Any object can be used to measure a distance. For example, paper clips, books, tissue boxes, etc. can all be used as tools for measuring.
This book measures 5 paper clips long:
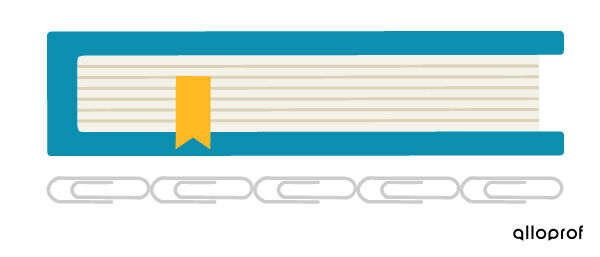
Read the concept sheet Measuring Lengths to learn how to measure lengths with objects.
Look at the length of what needs to be measured to choose an object for measuring a distance. Generally, the longer the length, the larger the object needed for measuring.
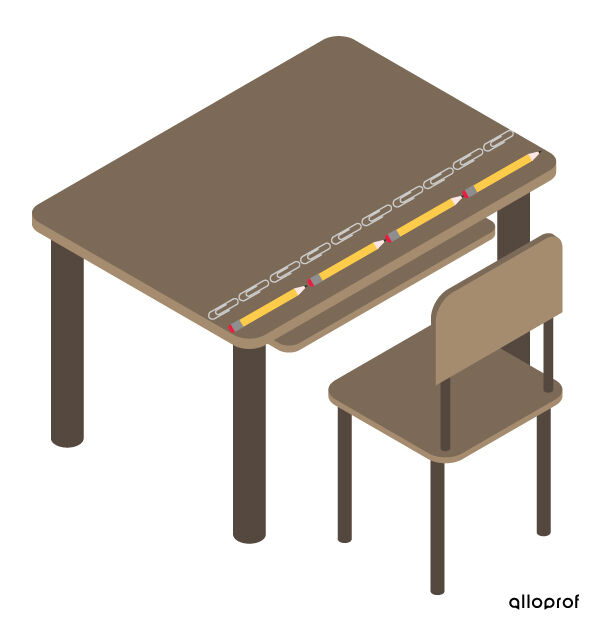
It is a better choice to measure the width of a desk using a pencil instead of paper clips since a huge number of paper clips would be needed!
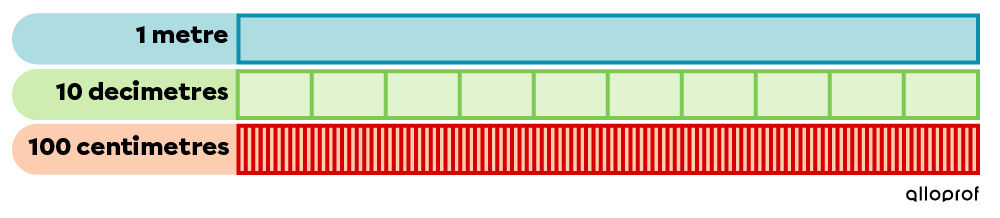
The metre (m) is the basic unit of measurement. It can be broken down into parts to get units like decimetres (dm) or centimetres (cm).
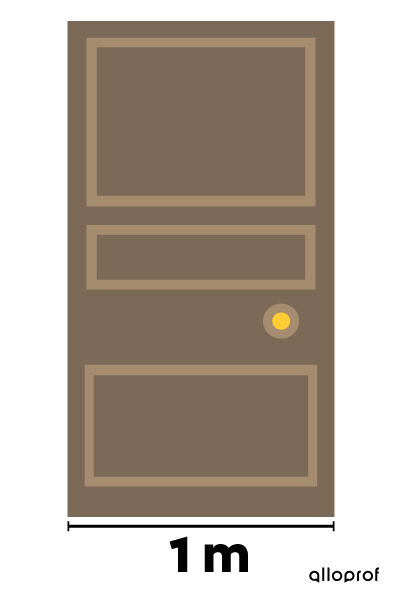
The width of a door is approximately 1 metre.
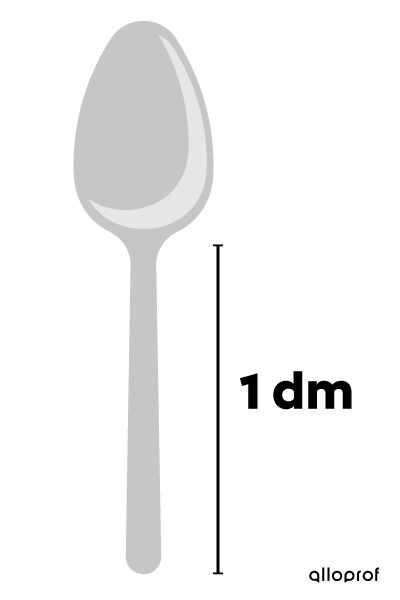
The length of a spoon handle is about 1 decimetre.

The side of a die is about 1 centimetre.
Observe the length of what needs to be measured to choose which unit of measurement to use. Generally, longer distances require larger units of measurement.
-
The width of a classroom is measured in metres.
-
The height of a desk is measured in decimetres.
-
The length of a pencil is measured in centimetres.
Measurements can be made in metres (m), decimetres (dm), centimetres (cm), or millimetres (mm).
The metre is the standard basic unit of measurement. It can be split into parts to get decimetres, centimetres, or millimetres.
Observe the length of what needs to be measured to choose which unit of measurement to use. Generally, longer distances require larger units of measurement.
-
The width of a classroom is measured in metres.
-
The height of a desk is measured in decimetres.
-
The length of a pencil is measured in centimetres.
-
The thickness of a book is measured in millimetres.
Units of measurement can be converted from one to the other using certain equivalent relationships.
-
1 m = 10 dm = 100 cm = 1000 mm
-
8 m = 80 dm = 800 cm = 8000 mm
Objects can be measured in kilometres (km), metres (m), decimetres (dm), centimetres (cm), or millimetres (mm).
Observe the length of what needs to be measured to choose which unit of measurement to use. Generally, longer distances require larger units of measurement.
-
The distance between two cities is measured in kilometres.
-
The width of a classroom is measured in metres.
-
The height of a desk is measured in decimetres.
-
The length of a pencil is measured in centimetres.
-
The thickness of a book is measured in millimetres.
-
The depth of a swimming pool is measured in metres.
Units of measurement can be converted from one form to the other using certain equivalent relationships.
1 km = 1000 m = 10 000 dm = 100 000 cm = 1 000 000 mm