Questions are interrogative sentences. They are used to ask for information.
Most common question types:
-
answered by yes or no
-
begin with an auxiliary verb or the verb to be
-
cannot be answered by yes or no
-
ask for a more complete answer
-
begin with question words
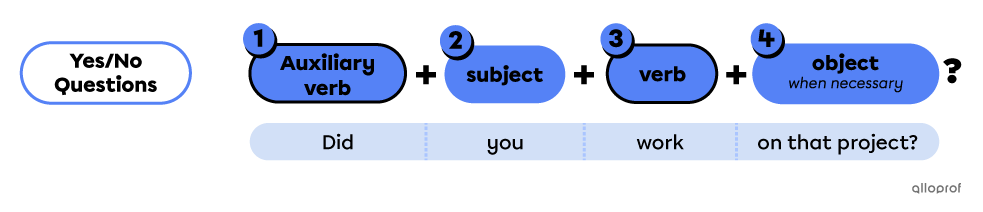
The 4 elements of a yes/no question:
-
The auxiliary verb indicates the verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The verb is the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
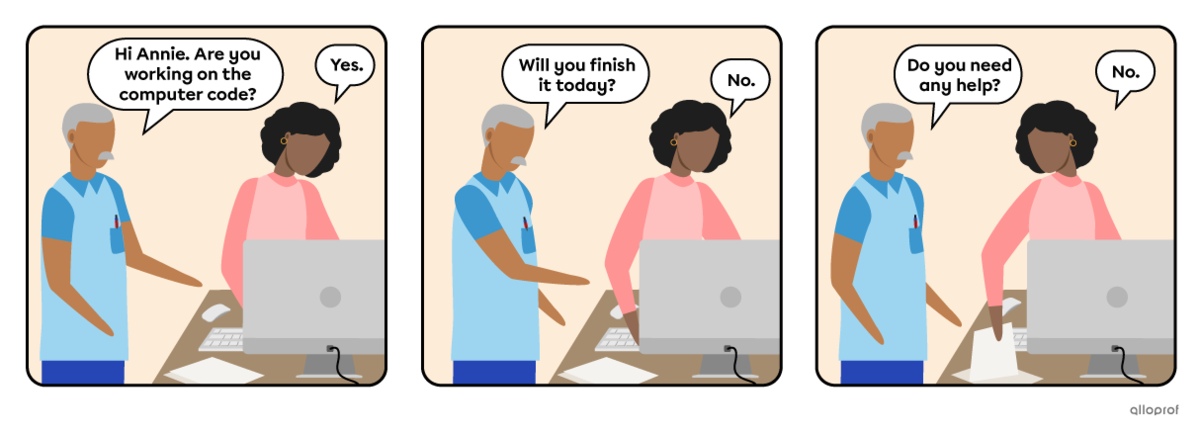

|
Auxiliary |
Subject |
Verb |
Object |
|
Are |
you |
working |
on the computer code? |
|
Will |
you |
finish |
it today? |
|
Do |
you |
need |
any help? |
Information questions use almost the same structure as yes/no questions, but they start with:
-
A question word indicating what the question is about.
Next, use the same yes/no questions form for the rest:
-
The auxiliary verb indicates the verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The verb is the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.


|
Question |
Auxiliary |
Subject |
Verb |
Object |
|
What |
are* |
you |
working |
on? |
|
When |
will |
you |
finish |
it? |
|
Why |
does |
it |
take |
so long? |
*In this example, to be is an auxiliary verb, not the main verb. The verb in the example is to work, conjugated in the present continuous.

