This section explains the procedures for determining whether a solution contains water.
A simple test can be performed to determine whether or not a liquid substance contains water. It consists of dipping a cobalt dichloride paper into it. This strip of paper is usually a powder blue colour and reacts specifically with water to obtain a pinkish colour.
-
Solution to be identified
-
Tweezers
-
Cobalt dichloride paper
-
Apron or smock
-
Safety glasses
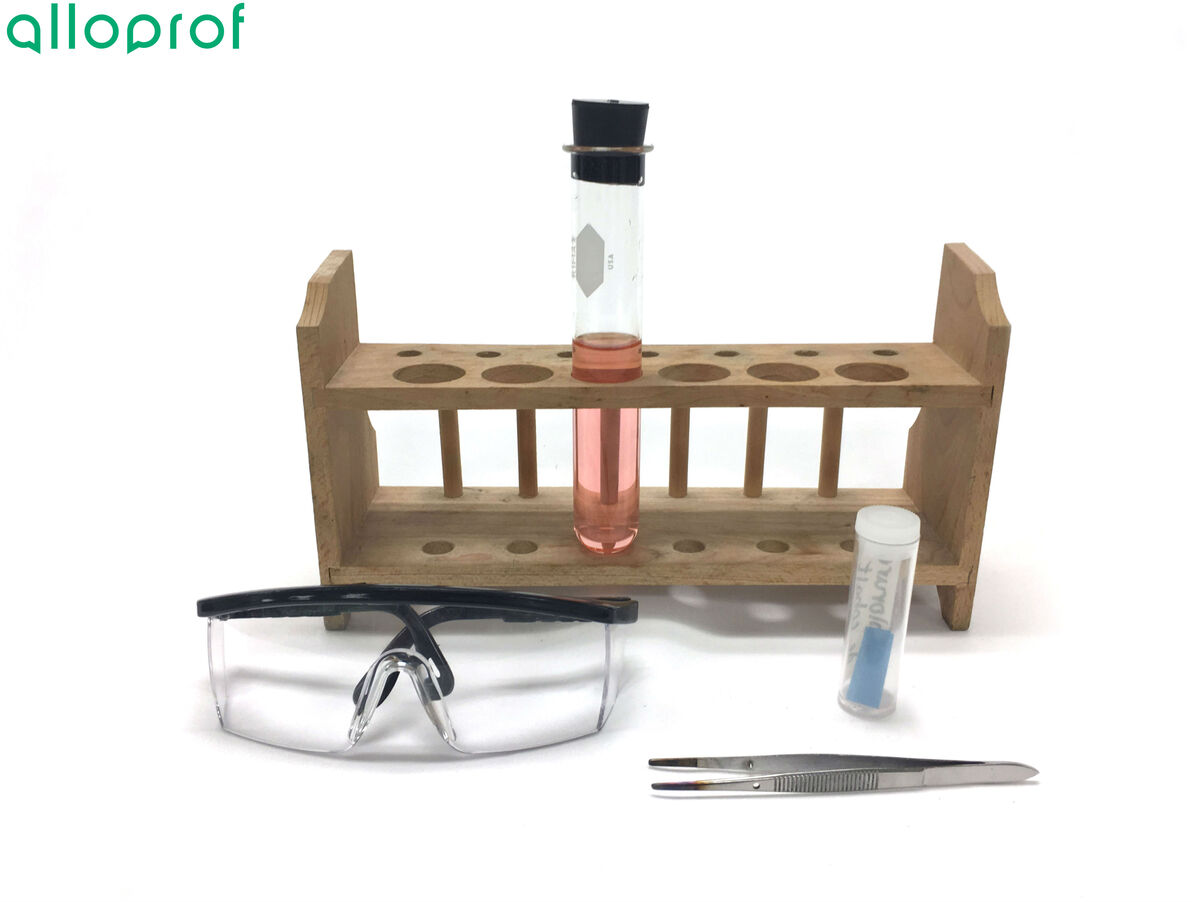

-
Take a strip of cobalt dichloride paper with tweezers.
