The United Nations (UN) is an international organization with 193 member states. The UN has several missions, including maintaining world peace and security, facilitating cooperation between countries and protecting human rights.
To find out more about the UN and its organs, see the following concept sheet:
The United Nations’ (UN) mission, objectives and operation
The UN’s objectives are defined in the UN Charter. It is an official guide for how the UN deals with various issues. The following concept sheet can help you further explore this topic:
The Charter of the United Nations
To achieve its missions, the UN has set up six organs. Each of them plays a specific role in the UN. The following diagram describes the organs:
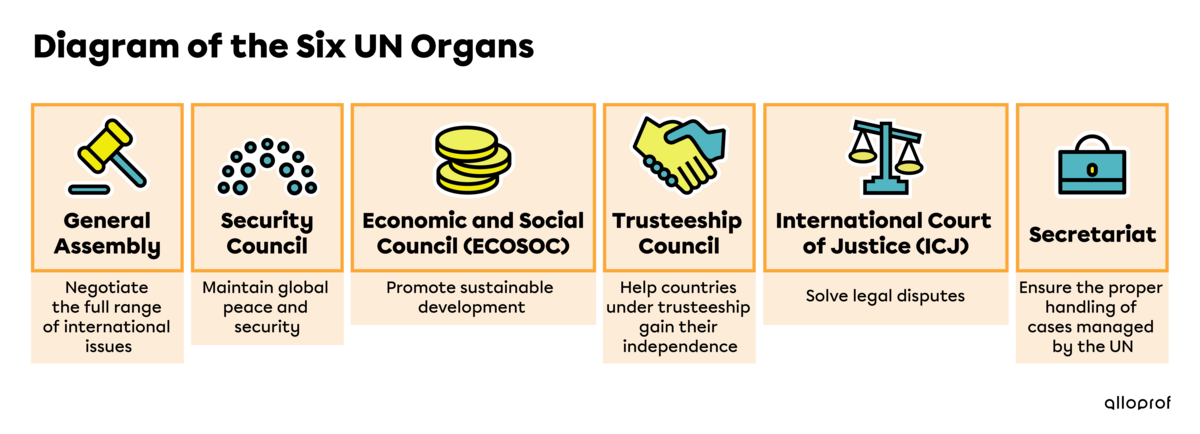
The General Assembly is where the 193 member states deliberate and decide on how to address global issues. To learn more about how the General Assembly works, see the following concept sheet:
The United Nations General Assembly
The Security Council maintains international peace and security. When it determines that there is a threat to peace, it proposes peaceful means for the parties concerned to settle their dispute. For more information on the Security Council, see the following concept sheet:
The UN Security Council
One of the UN’s primary goals is to prevent conflicts, but unfortunately some conflicts develop into wars. To convict war criminals, the United Nations has set up the International Criminal Tribunal (ICT). To find out more about the ICT, see the following concept sheet:
International Criminal Tribunals (ICTs)
Wars force people to flee the violence ravaging their country to find refuge in refugee camps. To provide these people with health care, food and other essential services, the UN created the UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR). To learn more about UNHCR’s role, see the following concept sheet: The UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR)
Boniface, Pascal. 50 idées reçues sur l'état du monde, 2015, p. 67.