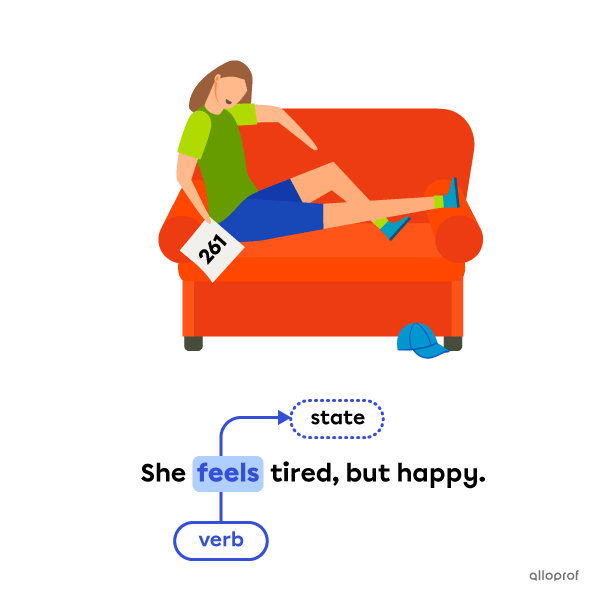
A verb is a word that expresses an action or a state of being.
The main verb is the most important verb of a sentence. Main verbs can be separated into three categories:
-
action verbs
-
stative verbs
-
linking verbs
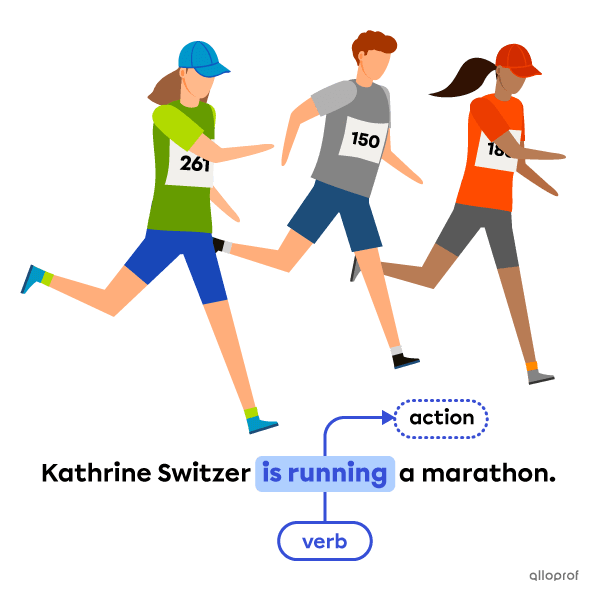
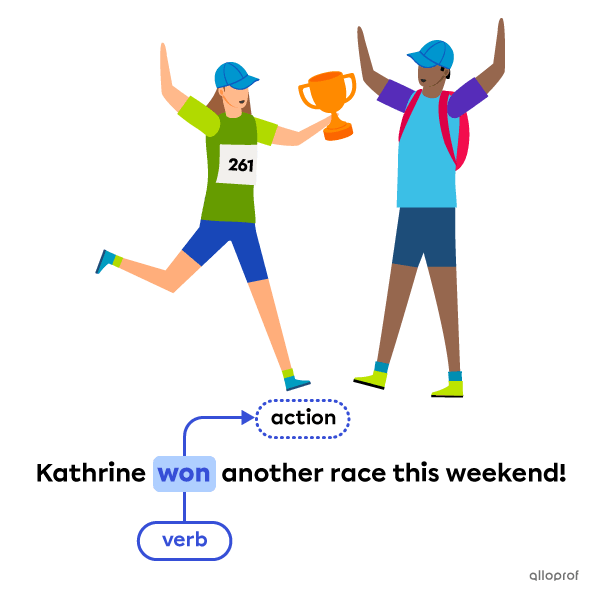
Action verbs, also known as dynamic verbs, indicate an action. The action can be physical or mental.