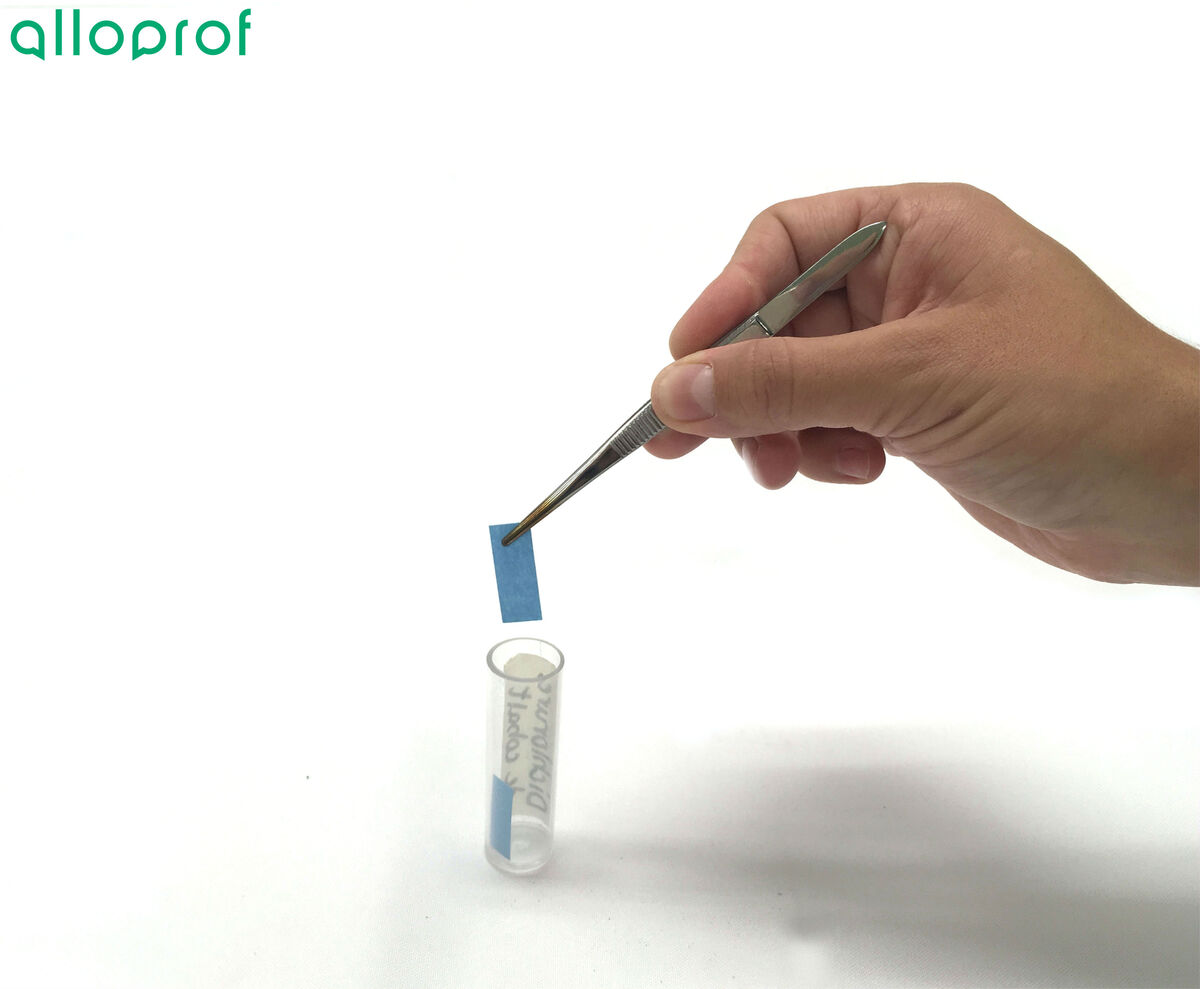

It is not useful to completely soak the cobalt dichloride paper in the liquid. Since the paper is held by the tweezers, they could become contaminated. Should the tweezers come in contact with liquid, they must be washed before reuse.
