-
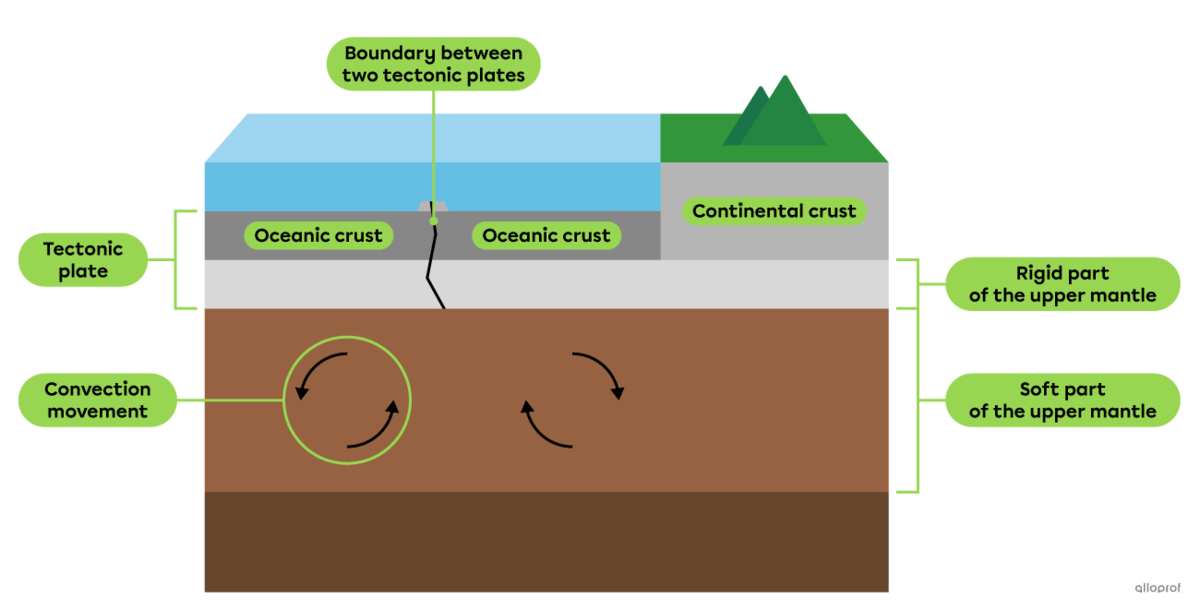
A tectonic plate is a rigid fragment of the lithosphere.
-
Convection is the circular motion of a substance caused by a change in temperature.
The theory of plate tectonics states, among other things, that:
-
The lithosphere is broken up into several pieces called tectonic plates or lithospheric plates.
-
Tectonic plates move relative to each other through convection movement in the soft part of the upper mantle.
-
The movement of tectonic plates is responsible for the formation of oceans, volcanoes and mountains. It can also cause earthquakes.
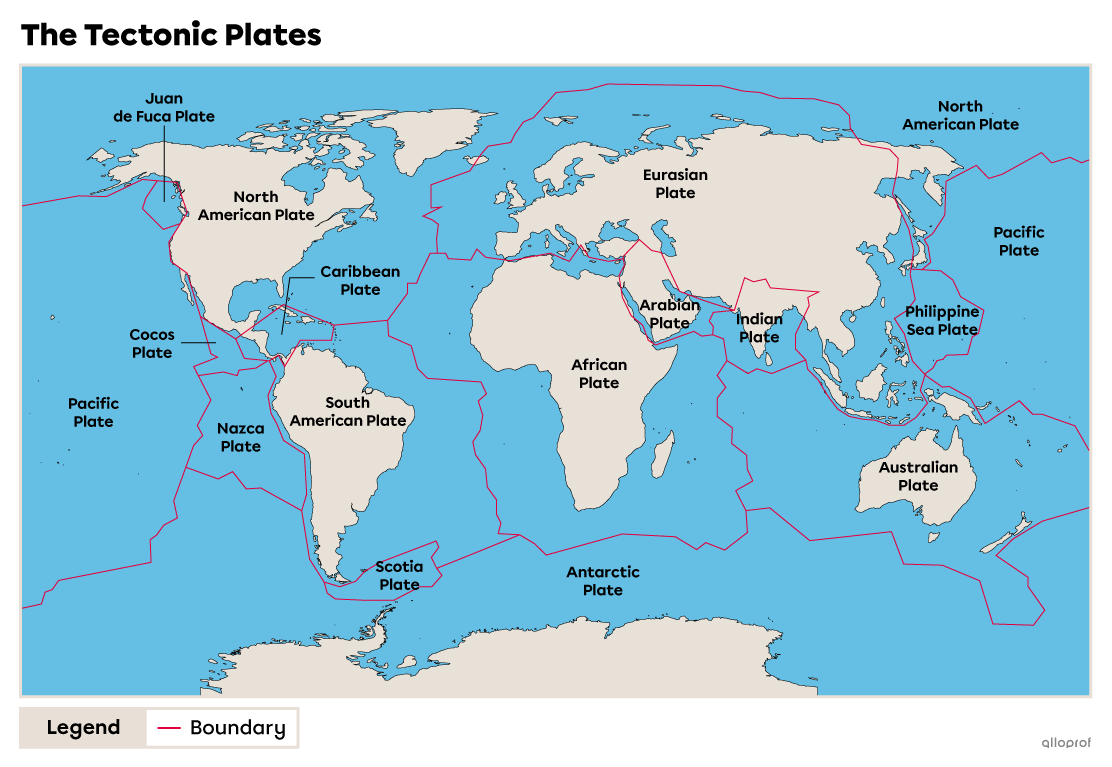
It is estimated that the lithosphere is divided into 15 main tectonic plates.
