An electric current is a flow of negative charges carried by electrons inside the conductive components of an electrical circuit.
Electric current can be direct or alternating. The type of current depends on how the electrons flow in the electrical circuit.
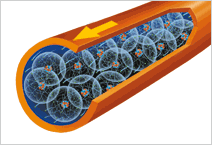
Direct current is an electric current in which electrons flow continuously in a single direction, in other words, from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of the power source.
Attention! In the past, it was believed that positive particles flowed to generate a current. The conventional direction of current was therefore established as flowing from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Today, we know that it is negative particles (electrons) that flow, but we still use the conventional direction of current to do some of calculations.
The abbreviations CC (continuous current) and DC (direct current) are used to indicate the presence of a direct current. This type of current is supplied by cells, batteries, direct current generators, and other sources of electric power. It is mainly used in portable technical objects, such as flashlights or cell phones, as well as in devices that cannot be powered by an electrical distribution network, such as satellites or automobiles.
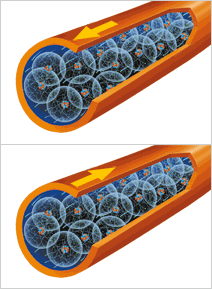
An alternating current is an electric current in which electrons flow alternately in one direction and then in the other, at regular intervals called cycles. The electrons flow back and forth in a regular pattern.
The abbreviation AC is used to indicate the presence of an alternating current. This is the type of current that powers our homes. Alternating current is generally produced by generators and alternators. This type of current is preferred for the transmission and distribution of electricity since it is easy to modify the voltage and it reduces energy losses.