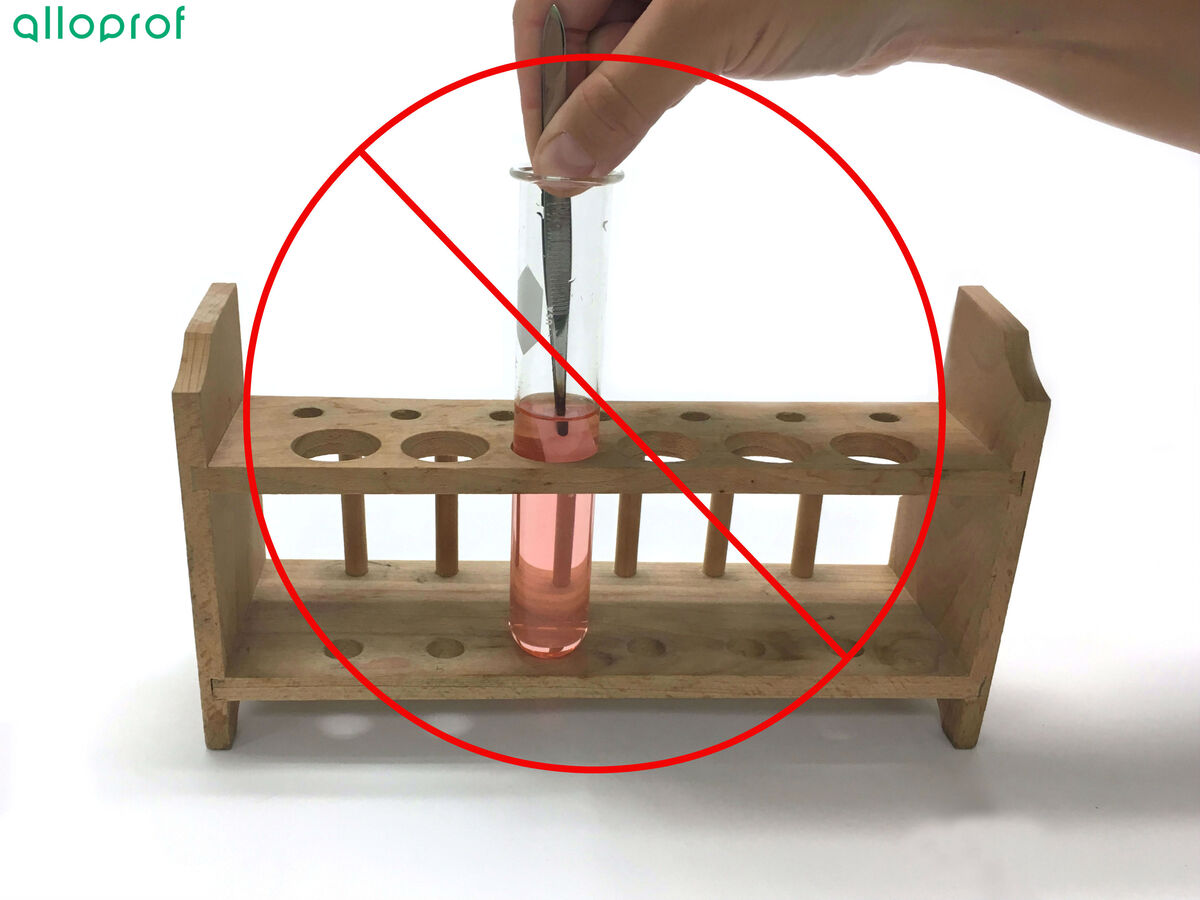
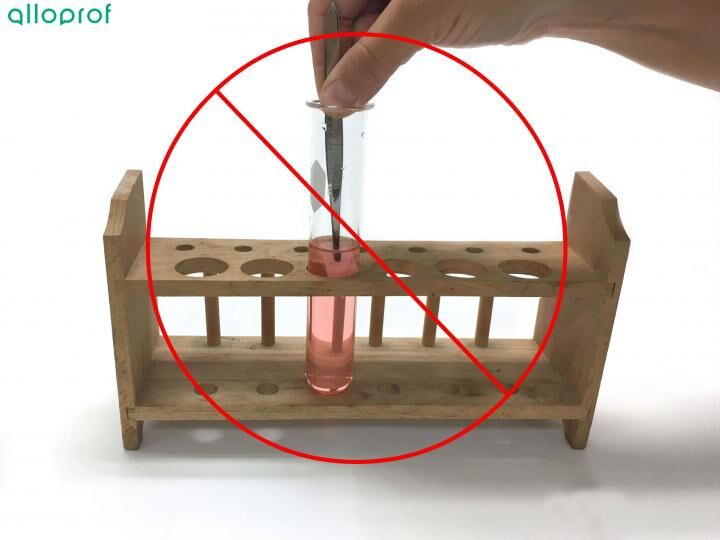
As well, do not use your hands to dip the cobalt dichloride paper in the liquid. Since the nature of the substance is unknown, dipping fingers into some types of liquid can be dangerous. It is therefore better to work with tweezers at all times.