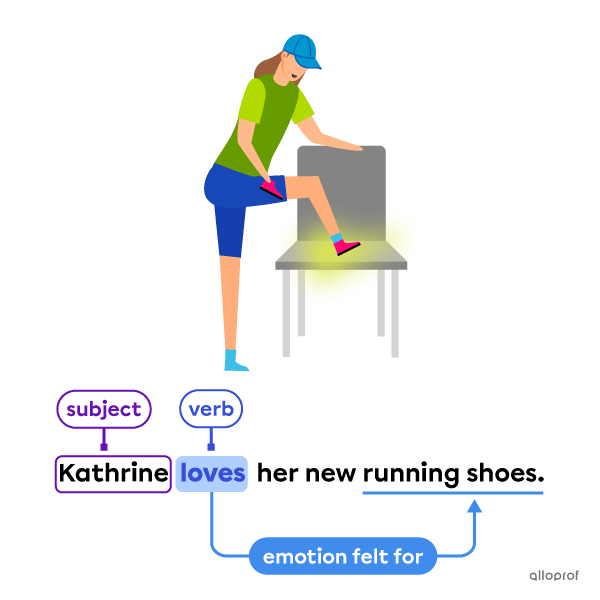
Some main verbs do not always refer to a dynamic action. Stative verbs refer to states of being, emotions, opinions, preferences, or senses.
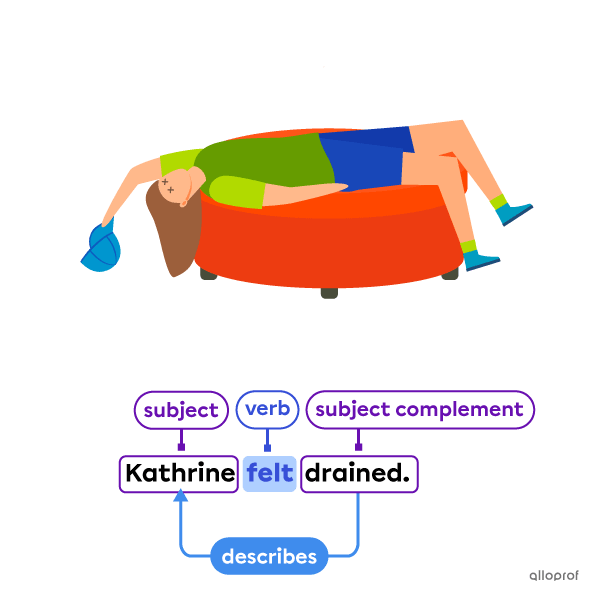
Main verbs are not always action verbs. A linking verb links the subject to a subject complement that describes, renames or identifies the subject. Linking verbs are never action verbs.
|
Common linking verb examples |
||||
|
to be |
to seem |
to become |
to feel |
to remain |
|
to stay |
to sound |
to taste |
to appear |
to smell |
Auxiliary verbs are used with a main verb to express:
-
verb tenses
-
verb moods
-
passive voice
The auxiliary verb to be is used in continuous/progressive tenses.

The auxiliary verb to have is used in perfect tenses.

