Contractions are shortened word forms.
They are used more often when speaking than writing.
|
Full Form |
Contraction |
|
do not |
don’t |
|
you will |
you’ll |
|
Use contractions for informal texts like: |
Do not use contractions for formal texts like: |
|
✔ emails & text messages |
X school assignments |
|
✔ cards |
X research papers |
|
✔ notes |
X scientific articles |
|
✔ character dialogues |
X cover letters |
|
✔ magazine or web articles |
X textbooks |
|
Use contractions for casual situations like: |
Use some contractions for formal occasions like: |
Do not use contractions for official occasions like: |
|
✔ chats with friends/family |
± speeches |
X events with protocols |
|
✔ dinner parties |
± job interviews |
X academic lectures |
|
✔ game nights |
± hosting a show |
X hosting the Nobel Prize |
|
✔ talking to coworkers |
± 1st time meeting someone |
X official ceremonies |
Many contractions are almost always used in speaking.
Contractions like: gonna, wanna or ain’t.
These contractions are informal. They are only used in situations when the speakers are very familiar. Like when talking to friends and family, or classmates and co-workers.
|
Use informal contractions for casual situations like: |
Do not use informal contractions for formal occasions like: |
Do not use contractions for official occasions like: |
|
✔ chats with friends/family |
X speeches |
X events with protocols |
|
✔ dinner parties |
X job interviews |
X academic lectures |
|
✔ game nights |
X hosting a show |
X hosting the Nobel Prize |
|
✔ talking to coworkers |
X 1st time meeting someone |
X official ceremonies |
As you have probably noticed, informal contractions do exist in written form. They are acceptable only in a few very informal situations.
|
Use informal contractions for informal texts like: |
|
✔ character dialogues |
|
✔ song lyrics |
|
✔ emails/text messages to friends or family |
|
✔ cards for close friends or family |
|
✔ notes for yourself or friends |
|
Do not use informal contractions for formal texts like: |
|
X school assignments |
|
X research papers |
|
X emails/text messages to anyone else |
|
X cards for anyone else |
|
X notes for anyone else |
|
X scientific articles |
|
X cover letters |
|
X textbooks |
|
X magazine or web articles |
|
Informal contraction |
Full form |
Example |
|
gonna |
going to |
I’m gonna be done tomorrow. |
|
gotta |
have got to |
You gotta work faster. |
|
have got a |
I gotta lot to do, you’re right. |
|
|
wanna |
want to |
What do you wanna work on first? |
|
gimme |
give me |
Gimme a minute to think. |
|
shoulda |
should |
You shoulda told me you needed help. |
|
coulda |
could have |
I don’t think I coulda done it without you. |
|
woulda |
would have |
It woulda taken you longer, for sure. |
|
betcha |
bet you |
I betcha we’ll finish all the work before tomorrow. |
|
ain’t |
am not |
That ain’t gonna happen. |
|
is not |
||
|
are not |
||
|
c’mon |
come on |
C’mon, you have to believe me. |
|
y’know |
you know |
You’re always doing things last minute, y’know. |
|
‘cause/’coz |
because |
But, I will help you ‘cause you’re my friend. |
|
‘round |
around |
If we work ‘round the clock, we’ll be okay. |
|
‘bout |
about |
That sounds ‘bout right. |
|
‘n |
and |
Then we could go for some fish ‘n chips. |
|
ol’ |
old |
We could stop by the ol’ seafood place. |
|
kinda |
kind of |
Good idea: I’m getting kinda hungry. |
|
sorta |
sort of |
It is getting sorta late. |
|
lotta |
a lot of |
We still have a lotta work to do though. |
|
-in’ |
verbs ending in -ing |
I guess we’ll be workin’ and not eatin’ then. |
To form contractions:
-
join words together
-
remove letter(s)
-
add apostrophe
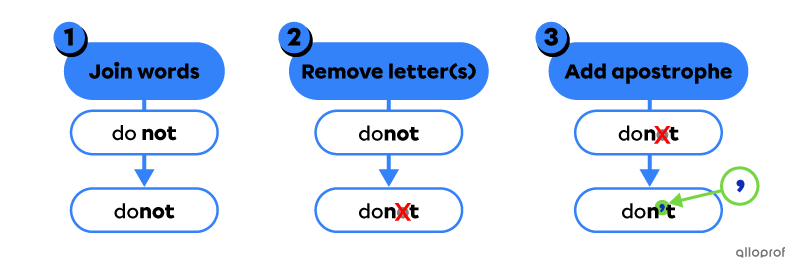
|
To be — Simple Present Affirmative form |
To be + not — Simple Present Negative form |
To be + not — Simple Past* |
||||
|
I am |
I’m |
I am not |
I’m not |
I was not |
I wasn’t |
|
|
he is |
he’s |
he is not |
he’s not |
he isn’t |
||
|
we are |
we’re |
we are not |
we’re not |
we aren’t |
we were not |
we weren’t |
*In the simple past, the affirmative form of the verb to be is never contracted.