There are two types of tectonic plates, depending on the type of crust that covers most of their surface.
-
Oceanic plates are mainly covered by oceanic crust. Some plates, such as the Pacific Plate, are entirely covered by oceanic crust.
-
Continental plates are mainly covered by continental crust. There is no plate entirely covered by continental crust. The Eurasian plate is one of the continental plates.
The density of a tectonic plate varies according to its age and the type of crust that covers it. Older tectonic plates and oceanic plates have the highest density. The line between two tectonic plates is called a boundary.
The movement of tectonic plates relative to each other can cause the following phenomena:
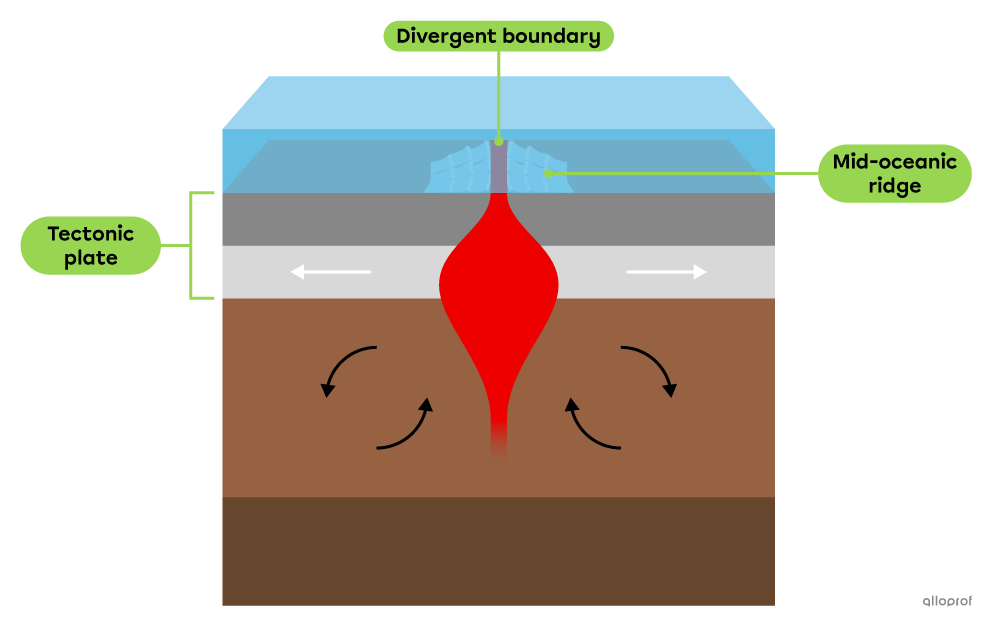
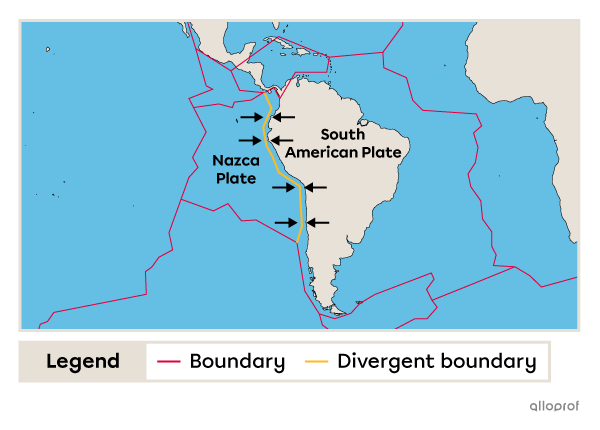
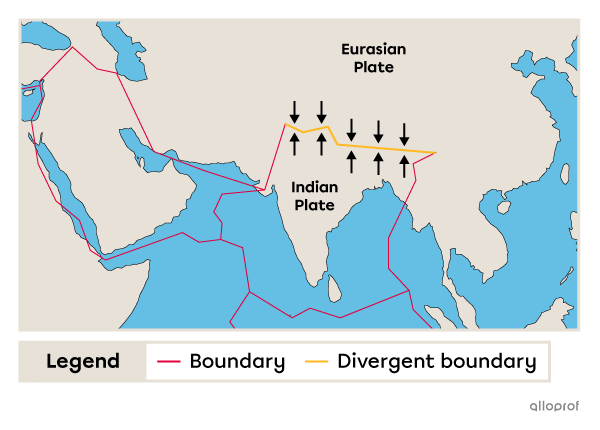
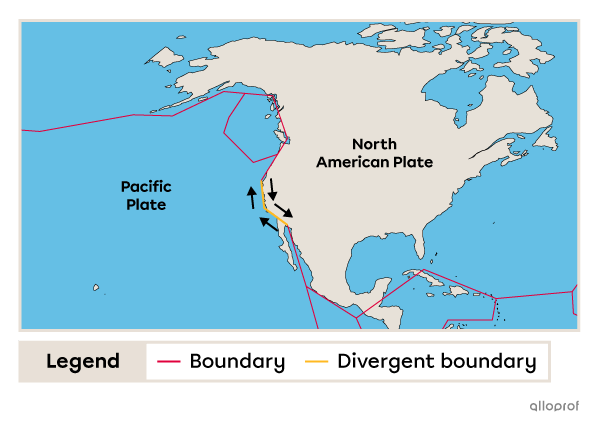
When two tectonic plates move apart, a gap forms at the boundary between them. This type of boundary is called a divergent boundary. It is usually found at the bottom of the oceans.
-
