A protractor is a tool used to measure angles (∠). The protractor is shaped like a semicircle.
Example:
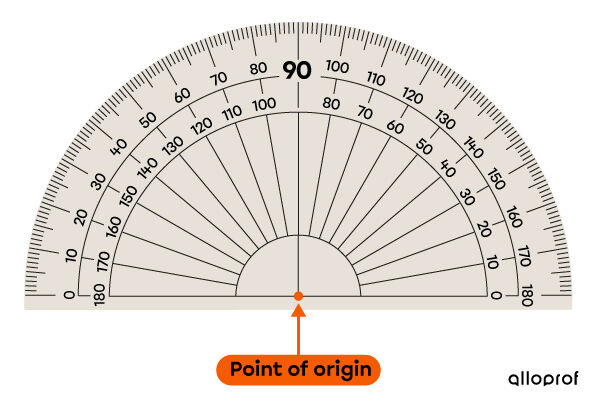
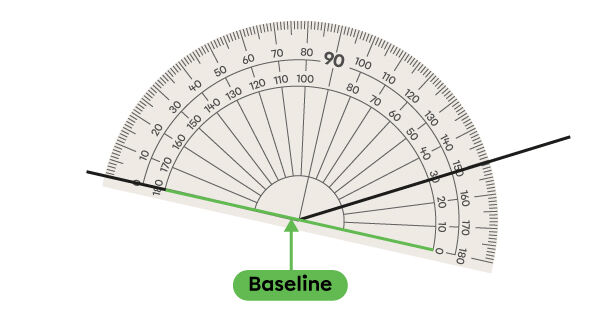
The point of origin is in the centre of the protractor.
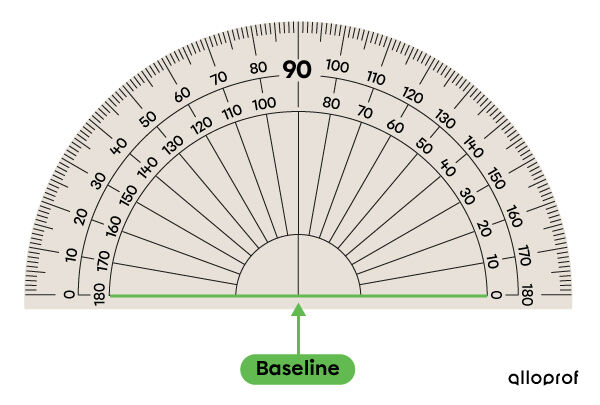
The line that passes through the point of origin is called the baseline.
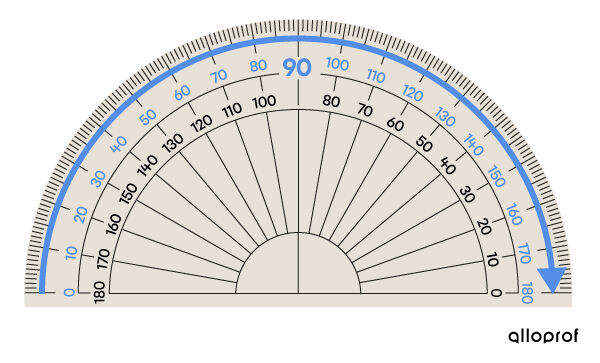
A protractor has two scales. One scale goes clockwise (from left to right) while the other goes counterclockwise (from right to left). Each scale is separated into 180 equal parts (intervals), every interval representing a unit of measurement called a degree (°).
The numbers in blue on this protractor represent the scale that is read in a clockwise direction (from left to right):
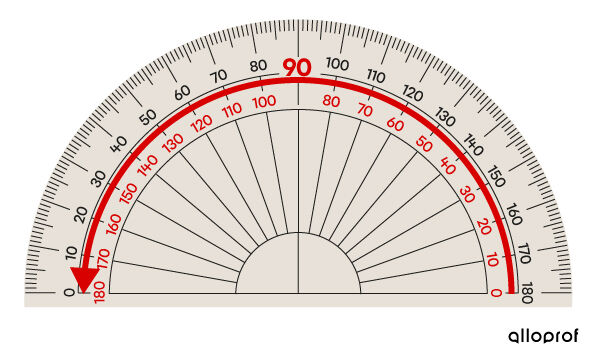
The numbers highlighted in red on the protractor represent the scale that is read in a counterclockwise direction (from right to left):
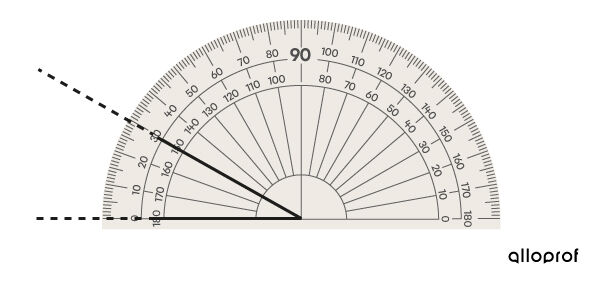
Extend the lines of an angle to better measure it with a protractor.