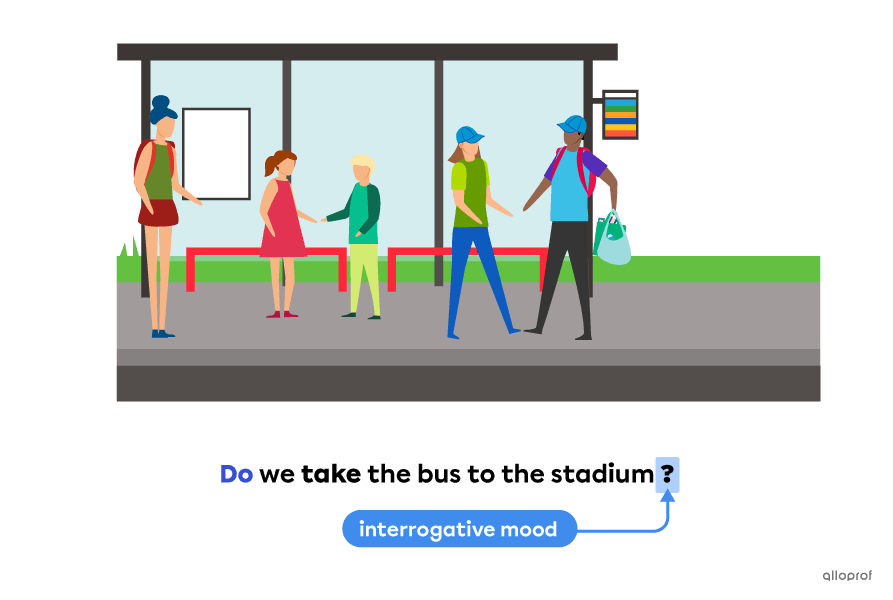
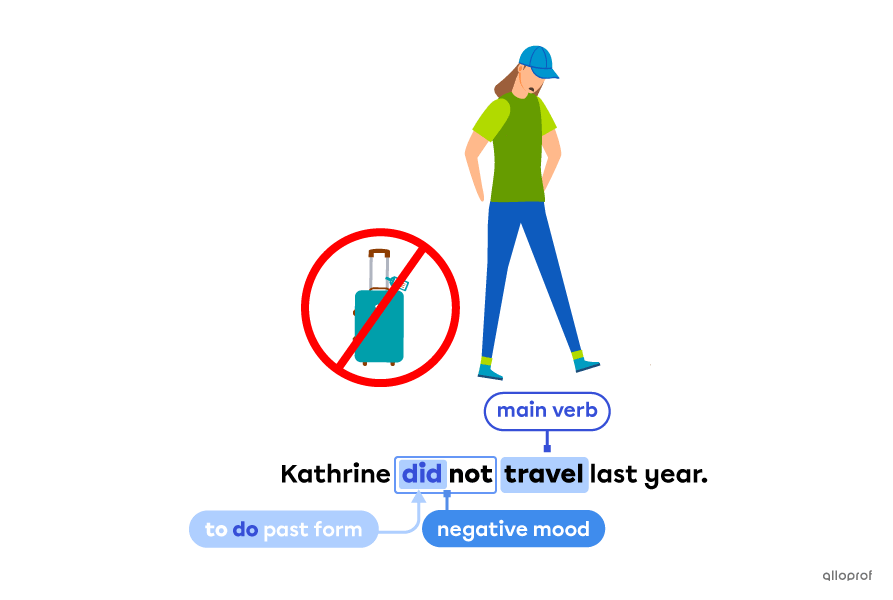
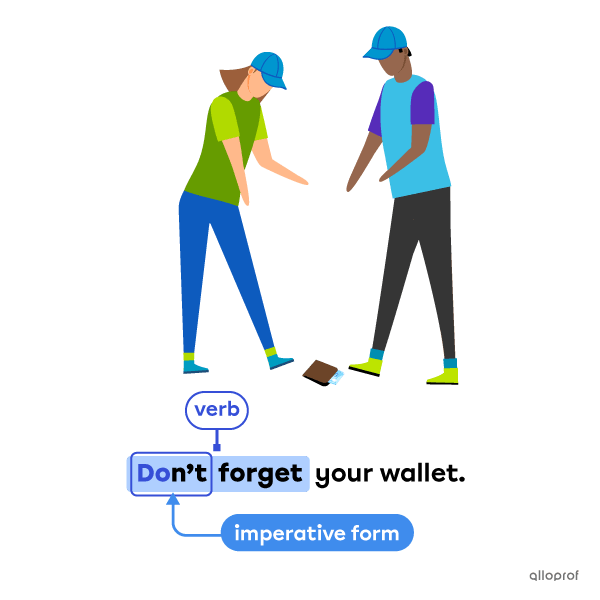
The auxiliary verb to do is used with the simple present and the simple past to express:
-
the interrogative mood—questions
-
the negative mood—do not/don’t & did not/didn’t
-
the imperative mood in the simple present negative form
Question in the simple present
Negative form in the simple past
Imperative mood in the simple present negative form
The auxiliary verb to do can be combined with a main verb to emphasize its meaning.