The space formed along a divergent boundary allows magma to rise to the surface.
-
The magma that reaches the ocean floor causes the formation of underwater volcanoes whose lava solidifies and forms the new oceanic crust.
-
The new oceanic crust accumulated along a divergent boundary forms a mountain range on the ocean floor known as a mid-oceanic ridge.
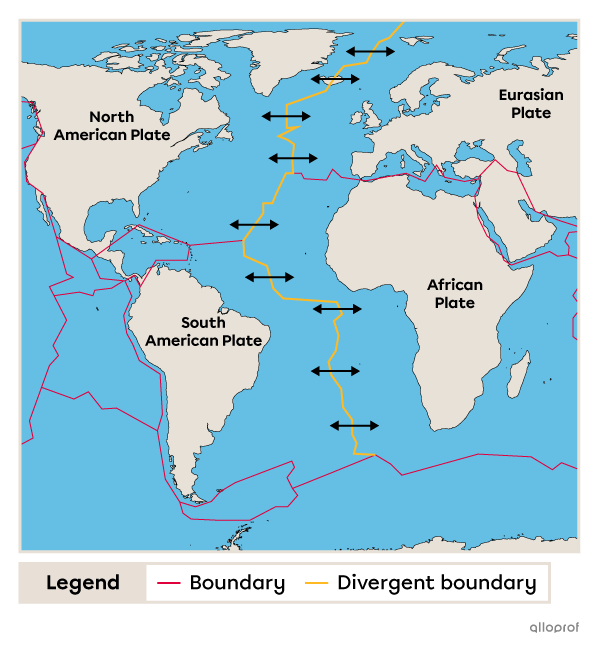
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an ocean floor mountain range in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. In the North Atlantic, it lies at the divergent boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. In the South Atlantic, it lies at the divergent boundary between the South American Plate and the African Plate.
A subduction zone is an area where an oceanic plate sinks under another younger or less dense tectonic plate during a collision.
Two tectonic plates collide when they move towards each other. The boundary between two colliding tectonic plates is called a convergent boundary.
Depending on the nature and age of the two colliding tectonic plates, different phenomena can occur.
