The state plays many roles, whether in education, health care, road infrastructure or support for businesses. But it is difficult for a state to fulfil these roles without sufficient financial resources. That’s why it tries to create wealth by exploiting its natural resources or supporting the training of its workforce.
Natural resources are necessary for the production of many goods. For example:
-
Agricultural land provides a large amount of food.
-
Oil produces fuel and is used to make plastic.
-
Bauxite is the principal ore used to make aluminum.
Mines are used to exploit minerals from below the ground. These minerals are then sold to companies that use them to create high-tech products such as batteries for electric cars or laptop screens.
Exploiting natural resources on its territory is an important way of creating wealth for a state or a country. However, these resources are unevenly distributed around the world, giving some countries an advantage over others.
Some countries have natural resources that they are unable to exploit for certain reasons:
-
Lack of infrastructure such as bridges and mines
-
Lack of capital to invest
-
Resources are already being exploited by foreign companies. Find out more about this topic in the concept sheet about neocolonialism.
-
A state is a territorial and political entity administered by a government. It has defined borders within which a population lives.
-
Capital is the assets or money owned by a person, company or state. Capital can be used to make investments.
-
Infrastructure includes all facilities that allow a company, a region or a state to function. Roads, bridges and buildings are examples of infrastructure.
To complete new projects, states and companies need financial resources, also known as capital. Among other things, capital is used to:
-
purchase land and equipment;
-
build a building;
-
pay employee salaries;
-
conduct research and for development;
-
pay to transport raw materials;
-
pay to transport finished goods for delivery to buyers.
This capital can come from the state. It can also come from private companies or local or foreign investors.
Several companies in an area want to export their products to other countries, but the city’s port is too small to accommodate large shipping vessels. Unfortunately, neither the companies nor the state have the financial resources to expand and modernize the port, so they are looking for an investor to fund this expansion project.
An engineering school trains 50 new engineers each year. The graduates join different companies and help to:
-
build roads and bridges;
-
install towers and high-voltage lines;
-
create new products or develop new solutions in a wide range of fields.
This example shows that the more skilled labour a country or company has, the more it can develop high-value projects, goods and services to create more wealth.
On the other hand, companies with a low-skilled workforce struggle to develop high-value goods or services, since employees lack the necessary knowledge and skills to develop them. These goods or services generally sell for less, so they generate less wealth.
Productive companies generally make higher profits, which can be used to:
-
upgrade their equipment and technologies;
-
develop new goods and services;
-
open new markets to sell their goods.
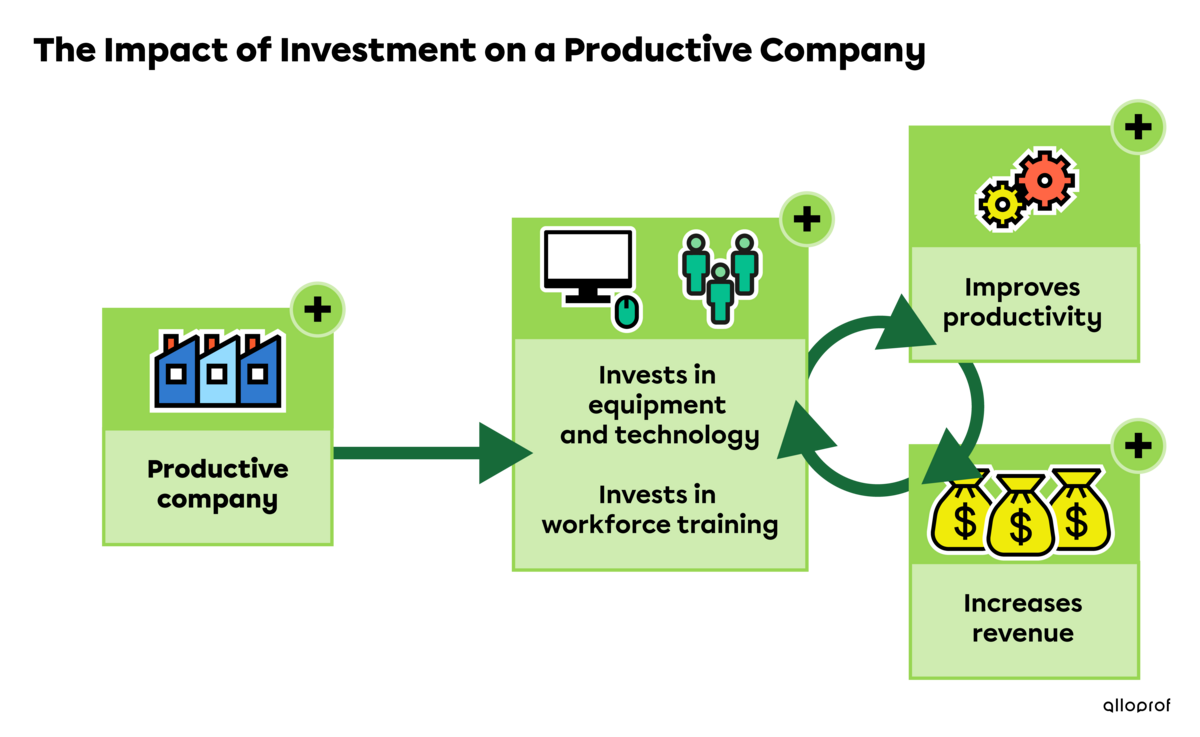
A forestry company has purchased a new piece of machinery that cuts and limbs a tree and loads it onto a transport truck in one action. This has increased the number of trees harvested from the forest in a single day as well as the company’s revenue.