Here are some examples:
|
Neutral meaning |
Emphasized meaning |
| I like your new suit. |
I do like your new suit. |
|
He didn’t notice the new car but he noticed the new hairstyle. |
He didn’t notice the new car but he did notice the new hairstyle. |
|
I did most of the work by myself. |
I did do most of the work by myself. |
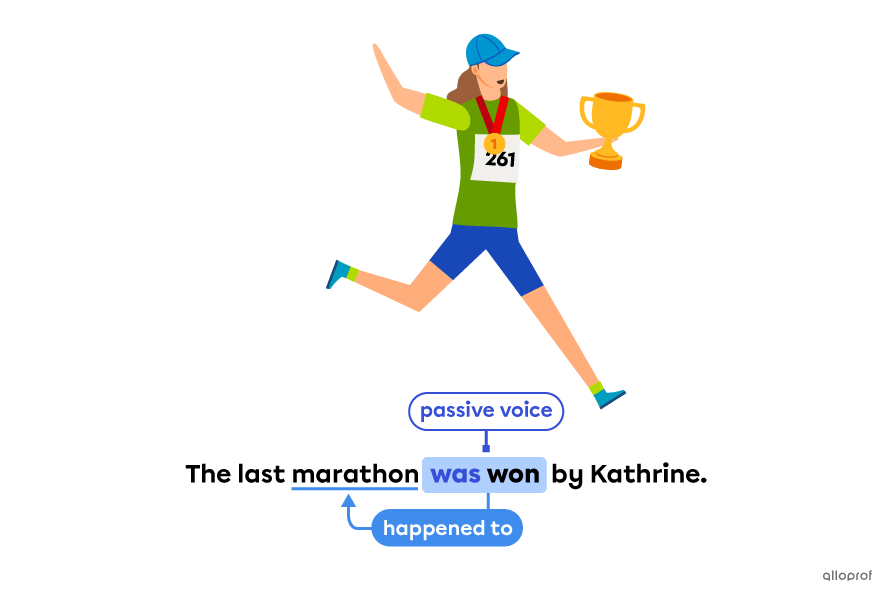
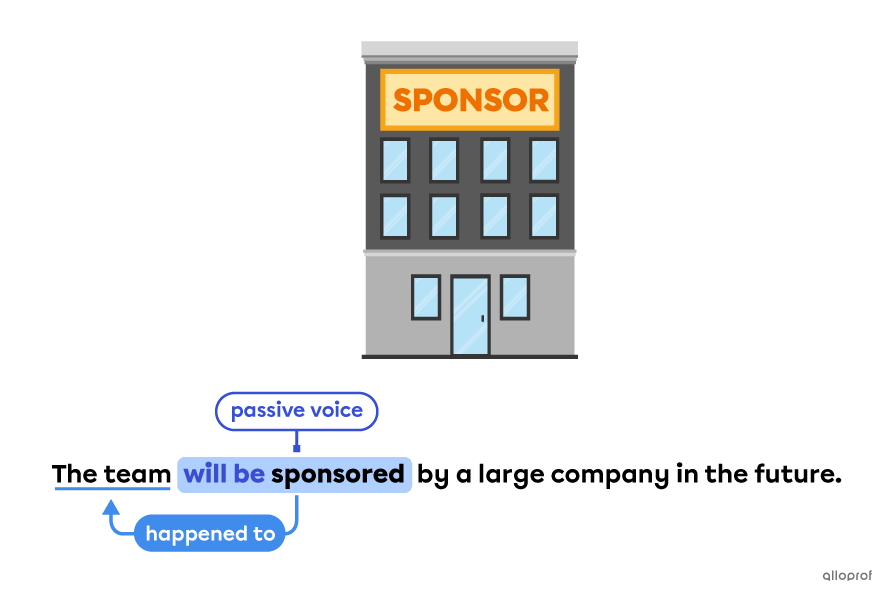
Passive voice means the subject receives the action of the verb instead of transferring it.
The auxiliary to be helps the main verb to form the passive voice.
Passive voice in the past
Passive voice in the future
Modals are also a type of auxiliary verbs.
