Between 1850 and 1914, a number of European countries took possession of almost all of Africa, even though it had already been occupied by hundreds of different commoners or people. The colonization of the African continent was mainly carried out by force of arms. After several conflicts, the Europeans subdued the local populations with their technologically superior armies.
Note: Image in English coming soon.
The European colonizers then occupied the land, imposing themselves on the indigenous populations. Their main aim was to gain access to the territory's natural resources in order to support their industrial production. As a result, several European states embarked on a race for African colonies.
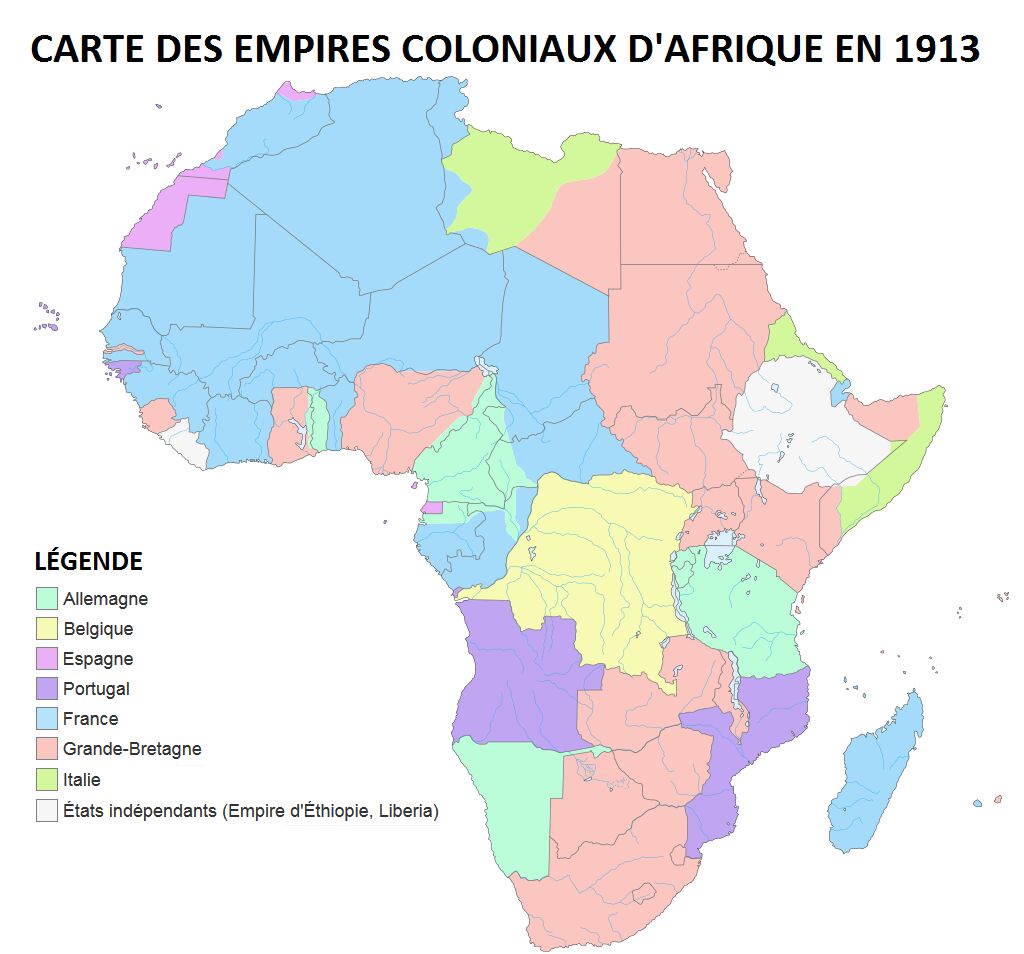
In the race for territories in Africa, various European countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Portugal, Spain, Belgium, Italy and Germany are in competition. This situation inevitably creates tensions between them. In 1884-1885, in order to prevent conflicts from breaking out, the Germans held a conference with a dozen other European countries and the United States to establish rules for the division of Africa. This historic meeting became known as the Berlin Conference.

Following the Berlin Conference, the territory of Africa was divided into around fifty territories; the borders that were drawn did not take account of the commoners or the people present. This led to a number of subsequent problems.
African populations have a very difficult time accepting the presence of European invaders. Even after several years, the Europeans were regarded as foreigners who stole the Africans' resources. To facilitate control of the colony, the mother countries tried to assimilate the inhabitants by imposing their culture on them. The colonizing countries therefore built schools in which they taught young Africans the language, religion, laws and history of their European mother country. Education therefore became a tool for assimilation. The main consequence of this was the acculturation of the Africans.
- Assimilation is when a colonizing country seeks to integrate a group or minority into its population by removing its distinctive character (its culture).
- Acculturation is a social phenomenon that occurs when one group of people adopts all or part of the culture of another group of people.