|
Question |
Auxiliary |
Subject |
Verb |
Object |
|
What |
are |
you |
doing? |
No object necessary |
|
|
Can |
I |
help? |
|
|
What |
do |
you |
mean? |
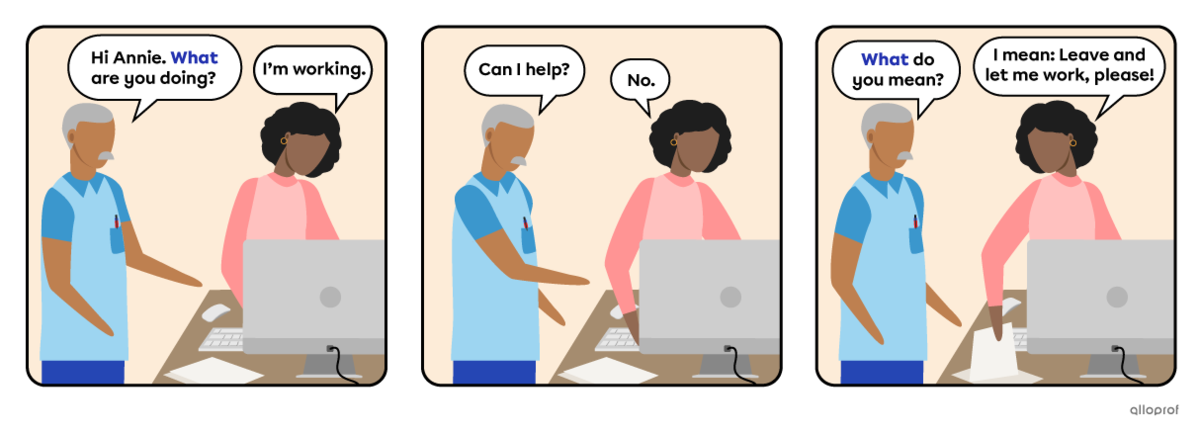
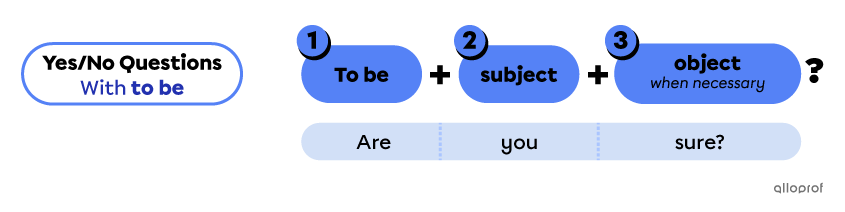
Questions with the verb to be do not use auxiliary verbs when they are in the simple present or simple past verb tenses.
The 3 elements of a yes/no question with to be are the following:
-
The verb to be is conjugated according to the subject and verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
Start with:
-
A question word indicating what the question is about.
Next, use the same yes/no questions form for the rest:
-
The verb to be, conjugated according to the subject and verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
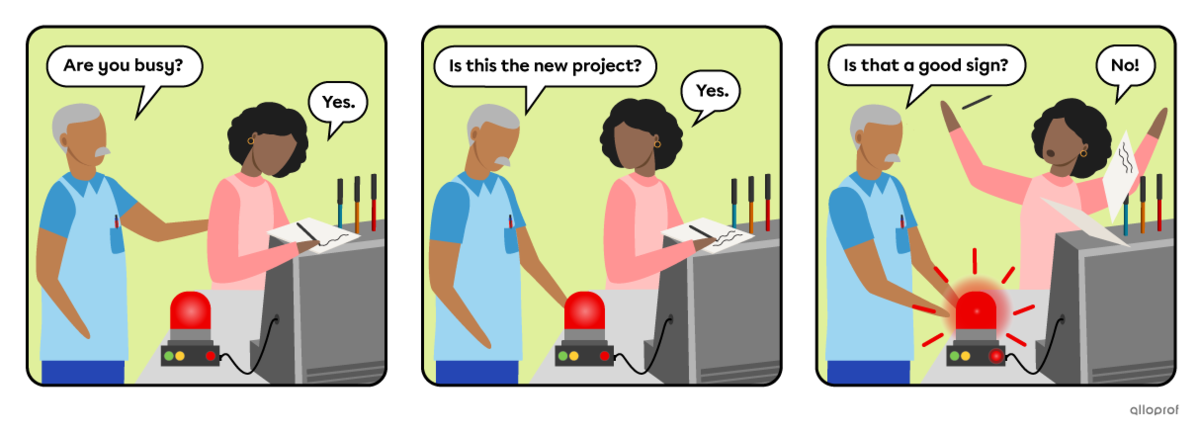


