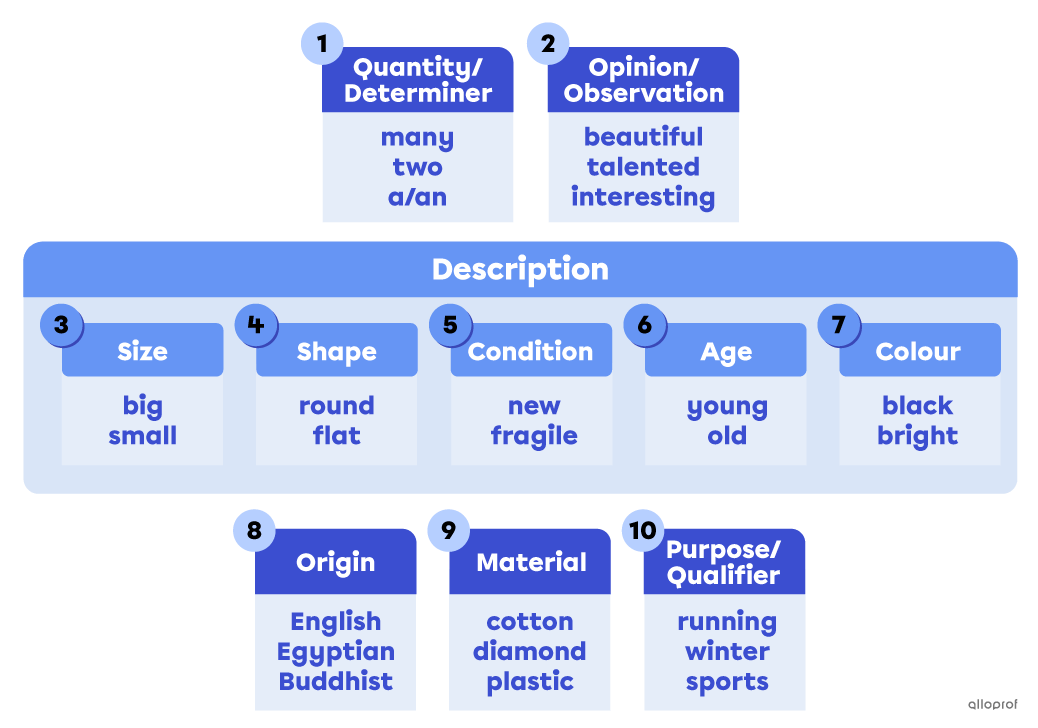
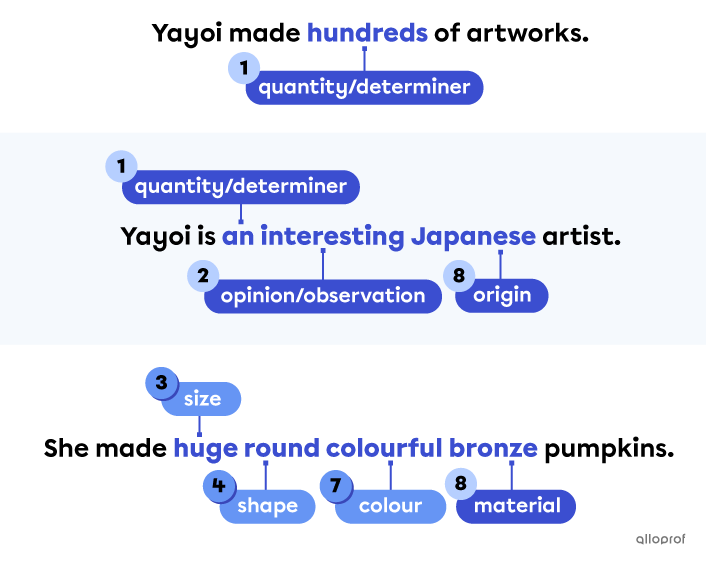
Adjectives do not have a plural or singular form: they always stay the same.
Only adjectives used as determiners have plural forms. They are the:
Comparative adjectives compare two things or people.
For example comparing two people’s age:
|
Person 1 |
Age comparison |
Person 2 |
|
Yayoi is |
older than |
Ushio. |
Superlative adjectives compare more than two things or people.
For example comparing one person’s age to several other people’s ages:
|
Person 1 |
Age comparison |
All other people |
|
Yayoi is |
the oldest |
artist in the group. |
Visit the Comparative & Superlative Adjectives concept sheet to learn more about them.
Possessive adjectives are used to indicate ownership of a noun, who it belongs to.
The possessive adjectives are:
-
my
-
his/her/its
-
our
-
your
-
their
Visit the Possessive Adjectives concept sheet to learn more about them.
Demonstrative adjectives are used to point something out or indicate the position of an object.
The demonstrative adjectives are:
-
this
-
that
-
these
-
those
Visit the Demonstrative Adjectives concept sheet to learn more about them.