-
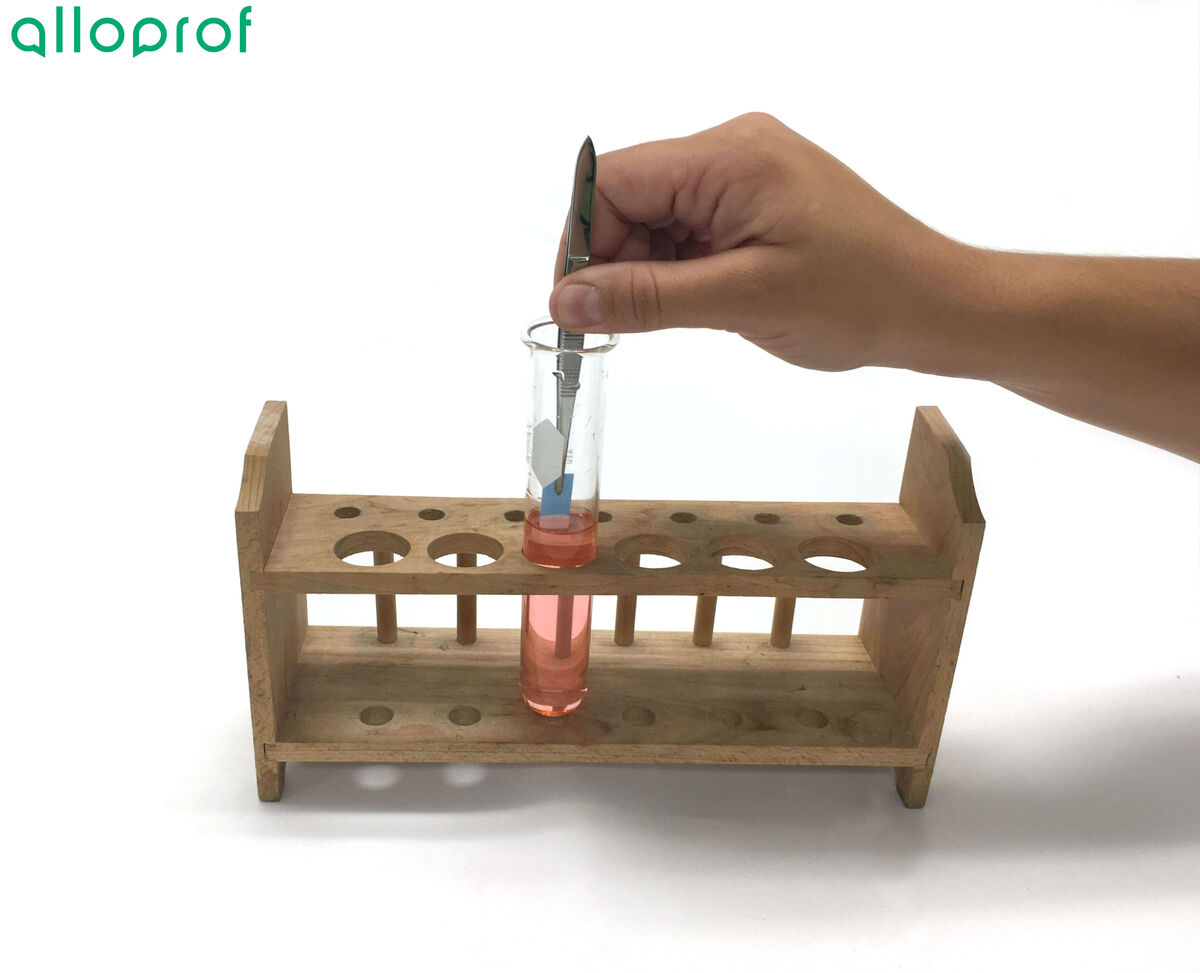
Dip the free end of the cobalt dichloride paper into the unknown liquid.