-
The denser oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate.
-
The oceanic plate melts as it sinks into the mantle, which can cause magma to form and rise below the continental plate.
-
Magma that rises to the surface of a continental plate leads to the formation of terrestrial volcanoes along the boundary between the two plates.
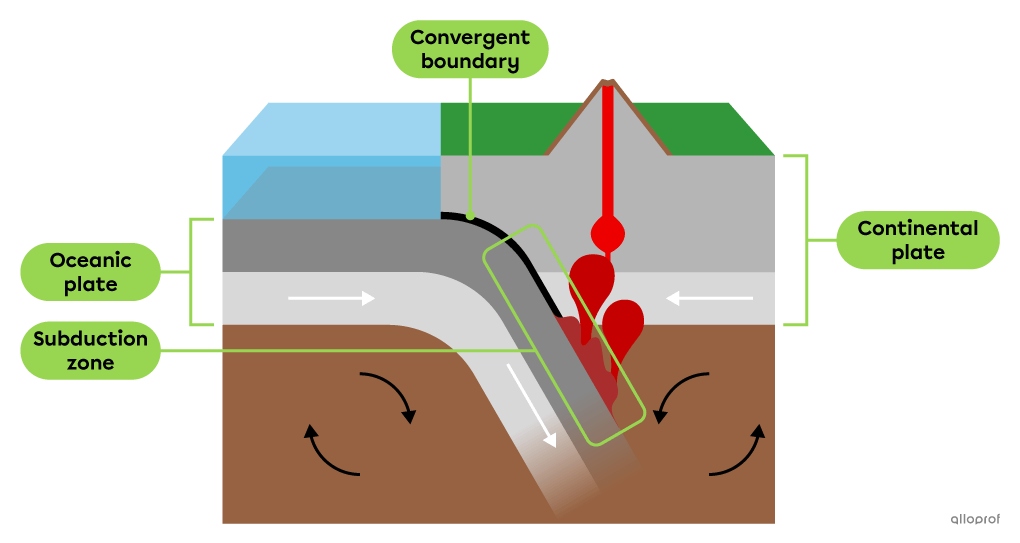
The Andes is the longest and highest mountain range in the world, with many volcanic peaks. It lies along the convergent boundary between the oceanic Nazca Plate and the continental South American Plate.
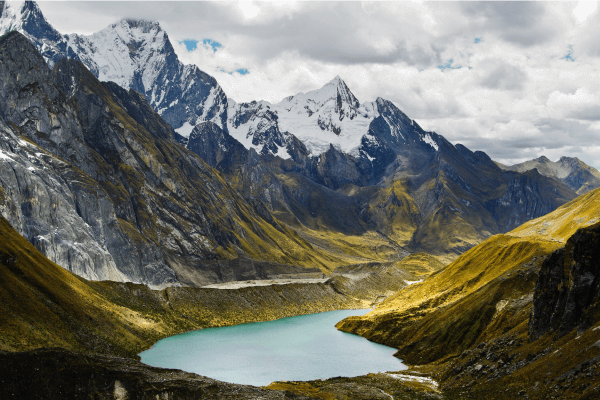

The Huayhuash mountain range in Peru.
Source: Jujubier, shutterstock.com
-
The older oceanic plate is denser, so it sinks under the younger oceanic plate.
-
The oceanic plate that sinks into the mantle disintegrates, which can cause magma to form and rise.
-
Magma that rises to the surface of an oceanic plate causes underwater volcanoes to form along the convergent boundary between the two plates.