Interrogative adjectives are used to modify a noun in information questions.
|
Interrogative Adjective |
Used to ask about: |
Example |
|
|
What |
|
Question |
 |
|
Possible answer: |
|||
|
Which |
|
Question: |
 |
|
Possible Answer: |
|||
|
Whose |
|
Question: |
 |
|
Possible answer: |
|||
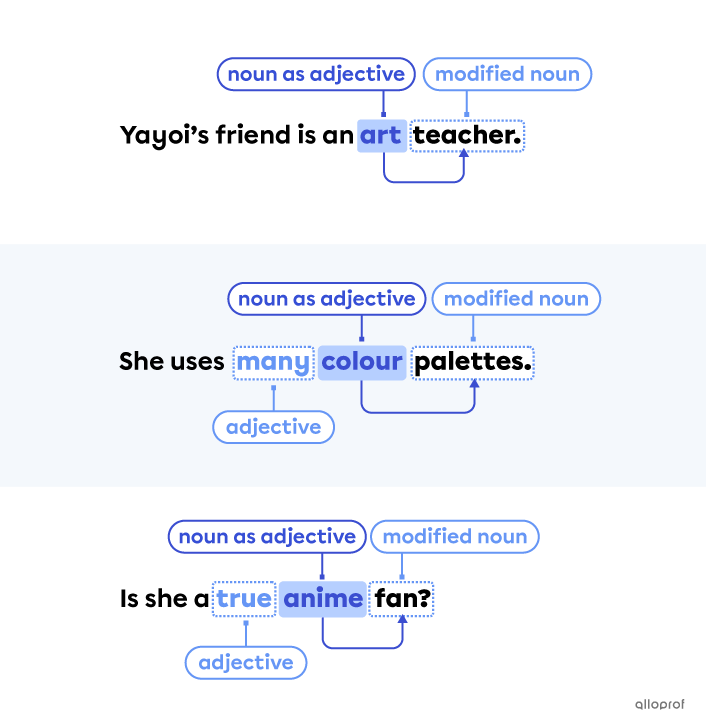
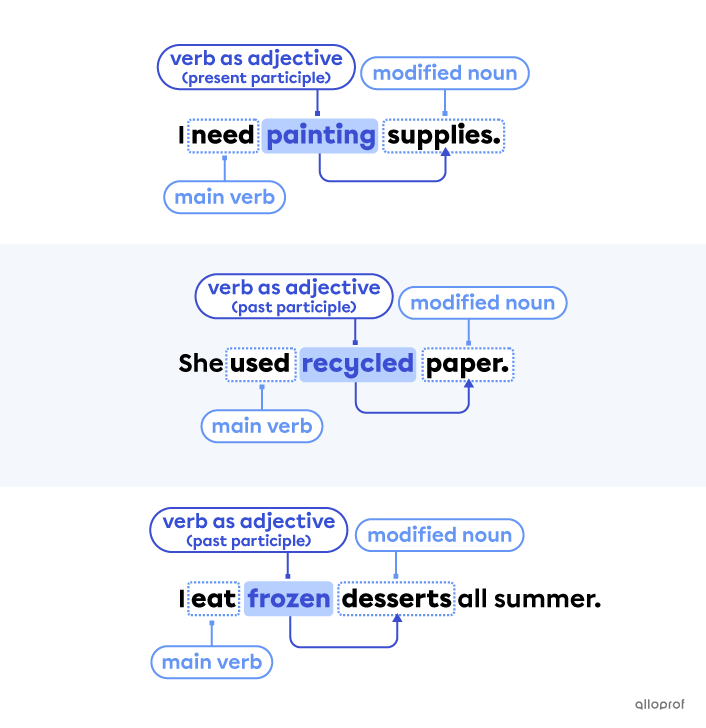
Verbs in the participle form can be used to modify or describe nouns. In these situations, they act just like adjectives.
The verb acting as an adjective is always placed before the noun it modifies or describes.
A proper adjective is the specific name used for a person, a place or a thing. Proper adjectives are based on proper nouns and also take capital letters.
|
Example: |
From the proper noun: |
Indicates: |
|
Yayoi is a Japanese artist. |
Japan |
Nationality: She is from Japan. |
|
We’re using a Canadian recipe. |
Canada |
Country of origin: it is from Canada. |
|
They bought a Victorian house. |
Victoria |
From the time period when Queen Victoria reigned. |
|
He has Herculean strength. |
Hercules |
It required great effort and strength. A reference to Hercules in Greek mythology. |
Compound adjectives are a combination of 2 or more words used to describe or modify the same noun.
|
Hyphens (-) in compound adjectives: |
Examples: |
|
|
placed before a noun |
✔ |
It is a long-term plan. |
|
placed after a noun |
X |
The plan is long term. |
|
formed with an adverb ending in -ly |
X |
It was an expertly planned project. |
|
Formation |
Examples |
|
 |
last-minute |
There are always last-minute |
 |
white-hot |
Be careful: The lamp is white-hot. |
 |
good-looking |
What a good-looking portrait! |
 |
old-fashioned |
Ushio uses old-fashioned canvases. |
 |
never-ending |
Skill improvement is a never-ending journey. |
 |
almost-completed |
I have a few almost-completed pieces. |
 |
five-star |
We went to a five-star restaurant. |
 |
world-famous |
They met a world-famous painter. |
 |
ground-breaking |
The installation uses ground-breaking technology. |
 |
water-soaked |
She tried the water-soaked paper method. |
 |
part-time |
I have a part-time job in a t-shirt printing shop. |
Compound adjectives using an adverb ending in -ly do not take a hyphen.
|
Forms |
Examples: |
|
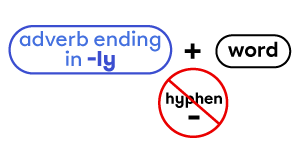 |
completely new |
Yayoi has a completely new studio. |
Yayoi, the character used in the examples, was inspired by the Japanese artist Yayoi Kusama. To learn more about her colourful life and work, visit the Yayoi Kusama Museum website.