-
Colonialism is a policy based on the occupation and economic, political or social exploitation of a territory by a foreign state.
-
Neocolonialism refers to a situation where a state is dependent on another state. This dependence is not official and can be economic, cultural or scientific.
When a colony gains its independence, it becomes a state with the same rights as any other country. It can then make its own decisions by passing its own laws, establishing its own trade agreements or exploiting its own natural resources. However, a relationship of economic domination often continues to exist between the former colony and the former mother country.
Mother countries are hesitant to give up the sources of wealth they control in the former colony. As such, they continue to play a large role in the new state’s economy.
The former French colony of Gabon has an abundance of oil resources. French companies primarily exploit these resources before exporting their production to other countries.
Omar Bongo, president of Gabon from 1967 to 2009, famously summed up the situation: “Africa without France is like a car without a driver, while France without Africa is like a car without gas.” (Translation provided by Alloprof)
This example shows the deep economic ties that can be created between a mother country and its former colonies that have highly coveted natural resources.
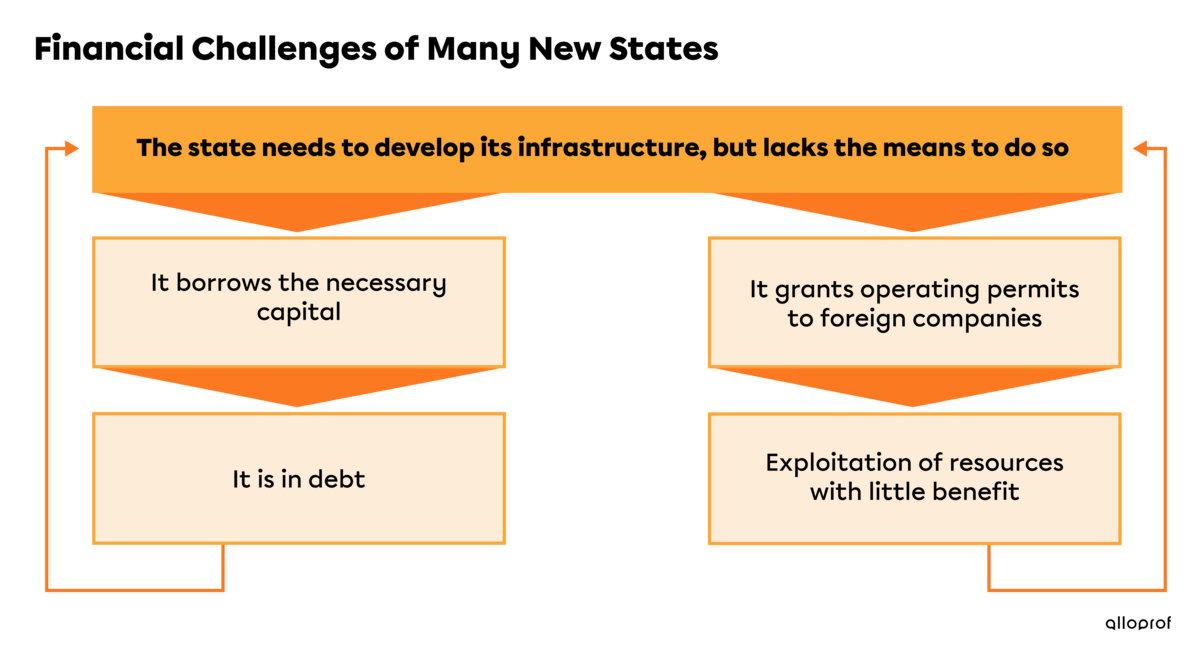
The root of this power relationship is the new nation’s need for financial resources to invest in infrastructure or social measures to benefit the population.
The new state sometimes lacks the resources to make these investments and must turn to other sources of funding, borrowing large amounts of money from its former mother country (which is a developed country) to obtain these investment funds, causing it to go deep into debt.
Developed countries continue to exploit natural resources in former colonies through foreign companies. These companies pay royalties to new or developing countries to exploit their natural resources, which they then export to developed countries. This generates little wealth for the new state since the natural resources are processed in developed countries.
Royalties are amounts of money that a company or state must pay to another state in exchange for the right to exploit a resource.
Tantalum is a metal with very useful properties for high-tech manufacturers. It is extracted from coltan, a mineral found in major quantities in areas of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Between 70% and 80% of coltan is currently mined from these areas by male, female and child miners who work under very harsh conditions.
Coltan mined in the DRC is sold on international markets and then processed and used to make a variety of devices, including cellphones, computers and video game consoles.
The following article provides more information on coltan mining and the issues related to its operation: Child miners.
Some aspects of this system resemble the trade established during the colonial period.
Africa and parts of Asia continue to feel the effects of colonization and decolonization. This partly explains the difficult economic and social conditions that these regions face and their limited participation in world trade.
To find out more, see the concept sheet on the level of development of countries.
Ladouceur, Maude and Alain Parent. Globe. Cahier d’apprentissage, 2014, p. 146-147.
Giguère Groulx, Jean-Félix et Marie-Hélène Laverdière. Immédiat. Richesse, 2017, p.20-23.