To have—Simple Present
|
Affirmative |
Negative |
||
|
Full form |
Contraction |
Full form |
Contraction |
|
he has |
he's |
he has not |
he hasn't |
|
I have |
I've |
I have not |
I haven't |
To have — Simple Past
|
Affirmative |
Negative |
||
|
Full form |
Contraction |
Full form |
Contraction |
|
had |
I’d |
had not |
I hadn't |



Will & Would—Affirmative forms
|
Full form |
Contraction |
|
will |
I’ll |
|
would |
I’d |
Auxiliaries + not—Negative forms
|
Full form |
Contraction |
|
do not |
don’t |
|
does not |
doesn’t |
|
did not |
didn’t |
|
will not |
won’t |
|
cannot |
can’t |
|
could not |
couldn’t |
|
would not |
wouldn’t |
|
should not |
shouldn’t |
|
must not |
mustn’t |



Not always contracts to n’t
|
Full form |
Contraction |
|
do not |
don’t |
|
are not |
aren’t |
|
could not |
couldn’t |
|
would not |
wouldn’t |
Is, has & us all contract to ’s
|
Full form |
Contraction |
|
Keith is |
Keith's |
|
she is |
she's |
|
Ann has |
Ann's |
|
let us |
let's |
Had, would & did all contract to ’d
|
Full form |
Contraction |
|
she had |
she'd |
|
he had |
he'd |
|
I would |
I'd |
|
How did… |
How'd |



Some contractions are commonly misspelled because they have homophones. They sound the same, but are spelled differently and have different meanings.
It is the case for:
|
your |
|
|
2nd peron singular/plural |
|
|
you're |
you + are |
|
its |
|
|
3rd person singular |
|
|
it's |
it + is |
|
it + has |
|
whose |
question word asking about ownership |
|
who's |
who + is |
|
who + has |

your coffee → the coffee is yours
you’re coffee → you are coffee
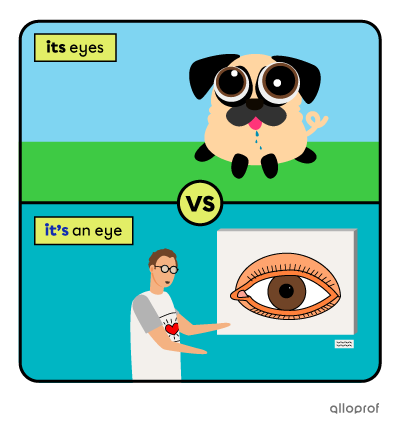
its eyes → the dog’s eyes
it’s an eye → it is an eye

Whose painting is this? → Who owns the painting.
Who’s painting this? → Who is using paint.
|
their |
|
|
3rd person plural |
|
|
there |
|
|
they're |
they + are |
|
theirs |
|
|
3rd person plural |
|
|
there's |
there + is |
|
there + has |

their cake → it’s Ann and Keith’s cake.
a cake there → the cake is at that place.
they’re cake → They are made of cake.

the paint is theirs → the paint belongs to Ann and Keith.
there’s paint on my t-shirt → the paint is on Keith’s T-shirt
The character used in the examples, Keith, was inspired by the artist Keith Haring. To learn more about his amazing art, visit the Keith Haring Foundation website.