There are many types of modals, here are some examples:
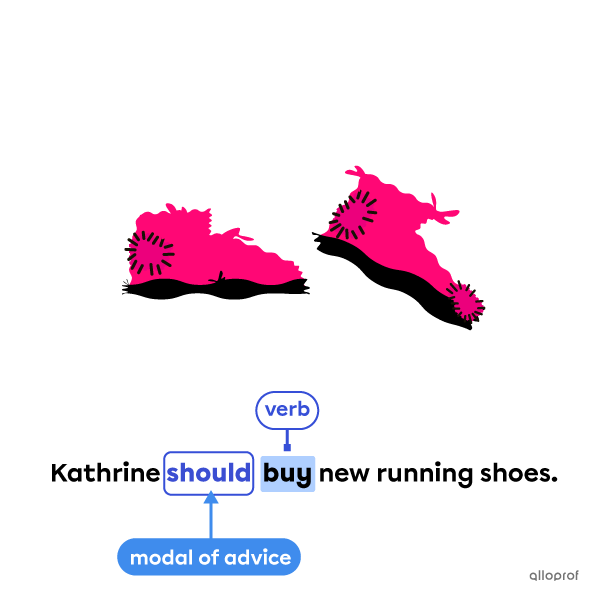
Advice modal
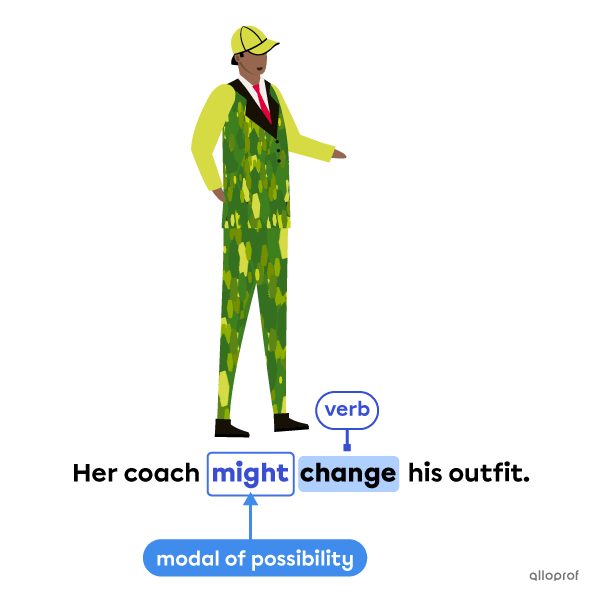
Possibility modal
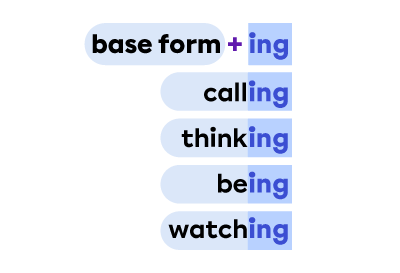
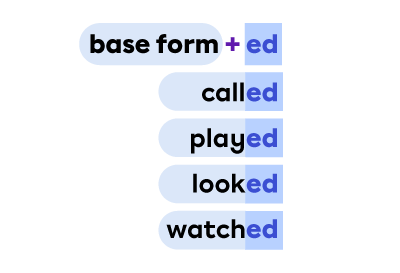
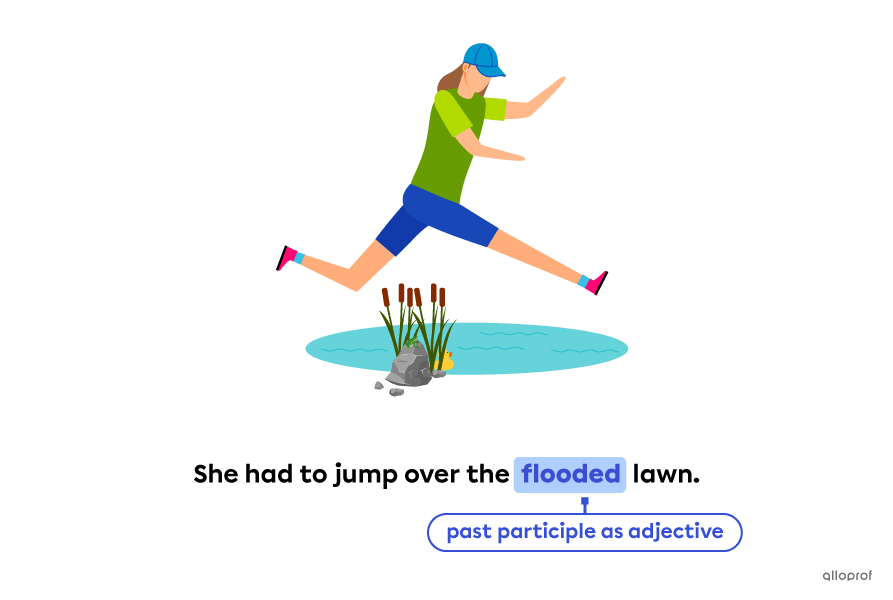
A participle is a verb form that can take the role of an adjective or a verb.