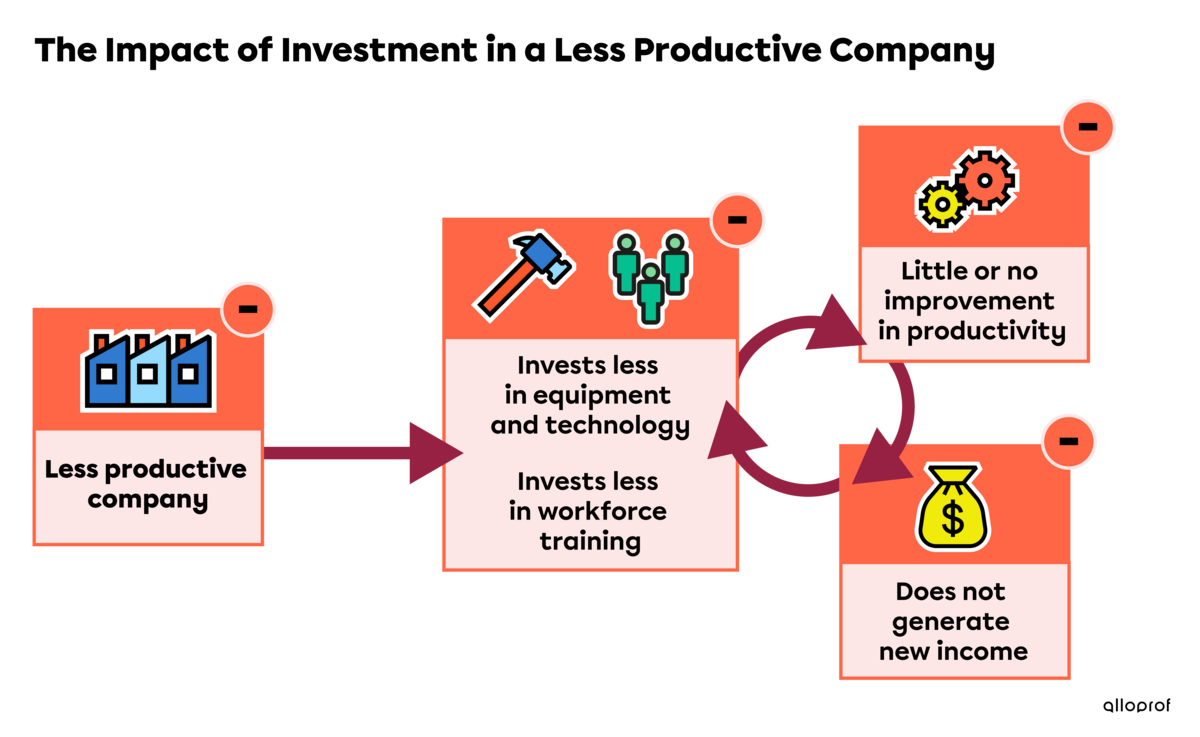
On the other hand, a company that produces less, whether due to lack of capital, skilled labour or inadequate infrastructure, has more difficulty developing. A less productive company creates less wealth for its country than a successful company.
States can take action in different ways to support the creation of wealth in their country, either by investing capital or by protecting their resources.
Some states lack the financial resources to adequately support their economies. This negatively impacts corporate productivity as well as the existence of transport and communication infrastructure. For example, a country that does not have enough financial resources (capital) can’t afford to build a port to accommodate larger shipping vessels that would increase trade. It also can’t cover the expenses needed to build a highway linking two major regions or to upgrade its Internet network.
Over the years, states have developed different strategies to create more wealth within their borders and for their populations. Below are examples of these strategies:
-
Investing in education to attract skilled labour that can help businesses grow
-
Investing in research and development programs to find new natural resources or new ways to exploit them (These investments also support the development of new technology.
-
Joining economic groupings allows states to find new investors to fund business development or infrastructure construction or to find new markets to sell more goods or services
-
Regulating the exploitation of natural resources to protect them (The government can use these regulations to make companies pay royalties, allowing it to supervise foreign companies.)
Royalties are amounts of money that a company or state must pay to another state in exchange for the right to exploit a resource.
Ladouceur, Maude et Alain Parent. Globe. Cahier d’apprentissage, 2014, p.163-165.
Giguère Groulx, Jean-Félix et Marie-Hélène Laverdière. Immédiat. Richesse, 2017, p.10-11.

