Here are two ways to find the inverse of a logarithmic function.
To determine the inverse of a logarithmic function with a graph, proceed as follows.
Graph the inverse of the following logarithmic function. ||y = -6\log_5 (x+4)+3||
-
Graph the logarithmic function in order to graph the inverse
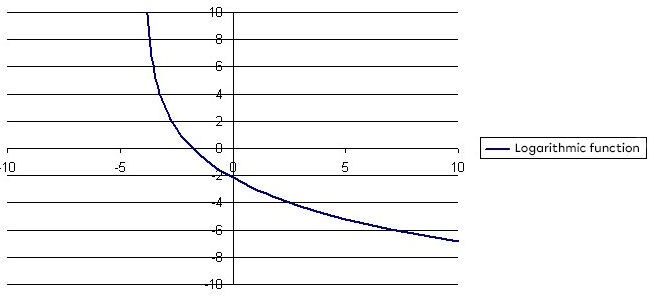
-
Draw the line |y = x|
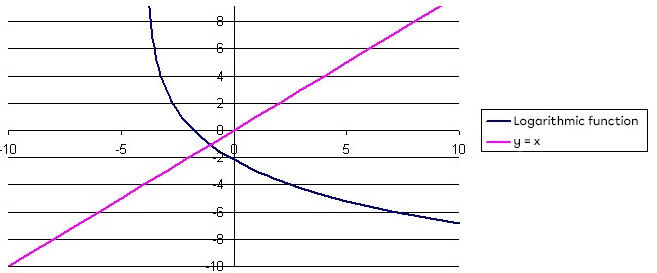
- Reflect the starting logarithmic function in terms of the line |y = x|
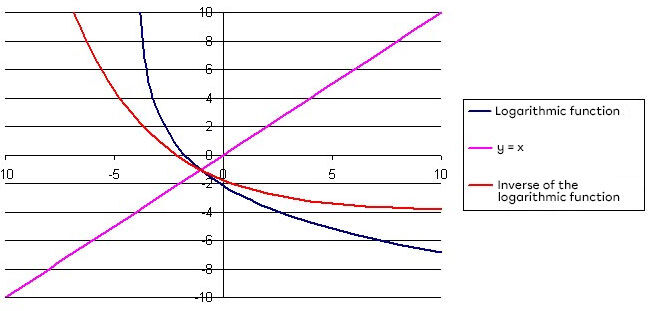
Therefore, we obtain the inverse of the starting logarithmic function.
To algebraically determine the inverse of a logarithmic function, proceed as follows.
-
Swap the variables |x| and |y| in the initial rule.
-
Isolate the expression containing the logarithm.
-
Switch to exponential form to isolate |y.|
Determine the inverse rule of the following logarithmic function algebraically.
||y = -4\log_7 (3(x-6))+8||
-
Swap the |x| and |y| variables in the initial rule
||x = -4\log_7 (3(y-6))+8||
-
Isolate the expression containing the logarithm
||\begin{align} x &= -4\log_7 (3(y-6))+8 \\ x - 8 &= -4\log_7 (3(y-6)) \\ \dfrac{\text{-}1}{4}(x - 8) &= log_7 (3(y-6)) \end{align}||
-
Switch to the exponential form to isolate |y|
||\begin{align} 7^{\dfrac{\text{-}1}{4}(x-8)} &= 3(y - 6) \\ \dfrac{7^{\frac{\text{-}1}{4}(x-8)}}{3} &= y - 6\\ \dfrac{7^{\frac{\text{-}1}{4}(x-8)}}{3}+6 &= y \\
{\dfrac{1} {3}}\normalsize(7)^{\dfrac{\text{-}1}{4}(x-8)}+6&= y \end{align}|| Therefore, | y^{-1} = \dfrac{1}{3}(7)^{\dfrac{\text{-}1}{4}(x-8)}+6| is the rule of the inverse.
It is important to note that the inverse of logarithmic functions are exponential functions.
When carefully observing the starting function and its inverse, note the following:
-
The parameter |h| becomes the parameter |k| of the inverse;
-
The parameter |k| becomes the parameter |h| of the inverse;
-
The inverse’s base |c| is the same as the starting function’s base;
-
The inverse’s parameter |a| is the reciprocal of the starting function’s parameter |b;|
-
The inverse’ s parameter |b| is the reciprocal of the starting function’s parameter |a.|
||y = \color{red}{a}\log_\color{magenta}{c} \big(\color{purple}{b}(x-\color{blue}{h})\big)+\color{green}{k}\ \ \Leftrightarrow \ \ y^{-1}=\color{purple}{\dfrac{1}{b}}(\color{magenta}{c})^{\color{red}{\dfrac{1}{a}}(x-\color{green}{k})}+\color{blue}{h}||