The present perfect expresses:
-
Present result
-
past action with present result
-
recently finished action
-
Unfinished time
-
past action not yet finished
-
time period still going on
-
Indefinite time
-
past actions at unspecified time
-
repeated past actions
-
Present results

Florence the explorer has discovered a new bird species.
She has tried to print it as a 3D model.
-
Unfinished time

Birds have been her favourite animals since she was a kid.

Today, she has seen the bird six times.
-
Indefinite time

Florence has written three books on birds in the last few years.

“I have taken a lot of bird pictures in my career.”
Some keywords and phrases are often used with the present perfect.
| Words like: | Phrases like: |
|
|
Present perfect expresses:
-
Present result

She has fallen in the water.
-
present result → She is now wet.
Simple past expresses:
-
Past action

She fell in the water.
-
not connected to the present
Present perfect expresses:
-
Unfinished time
Simple past expresses:
-
Finished time

I have worked 60 hours this week.
-
60 hours done
-
the week isn't finished

I worked 60 hours this week.
-
60 hours completed
-
the week is over
Present perfect expresses:
-
Indefinite time

She has been here before.
-
specific time is not mentioned
-
she knows the place
Simple past expresses:
-
Specific time

She was here last week.
-
specific time → last week
-
she isn’t at the location anymore
Points to remember when forming affirmative sentences in the present perfect
-
Use the past participle form of the verb.
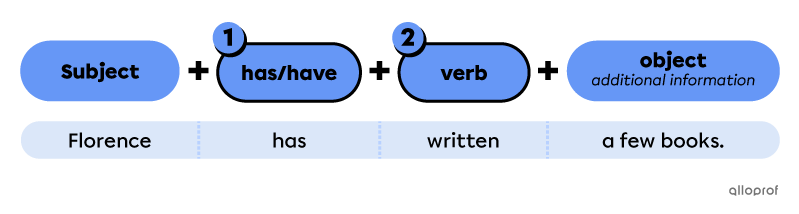

“I have bought a new camera.”
“I've bought* a new camera.”

She has researched her subject for hours.
She's researched* her subject for hours.

She has packed her suitcase.
She's packed* her suitcase.
*Affirmative contraction form
Points to remember when forming negative sentences in the present perfect
-
Use the auxiliary has/have.
-
Place the function word not between the auxiliary and the verb.
-
Use the past participle verb form.
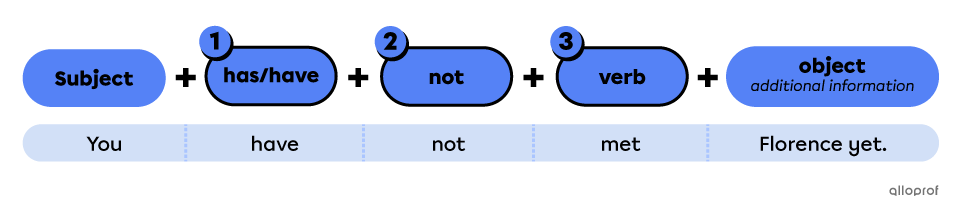

“I have not flown 1st class before.”
“I haven't flown* 1st class before.”

Florence has not enjoyed the turbulence during the flight.
Florence hasn’t enjoyed* the turbulence during the flight.

“Poor dear, you have not eaten anything during the whole flight.”
“Poor dear, you haven’t eaten* anything during the whole flight.”
*Negative contraction form
Points to remember when forming questions in the present perfect
-
Start with the auxiliary has/have for yes/no questions.
-
Use the past participle verb form.
For information questions only:
-
Start with a question word.
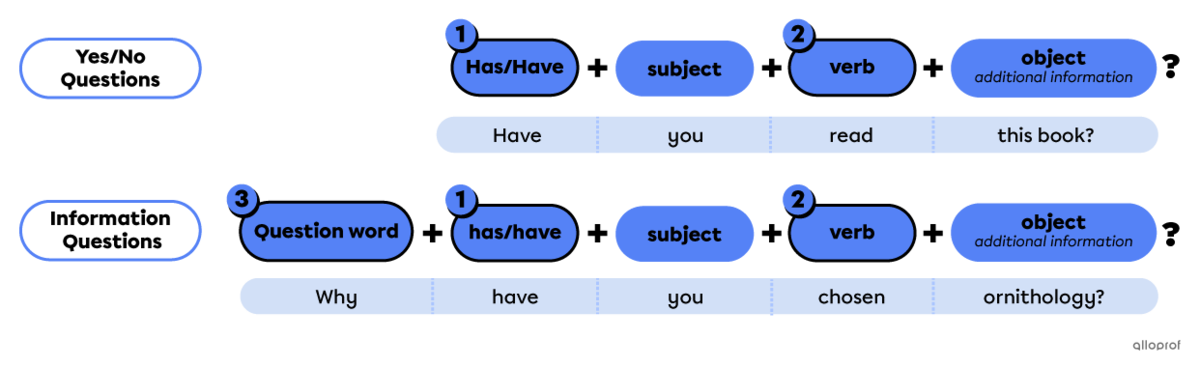

“Have you visited Cat Island?”

“What have you bought?”

Have you forgotten the keys in the car again?
Florence, the character used in the examples, was inspired by the ornithologist and author Florence Merriam Bailey. To learn more about her extraordinary life and work, visit the New York Historical Society Museum & Library.