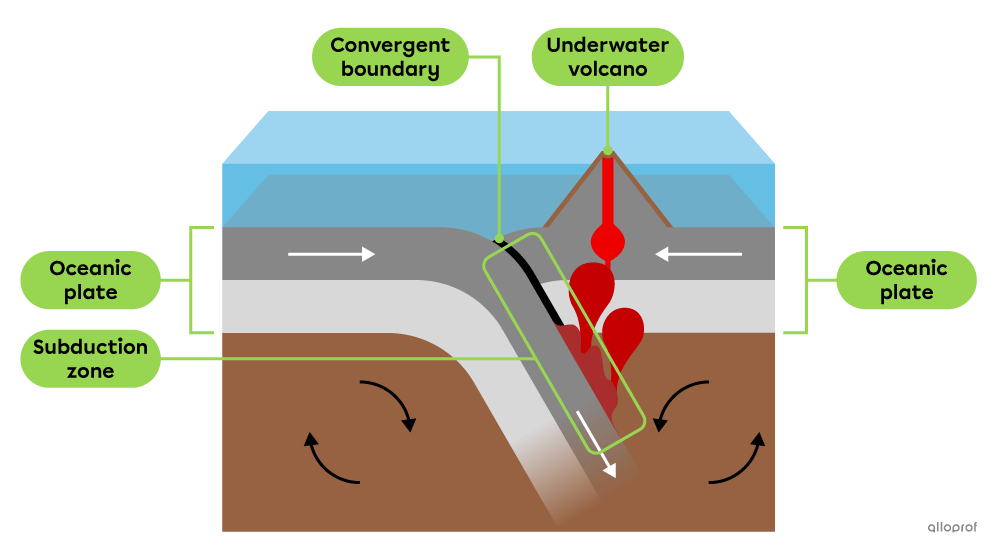
The Lesser Antilles is a series of volcanic islands formed along a convergent boundary due to the collision of two oceanic plates: the South American Plate subducts under the Caribbean Plate.
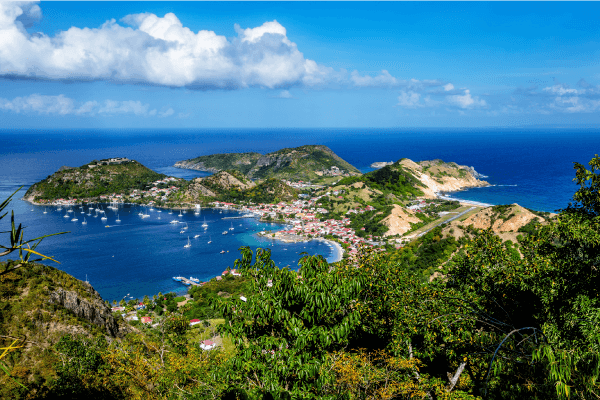
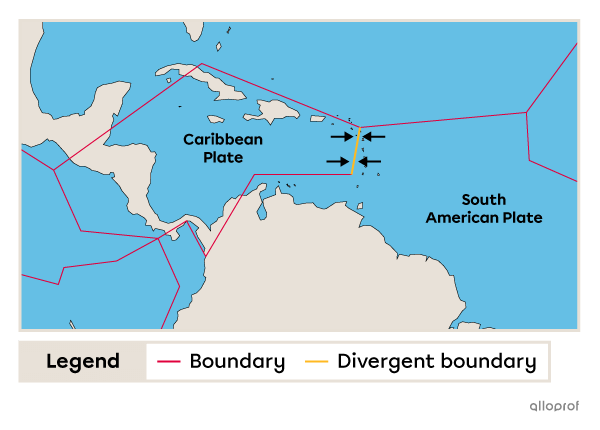

The Lesser Antilles is a series of volcanic islands formed at the convergent boundary between the Caribbean Plate and the South American Plate.
Source: Iryna Shpulak, shutterstock.com
When two continental plates collide, neither is dense enough to sink beneath the other. As a result, the two plates compress and rise to form high mountain ranges.
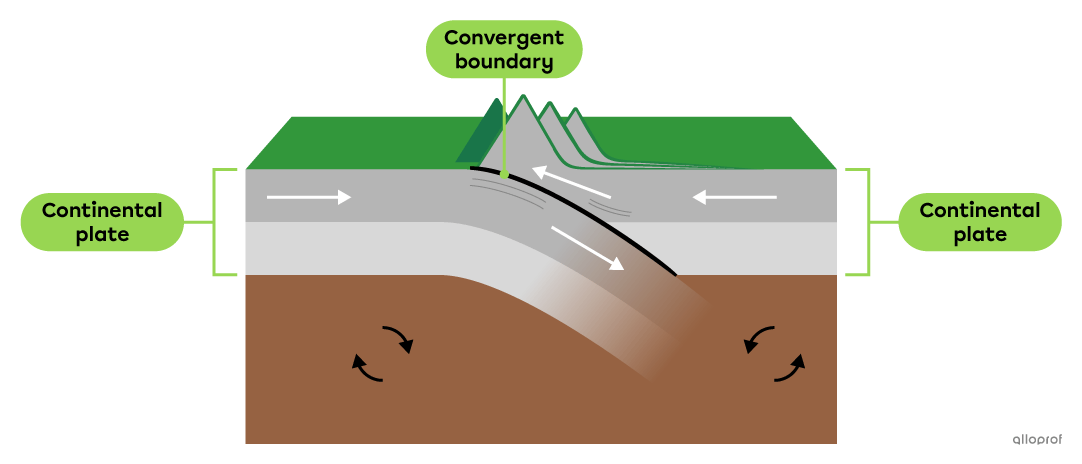
The Himalayas are a mountain range formed by the collision of two continental plates, the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate.
