When performing a multiplication, sometimes you need to find the value of a missing number. This is called finding the missing term.
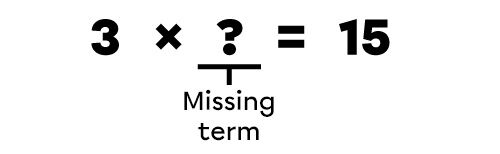
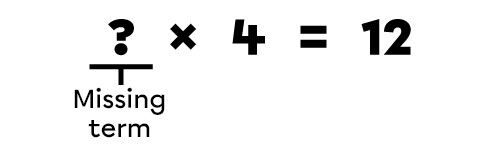
To find the missing term, you must perform a division. Divide the end result by the known term.
In the operation ? × 4 = 12, I ask myself which number, when multiplied by 4, equals 12.
I take the end result and I divide it by the known term.
12 ÷ 4 = ?
Since 12 ÷ 4 = 3, I know that the missing term is 3. I can verify if the missing term is correct by performing the starting multiplication.
3 × 4 = 12
To find the missing term, you must perform a division. You take the end result and you divide it by the known term.
In the operation 3 × ? = 15, I ask myself which number, when multiplied by 3, equals 15.
I take the end result and I divide it by the known term.
15 ÷ 3 = ?
Since 15 ÷ 3 = 5, I know that the missing term is 5. I can verify if the missing term is correct by performing the starting multiplication.
3 × 5 = 15