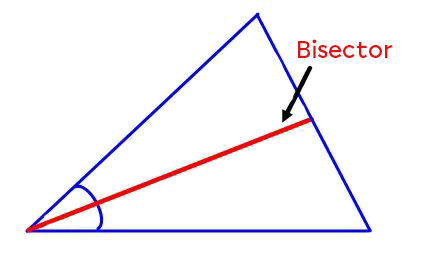
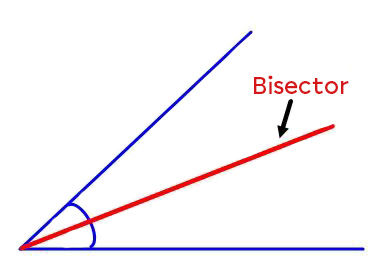
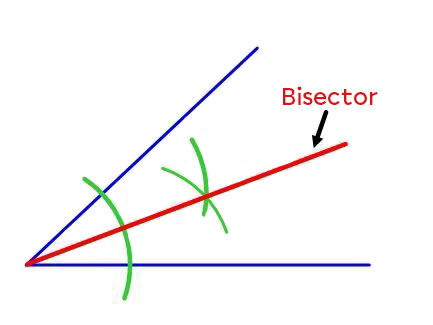
The bisector is a line (or line segment) that divides an angle into two equal angles.
A bisector can be considered the axis of symmetry of an angle. Thus, each point belonging to a bisector is located the same distance from the two sides that make up the angle.
We can draw the bisector of an angle in two ways:
We can construct the bisector of an angle, whether it is included in a plane figure or not.
-
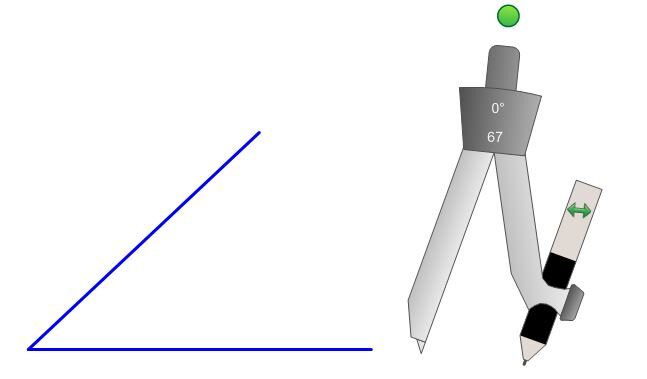
Open the compass and keep the same opening for all steps of the construction.
-
Place the compass’ sharp point on the angle’s apex (vertex) and draw an arc that intersects both sides of the angle.
-
Place the compass’ sharp point on an intersection of the circle’s arc and one side of the angle. Draw a new arc in the angle opening. Repeat the operation from the other intersection point.
-
Using a ruler, draw the straight line that connects the angle’s vertex to the intersection point of the last two drawn arcs. This straight line is the bisector of the angle.
-
Open the compass and keep the same opening for all steps of the construction.
-
Place the compass’ sharp point on the angle’s apex (vertex) and draw an arc that intersects both sides of the angle.
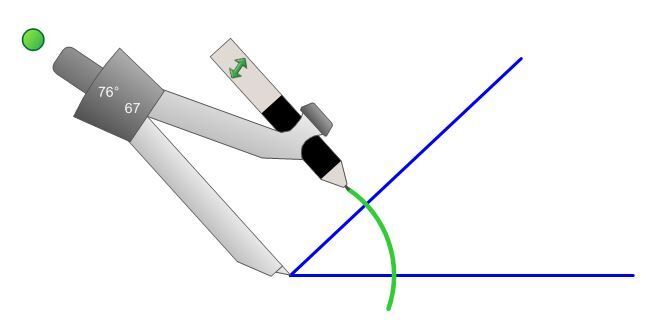
-
Place the compass’ sharp point at an intersection of the circle’s arc and one side of the angle. Draw a new arc in the angle opening. Repeat the operation from the other intersection point.
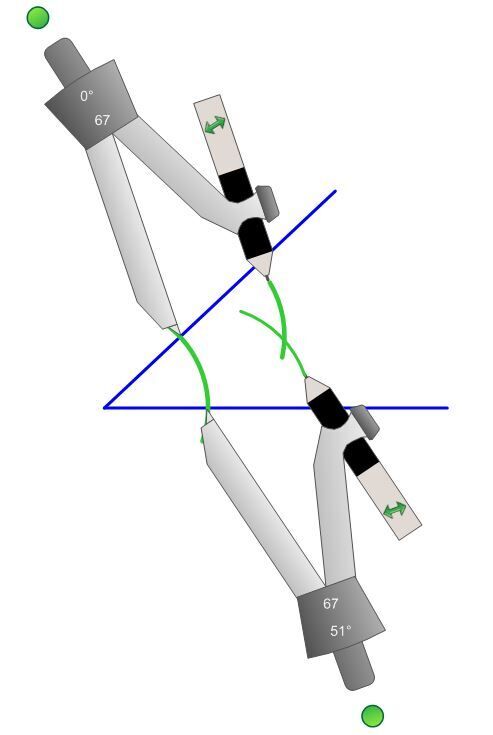
-
Using a ruler, draw the straight line that connects the angle’s vertex to the intersection point of the last two arcs drawn. This line is the angle’s bisector.
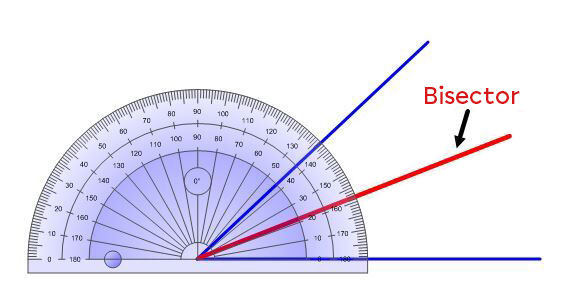
You can use a protractor to draw the bisector of an angle by following these steps:
-
With a protractor, measure the angle you want to separate into two equal parts.
-
Divide the angle value in half.
-
Trace the angle calculated in step 2 using the protractor and a ruler.
-
Using a protractor, measure the angle you want to separate into two equal parts.
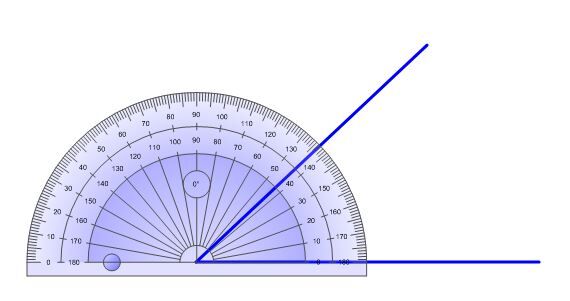
-
Divide the angle’s value in half.
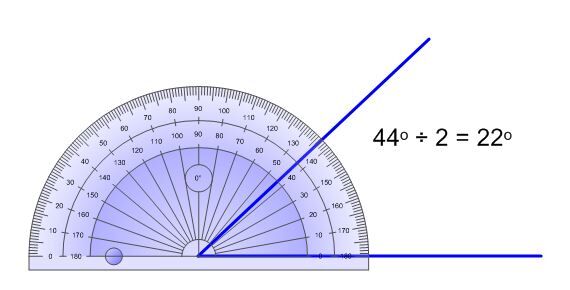
-
Draw the angle calculated in step 2 using the protractor and a ruler.