A cloud is the phenomenon that can be observed when water vapour contained in the atmosphere cools and condenses.
The formation of clouds is one of the most important stages in the water cycle. When water evaporates from the Earth’s surface, the vapour produced rises into the atmosphere where the temperature cools. In relation to this decrease in temperature, the water vapour enters a new phase and becomes liquid or solid depending on the temperature at which the phenomenon occurs. A cloud is thus made up of fine water droplets or even ice crystals resulting from the condensation of water vapour around particles suspended in the air, very often dust.
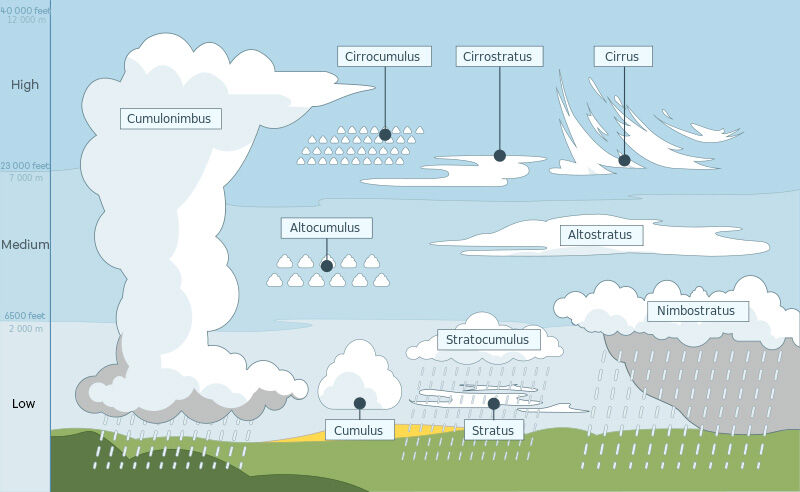
Clouds provide information about the weather; it is useful to identify them in order to make weather forecasts. Depending on their altitude, shape, and direction of their development (vertical or horizontal), clouds are classified into different types.
There are 10 main categories of clouds which are grouped into 4 classes according to the altitude at which the cloud forms. To designate the altitude, we therefore use the following prefixes.
|
Cirro- |
High-level clouds occurring above 6 000 m |
|
Alto- |
Mid-level clouds occurring between 2 000 and 6 000 m |
|
Strato- |
Low-level clouds occurring below 2000 m |
|
Cumulo- |
Large vertically extended clouds |
Furthermore, the appearances of some clouds are described by Latin names.
|
Stratus |
Cloud that constitutes a greyish layer covering the entire sky and made up of fine water droplets |
|
Cirrus |
Separate cloud in the form of white filaments of fibrous or hairy appearance; composed of ice crystals |
|
Cumulus |
Cloud with well-defined contours, and a cauliflower-like upper part; it is bright white |
|
Nimbus |
Rain precursor cloud |
By using these different terms and combining them, the 10 main categories of clouds can be described and identified.
|
|
|
|
Cumulus |
Cumulonimbus |
|
|
|
|
|
Stratus |
Nimbostratus |
Stratocumulus |
|
|
|
|
Altostratus |
Altocumulus |
|
|
|
|
|
Cirrus |
Cirro-stratus |
Cirrocumulus |