-
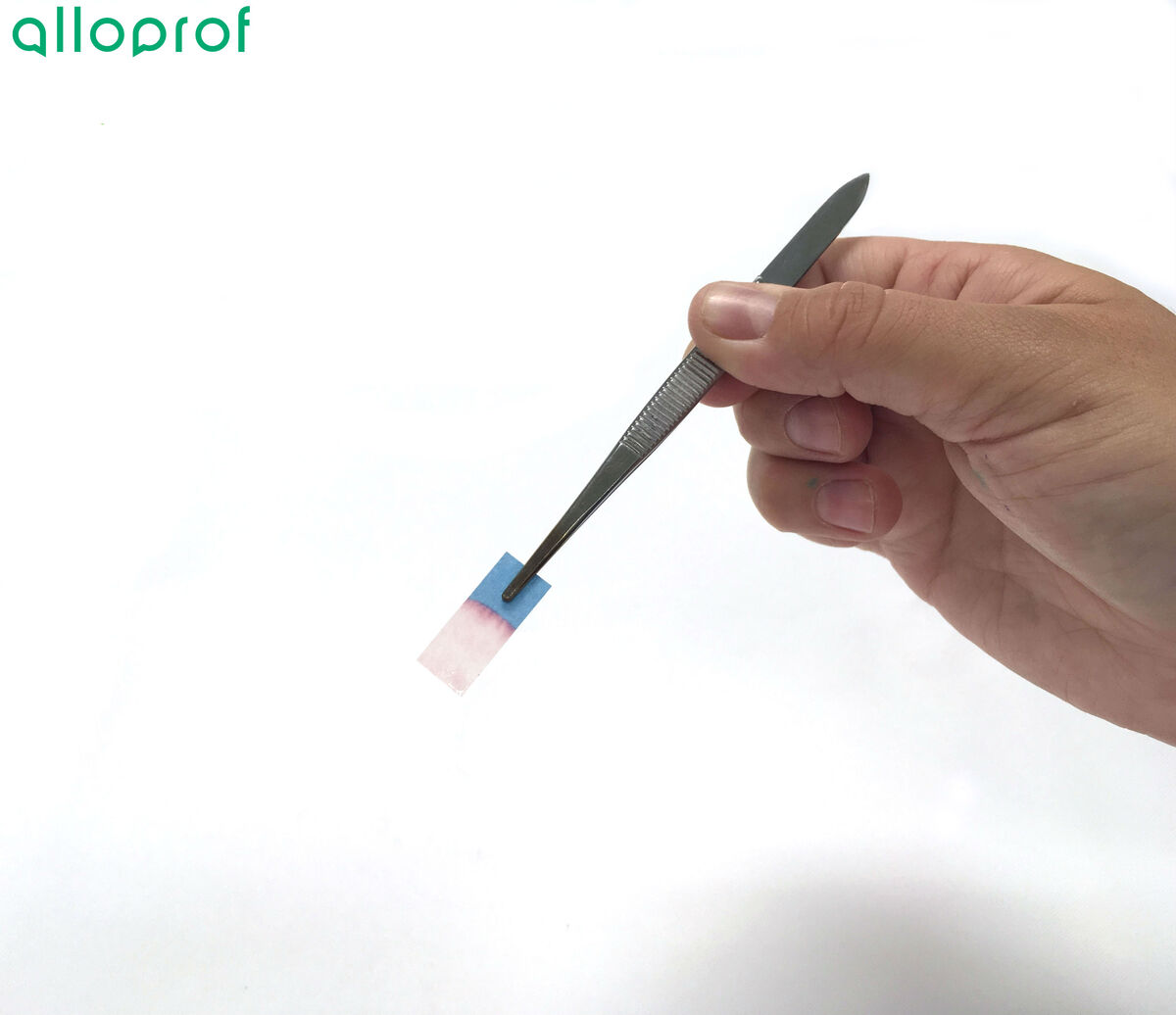
Observe the colour of the cobalt dichloride paper.
-
Discard the used cobalt dichloride paper and clean the equipment.