Example:
To measure an angle (∠) with a protractor, follow these steps:
-
Place the point of origin of the protractor directly on the angle’s vertex.
-
Make sure the baseline is aligned with one of the lines that form the angle.
-
Starting from the baseline (0°), find the measurement through which the other angle’s line passes.
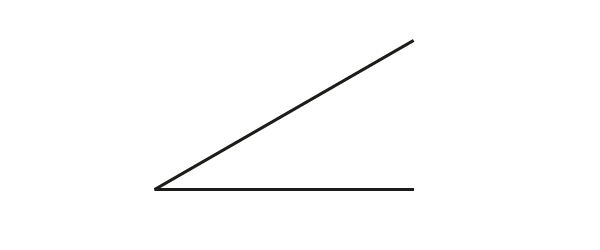
What is the measurement of the following angle?
-
Place the point of origin of a protractor directly on the angle’s vertex.
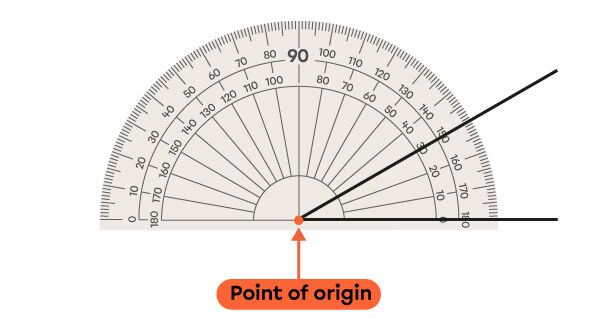
-
Make sure the baseline is aligned with one of the lines that form the angle.
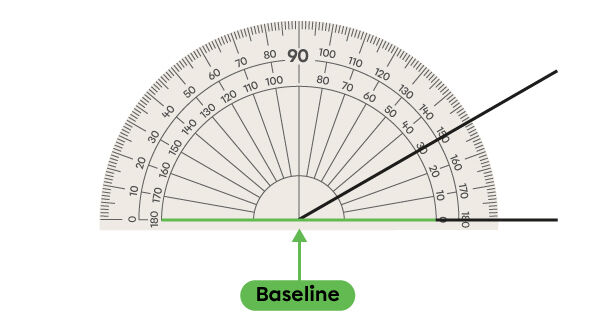
-
Starting from the baseline (0°), find the measurement through which the other angle’s line passes.
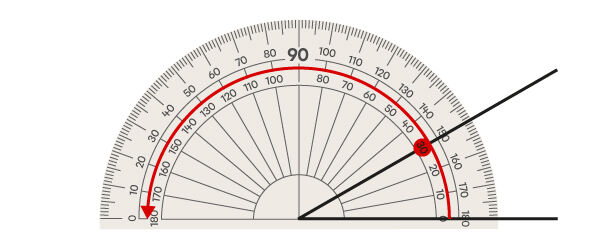
Here, read the numbers starting from zero in a counterclockwise direction (right to left).
The angle measures 30°.
What is the measurement of the following angle?
-
Place the point of origin of a protractor directly on the angle’s vertex.
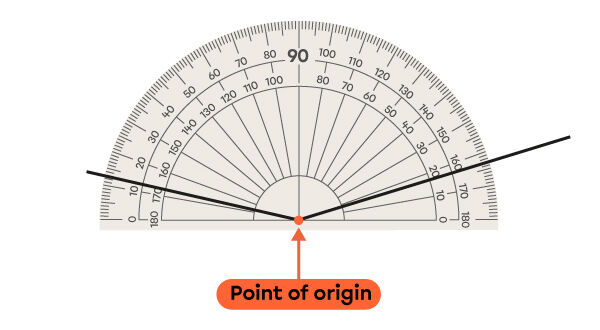
-
Make sure the baseline is aligned with one of the lines that form the angle.
Since it is not aligned, move the protractor making sure that the point of origin remains on the vertex of the angle.
-
Starting from the baseline (0°), find the measurement through which the other angle’s line passes.
Here, read the numbers starting from zero in a clockwise direction (left to right).
The angle measures 150°.

It is important to choose the right scale on a protractor (clockwise or counterclockwise). As a guide, refer to the type of angle you are measuring by keeping in mind the following:
- An acute angle is less than 90°;
- A right angle is 90°;
- An obtuse angle measures between 90° and 180°.