|
To be |
Subject |
Object |
|
Are |
you |
busy? |
|
Is |
this |
the new project? |
|
Is |
that |
a good sign? |
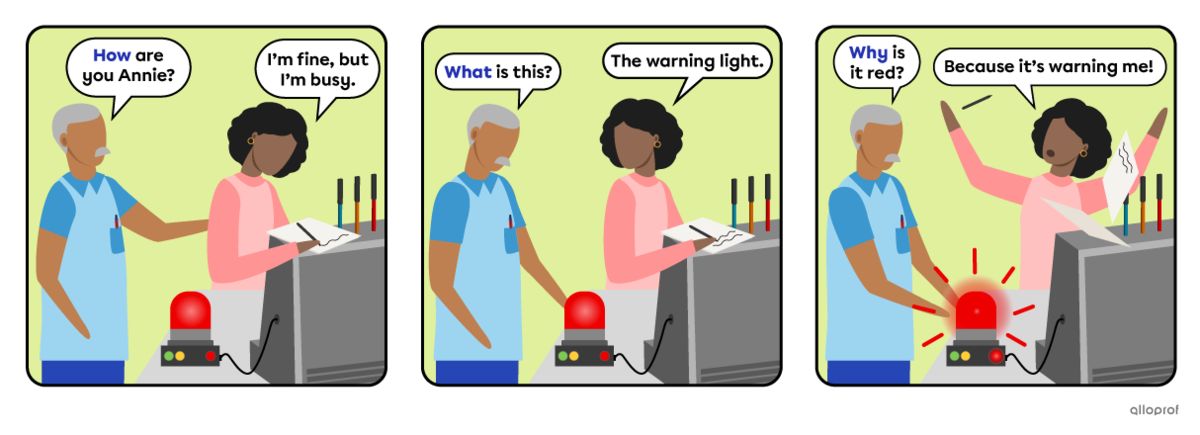
|
Question |
To be |
Subject |
Object |
|
How |
are |
you |
Annie? |
|
What |
is |
this? |
* |
|
Why |
is |
it |
red? |
*object not necessary
Question words, also known as Wh- words, are used to ask information questions. They indicate what the question is about.
The most commonly used ones are:
|
Question word |
Asking information about |
|
What |
things & actions |
|
Who |
people |
|
Where |
places |
|
When |
time |
|
Why |
reasons & explanations |
|
Which |
choice |
|
Whose |
possession |
|
How |
in what way |
|
How many |
countable quantity |
|
How much |
uncountable quantity |
It is 4:00, time for Annie’s coffee break.
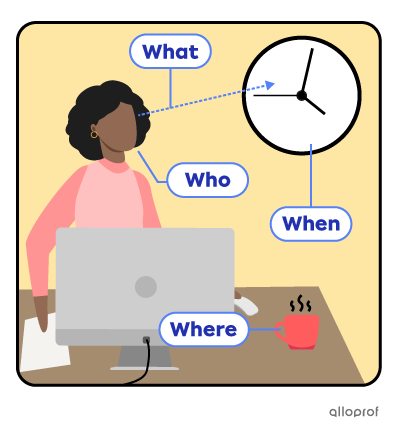
|
What |
|
things & actions |
|
What is Annie looking at? |
She is looking at the clock. |
|
|
Who |
|
people |
|
Who is looking at the clock? |
Annie is looking at the clock. |
|
|
When |
|
time |
|
When is the coffee break? |
It is at 4 o’clock. |
|
|
Where |
|
places |
|
Where is Annie’s coffee mug? |
It is on her desk. |
|
She walks to the coffee machine; Terry is already there.
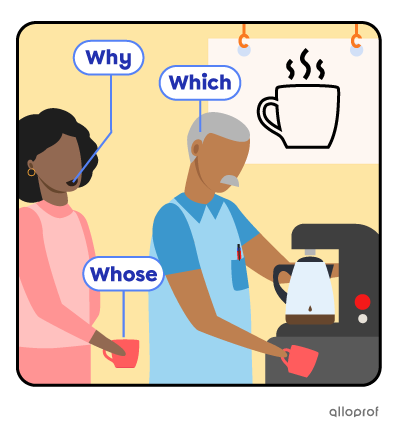

|
Why |
|
reasons |
|
Why is Annie smiling? |
Because she’s going to get the delicious coffee she loves so much! |
|
|
Which |
|
choice |
|
Which one of you was there first? |
Terry was there first. |
|
|
Whose |
|
possession |
|
Whose mug is Annie holding? |
It’s her own coffee mug (it’s Annie’s mug). |
|
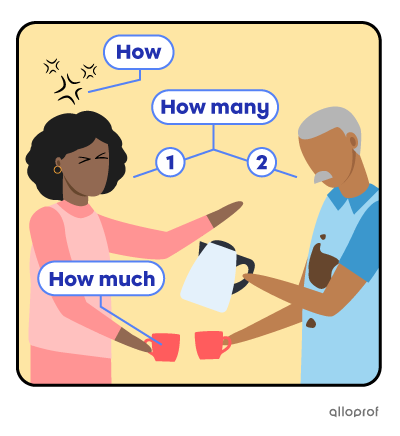
Annie is upset because Terry spilled all the coffee on his shirt, again.
|
How |
|
in what way |
|
How is Annie feeling at the moment? |
She is upset. |
|
|
How many |
|
countable quantity |
|
How many people are standing by the coffee machine? |
There are two people. |
|
|
How much |
|
uncountable quantity |
|
How much coffee is Annie going to drink? |
None at all, because Terry spilled all of it. |
|
Words can be added to question words for more precision.
Nouns can be added to what, which and whose.
|
What |
colour |
is this? |
|
Which |
problem |
are we fixing? |
|
Whose |
mug |
did you break? |
Adjectives or adverbs can be added to how.
|
How |
big |
is the rocket’s fuel tank? |
|
How |
different |
is the new computer system? |
|
How |
quickly |
can you fix the problem? |
|
How |
soon |
is the rocket launch? |
|
Question Types |
Uses |
Example |
To learn more visit |
|
Negative Questions |
Question used in the negative form. |
Isn't it interesting? |
|
|
Tag Questions |
Short questions are the end of statements. |
You understand, don't you? |
|
|
Subject Questions |
Questions where the question is the subject of the verb. |
What happened? |
|
|
Rhetorical Questions |
Questions not looking for answers. |
Can you imagine? |
The character of Annie used in the examples is inspired by Annie Easley, an American mathematician, a computer scientist and a rocket scientist. To learn more about her life and accomplishments, visit the NASA website.