In some settings, to avoid cross-contamination, it is best to use a dropper to perform the cobalt dichloride paper test. Simply take a few drops of the solution to be identified and place them on a strip of cobalt dichloride paper placed in a watch glass.
The following results can be achieved.
-
If the cobalt dichloride paper turns pinkish, the solution contains water. It gives no information about the amount of water, nor about whether the solution consists of pure water. However, it is possible to assert that the liquid contains water.
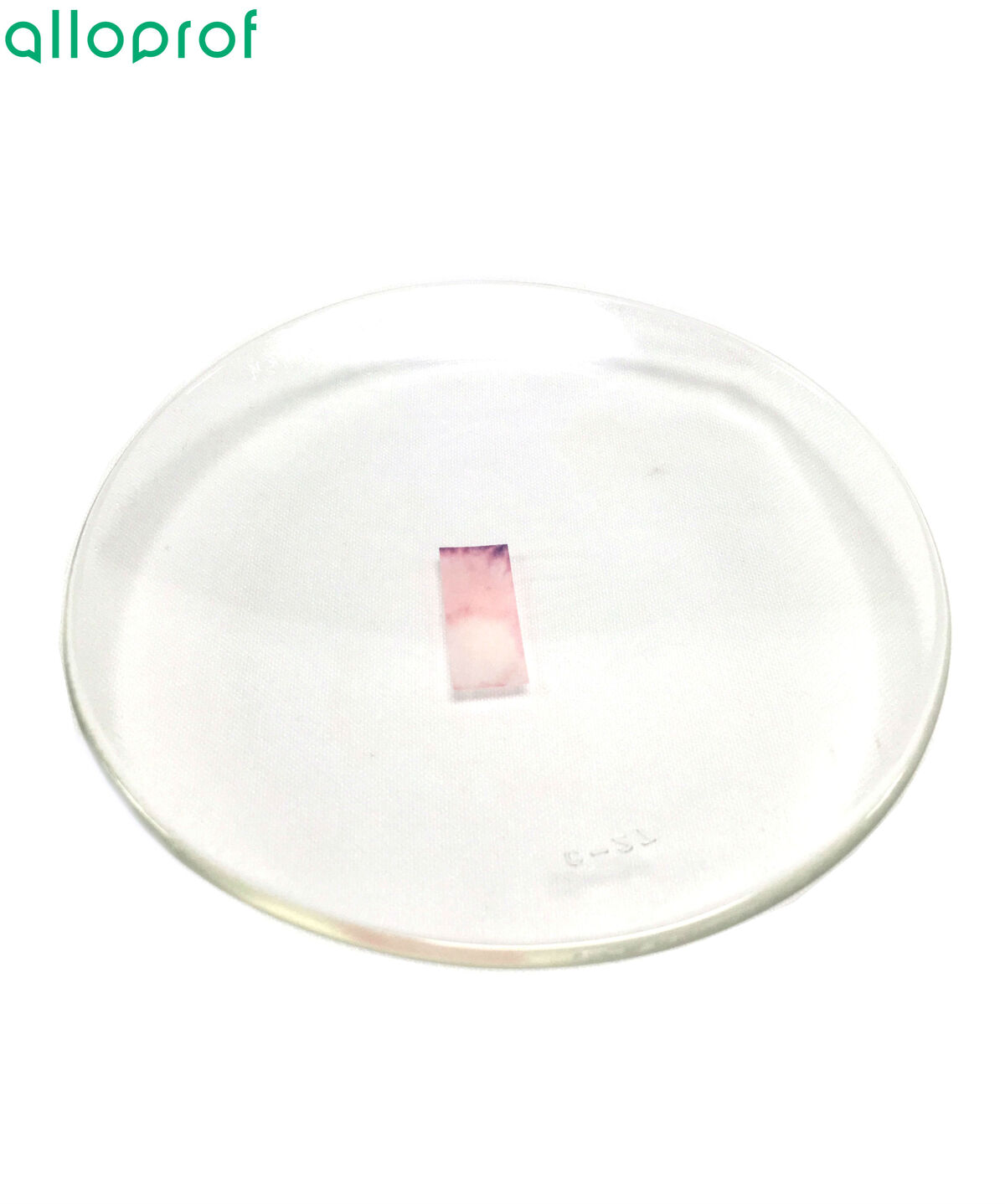
-
If the cobalt dichloride paper does not change colour, that is, if it remains blue, the solution does not contain water.