|
Uses: |
Form: |
|
|

|
Uses: |
Form for regular verbs*: |
|
|
*For irregular verbs, form will vary.
The perfect participle combines having, a present participle, with a past participle.
Perfect participle uses:
-
actions completed in the past
-
forms an active sentence with a past participle
-
expresses time passed between 2 actions

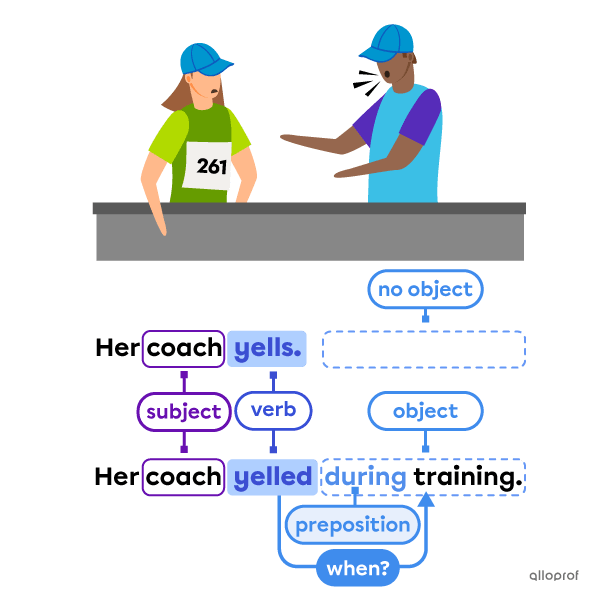
Transitive verbs need a direct object to complete an action. The subject transfers the action on the object.
Transitive verbs answer the questions:
-
Who?
-
What?
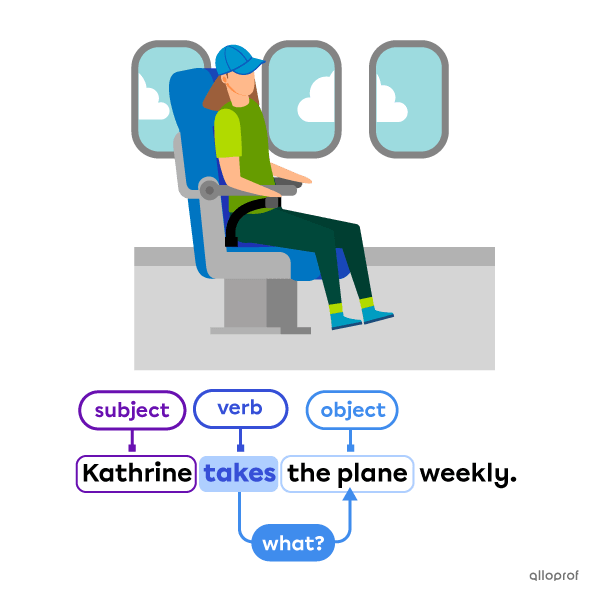
Intransitive verbs do not need an object to complete an action.
They can have an object, and when they do, prepositions or adverbs are generally necessary.
Intransitive verbs can answer the questions:
-
When?
-
Where?
-
How?
-
Why?