this, they often use limited resources to maximize profits.
-
The economy is the management of a region or country’s resources. The economy generally involves the exploitation of resources and the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
-
The market is a place of exchange where commercial activities take place. This is a meeting place for sellers (supply) who have a good or a service to sell and buyers (demand) who want to pay money for a product. There are regional (Quebec), national (Canada), continental (North America) and international (global) markets.
Despite the efforts of economists and governments, the economy fluctuates and experiences periods of growth and slowdown. Here are the main concepts used to characterize economic fluctuations:
These economic concepts have been used since the industrial revolution.
Three factors influence economic growth:
-
work (the number of hours worked by the workforce)
-
capital (money invested)
-
techniques (knowledge and technologies used)
-
Economic growth occurs when the quantity of goods and services produced in a country increases over a certain period of time. A country’s economic growth is usually measured annually.
-
Capital is the assets or money owned by a person, company or state. Capital can be used to make investments.
Economic growth can occur when a company increases production or improves productivity. More investments (more capital) or better technologies can also have an influence.
A country’s economic growth is calculated by measuring its gross domestic product (GDP). GDP is used to quantify economic growth as a percentage. Economic growth is calculated by taking inflation into account. This reduces the effects of inflation on the GDP and allows the GDP to be calculated more accurately over time.
-
Gross domestic product (GDP) is used to calculate a country’s wealth by measuring the total value of all goods and services produced within that country over a given period (usually 1 year).
-
Inflation is the general and continuous increase in the price of goods.
Canada’s annual GDP growth was 1.90% in 2018 and 2.98% in 2017, meaning its economic growth was higher in 2017. (Perspective Monde, n.d.)
However, economic growth can have negative effects such as the depletion and scarcity of resources. Although it can lead to better standards of living, it doesn’t mean this is the case for the entire population. For example, a country’s economic growth may be very high, but might only benefit one group in society. Unfortunately, living standards may not improve for the rest of the population.

When the quantity of metals or minerals present in a mine has been exploited, the mine must close, as the resource is exhausted.
Source: Zachary Satko, Shutterstock.com
To learn more about this topic, see the concept sheet on wealth inequality.
Economic growth is only one of the many facets of economic development. Economic development is the process by which a community’s quality of life and overall standards of living are improved. Economic development is calculated using several measures, such as:
-
the GDP
-
the Poverty Index
-
life expectancy
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a socioeconomic indicator that determines the average quality of life of a country’s population by measuring life expectancy, level of education (access to education) and economic output (GDP per capita). The HDI ranges from 0 to 1. The closer the index is to 1, the higher the quality of life.
For example, Canada’s HDI in 2014 was 0.91, while Ghana’s was 0.58.
This information is used to better analyze how the wealth created by economic growth is distributed across a population. Specifically, does the entire population benefit from economic growth or just certain groups?
To find out more about economic development, see the concept sheet on the level of development of countries.
An economic crisis occurs when the economic situation of an activity sector or the entire global economy rapidly deteriorates. An economic crisis may have limited consequences, but it can also affect many sectors of economic activity and last for several months or even years. This is known as a recession or economic depression, depending on the case.
There can be various signs of an economic crisis, including a declining GDP, rising unemployment and business closures.
The global economy was disrupted in 2008 when many homeowners in the United States were unable to pay back the money they borrowed to buy their homes. This caused house prices to fall and created problems for the banks that had loaned large amounts of money to homeowners, with some banks going bankrupt. This was the catalyst for a global financial crisis. It took several years and numerous measures for the economy to recover.
A recession occurs when economic growth slows down or declines significantly and last more than a few months.
A recession can be triggered by a drop in production or by a natural disaster, causing the GDP to fall and unemployment to rise. During a recession, lower production and higher unemployment lead to a drop in consumption. All these elements are interconnected, meaning when one changes, the others follow. During a recession, people can lose faith in the economy and their government. In addition to buying less, people may decide to withdraw their money from the bank, creating an imbalance in the lending and savings system.
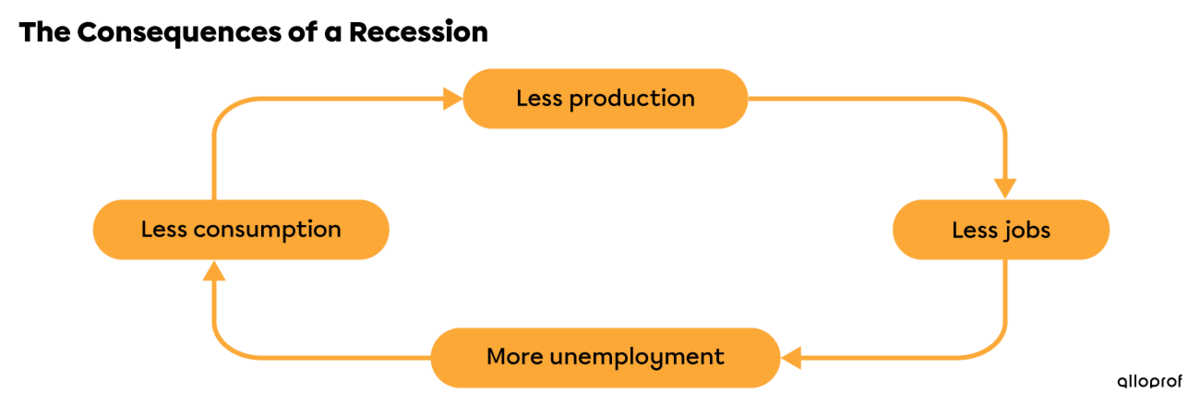
The government may try to end the recession by stimulating job creation and encouraging consumption.
An economic depression is a severe economic crisis that lasts for several years, as opposed to an economic recession which is shorter.
During an economic depression, production (measured by GDP), employment and consumption decline significantly. The consequences of an economic depression (business closures, high unemployment rate, etc.) are worse than the impacts of a recession. In the last century, the global economy experienced several recessions, but only one economic depression: the Great Depression.
Several factors led to the Great Depression. To learn more about this topic, consult the concept sheet on the Roaring Twenties and the Great Depression.
Economic recovery occurs when the economy experiences a new period of growth after a crisis, recession or depression.
It typically takes longer for the economy to recover than the duration of the depression or recession. New businesses or jobs are slowly created, lowering unemployment. People gradually regain confidence in the system, start reinvesting their money in the bank or the stock market and spend money again. GDP slowly returns to pre-recession or depression levels, eventually exceeding them.
Perspective monde. (n.d). Croissance annuelle du PIB (%), Canada. Université de Sherbrooke. https://perspective.usherbrooke.ca/bilan/tend/CAN/en/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG.html