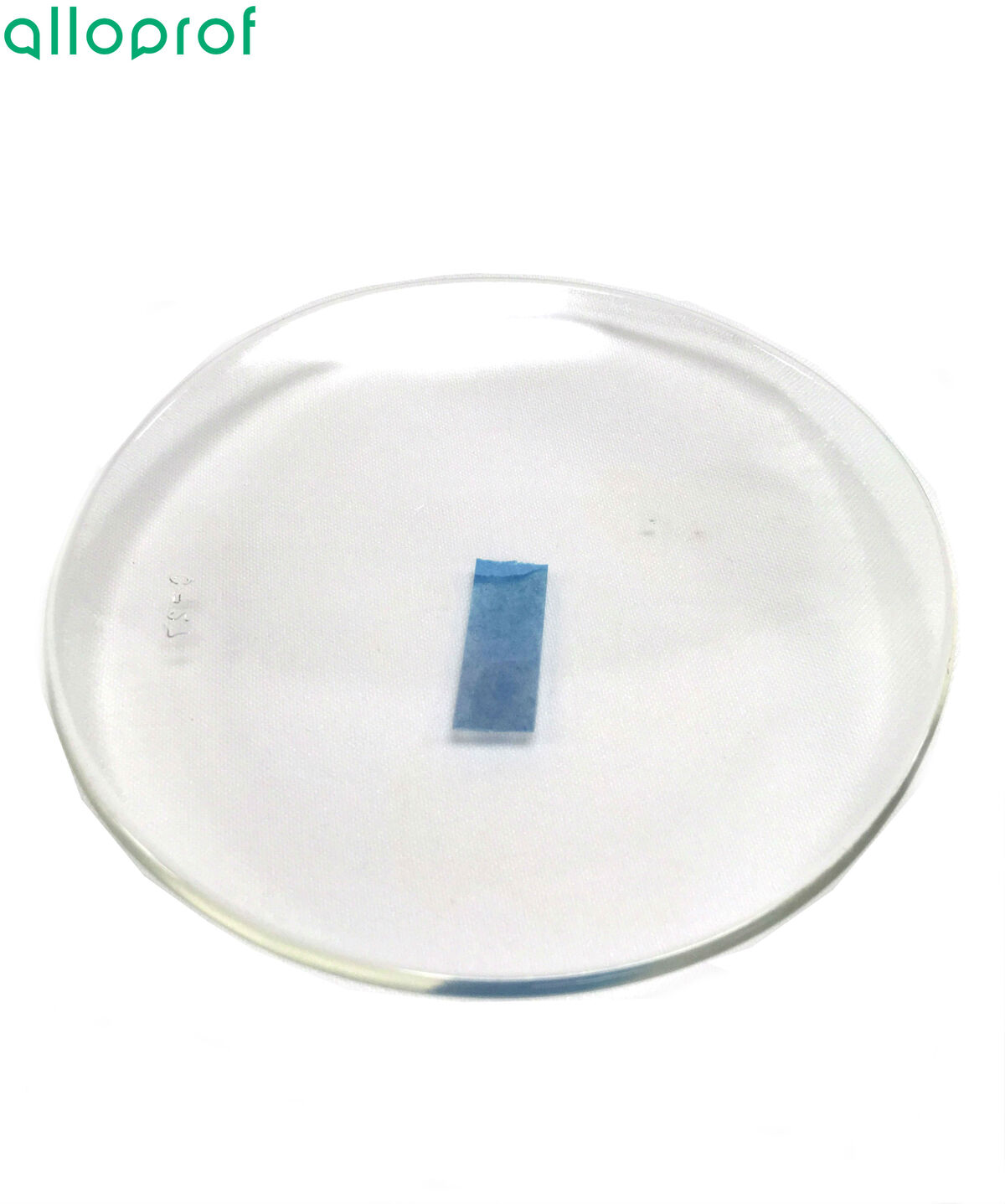
The reaction of water with the cobalt dichloride paper is considered to be reversible. If we allowed the cobalt dichloride paper to dry after use, it would regain its blue colour.