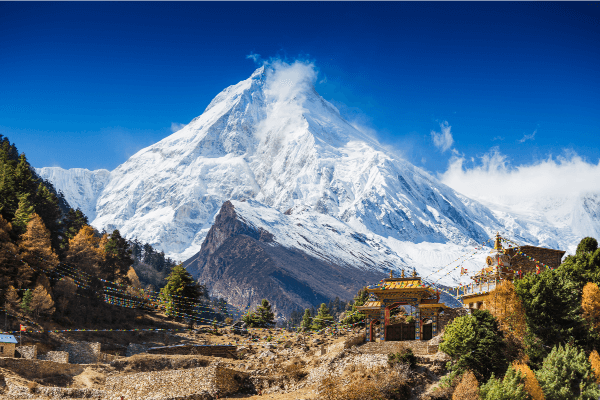

Mount Manaslu is one of the Himalayan mountains in Nepal.
Source: Olga Danylenko, shutterstock.com
When two tectonic plates move in parallel and opposite directions, they rub against each other. The boundary between two tectonic plates that undergo friction is called a transform boundary.
-
The plane on which two tectonic plates rub against each other is called a fault.
-
The friction along the fault releases enormous amounts of energy, which can cause earthquakes.
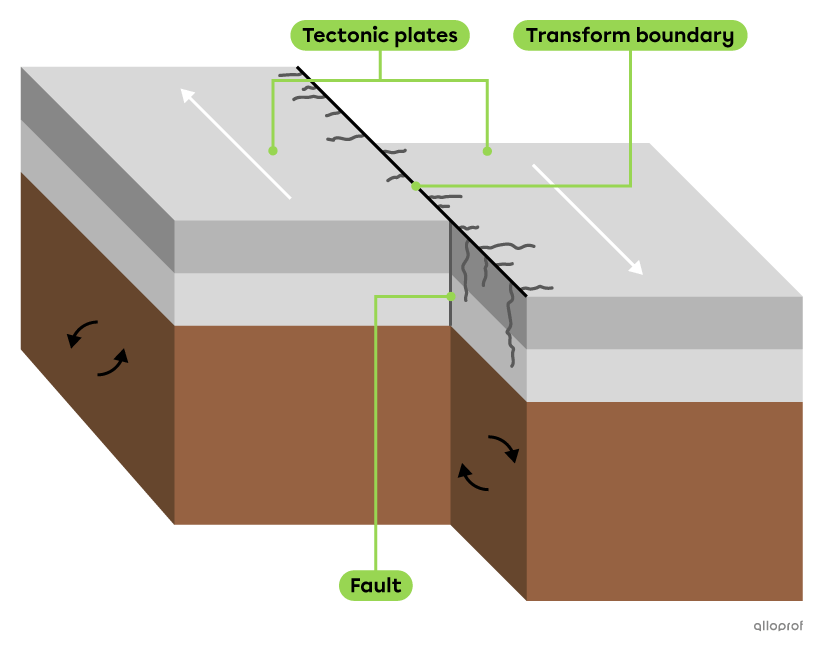
The San Andreas Fault is a friction zone at the transform boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The large amounts of energy released by the movement of the plates cause many earthquakes in California, USA.
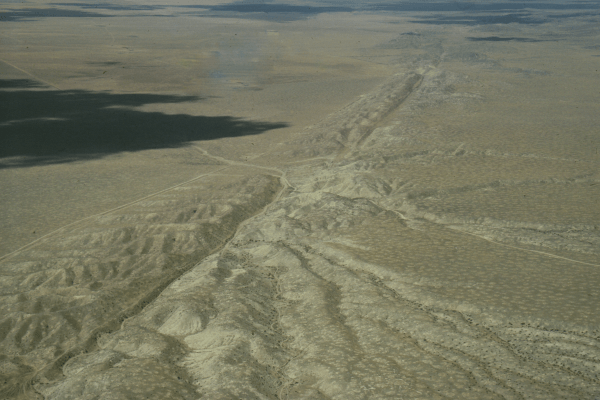

The San Andreas Fault can be seen in the deserts of California, USA.