Combustion is an oxidation reaction that releases energy.
The combustion of glucose during cellular respiration takes place according to the following chemical equation.
||\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_{6\ \text{(aq)}}+6\ \text{O}_{2\ \text{(g)}}\rightarrow 6\ \text{CO}_{2\ \text{(g)}}+6\ \text{H}_2\text{O}_{\text{(l)}}+\text{Energy}||
The combustion of methane |(\text{CH}_4),| the main constituent in natural gas, takes place according to the following chemical equation.
||\text{CH}_{4\ \text{(g)}}+2\ \text{O}_{2\ \text{(g)}}\rightarrow\text{CO}_{2\ \text{(g)}}+2\ \text{H}_2\text{O}_{\text{(l)}}+\text{Energy}||
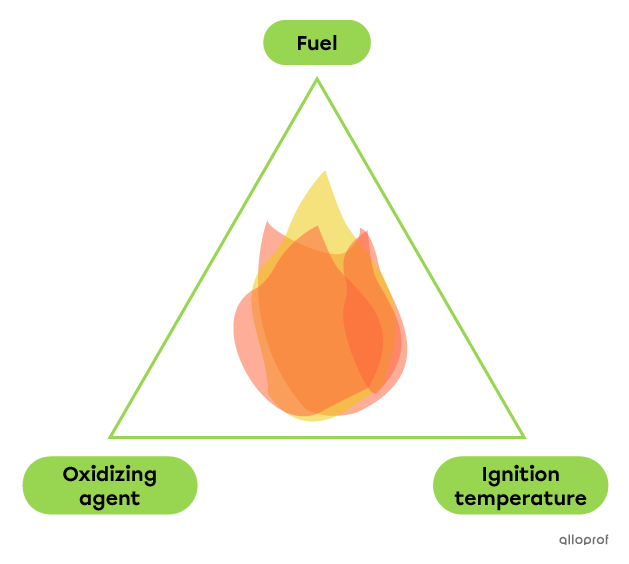
The fire triangle helps us remember the 3 elements required for combustion to take place. These elements are :
- A fuel
- An oxidizing agent
- The reaching of the ignition temperature
If one of the elements is no longer present, combustion stops.
-
Fuel is the substance that burns. Examples include wood, paper, and fossil fuels (oil, coal, natural gas, etc.).
-
The oxidizing agent is the substance that sustains the combustion. The most common oxidizer is oxygen |(\text{O}_2),| because it is present in the air.
-
The ignition temperature is the minimum temperature the fuel and oxidizing agent must reach to initiate combustion. This temperature is specific to each substance.
If you try to light a campfire with damp wood, you’re unlikely to have much success. This is because some of the heat applied to wet wood is absorbed by the water, which allows it to vaporize. As a result, much more heat is required to reach the wood's ignition temperature, making it more difficult to start a fire.
Combustion reactions can be classified into 3 types based on how combustion is initiated and the rate at which energy is released.
Rapid combustion releases energy rapidly in the form of light and heat. Rapid combustion is usually triggered by a flame or spark.
Here are a few examples of rapid combustion.

serhii.suravikin, Shutterstock.com
Spontaneous combustion releases energy rapidly, just like rapid combustion, but is initiated without the aid of a flame or spark.
Spontaneous combustion occurs when the heat of the surrounding environment allows a substance to reach its ignition temperature.
Here are a few examples of situations that can lead to spontaneous combustion.
-
In periods of drought, the risk of forest fires is higher. The oxygen |(\text{O}_2)| present in the air and the ambient heat can spontaneously ignite trees.
-
The heat released by the organic matter in hay can start a barn fire.
-
Potassium |(\text{K})| must be stored in oil because its reaction with water |(\text{H}_2\text{O})| produces hydrogen |(\text{H}_2)| and generates a lot of heat. This heat is sufficient for the |\text{H}_2| to spontaneously ignite on contact with |\text{O}_2| in the air.
Slow combustion releases energy much more slowly than rapid and spontaneous combustion.
Although there may be a noticeable release of heat, slow combustion does not usually produce flames.
Here are a few examples of slow combustion.
The cellular respiration that takes place in the mitochondria of cells.
Barou abdennaser, Shutterstock.com

The decomposition of food scraps into compost.
pikselstock, Shutterstock.com

The oxidation of metals (corrosion).




