
The UN flag was adopted in 1947. The blue background and olive branches symbolize peace.
With 193 member states, the United Nations (UN) is the largest international organization in the world. Thanks to its founding Charter (the document that outlines its main principles) and its various institutions, the UN pursues its mission and objectives.
An institution is an organization governed by rules and laws that plays a specific role in society. Its role may be political, social, economic, religious, etc.
To better understand what an institution is, you can watch the video What is… an institution?.
The United Nations was created after World War II. In 1945, the main victorious states created an organization to prevent another large-scale conflict from happening again. In fact, the UN’s main purpose is to prevent another world conflict. This organization has four main objectives that address collective and global issues:
-
maintaining international peace and security
-
encouraging international cooperation
-
fighting poverty
-
ensuring the protection of human rights
At the beginning of the 21st century, the UN expanded its mission to address humanitarian issues such as climate change, sustainable development, disarmament, terrorism, humanitarian and health crises, gender equality, governance, food security, etc. To address these issues, the UN has set up organizations, programs and funds with their own specific objectives, leadership and member states.
An organization is an organized set of services and people that form an association or group with specific and common goals.
Examples: The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO)
A program is a set of actions and projects pursued by a group, organization or political party to resolve a specific issue.
Examples: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Food Programme (WFP)
A fund is a special account containing a more or less large amount of money to be used for political purposes.
Examples: International Monetary Fund (IMF), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
|
Maintaining international peace and security |
|
|
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees |
Protect refugees around the world by helping them return to their home country or, if this is not possible, by helping them rebuild their lives in another country. |
|
Ensure peacekeeping by organizing non-violent missions around the world in areas of tension and conflict. |
|
|
Encouraging international cooperation |
|
|
Resolve tensions and conflicts that exist between different states. |
|
|
Promote sustainable development by encouraging cooperation between member states. |
|
|
Reduce poverty and improve living standards by providing financial support to developing countries to invest in education, health, etc. |
|
|
Fighting poverty |
|
|
Help end poverty and reduce inequality and discrimination. |
|
|
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)* |
Fight world hunger and share knowledge and techniques to help countries develop. |
|
Bring all peoples to the highest possible level of health. |
|
|
Fight hunger and malnutrition worldwide. |
|
|
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)* |
Improve global education and protect heritage. |
|
Protecting human rights |
|
|
Promote and protect all human rights. |
|
|
Defend children’s rights and improve their living conditions. |
|
|
Ensure decent working conditions for all workers by establishing international standards. |
|
|
Ensure the stability of the international monetary system and provide assistance to countries experiencing financial difficulties. |
|
* Independent organization working with the UN.
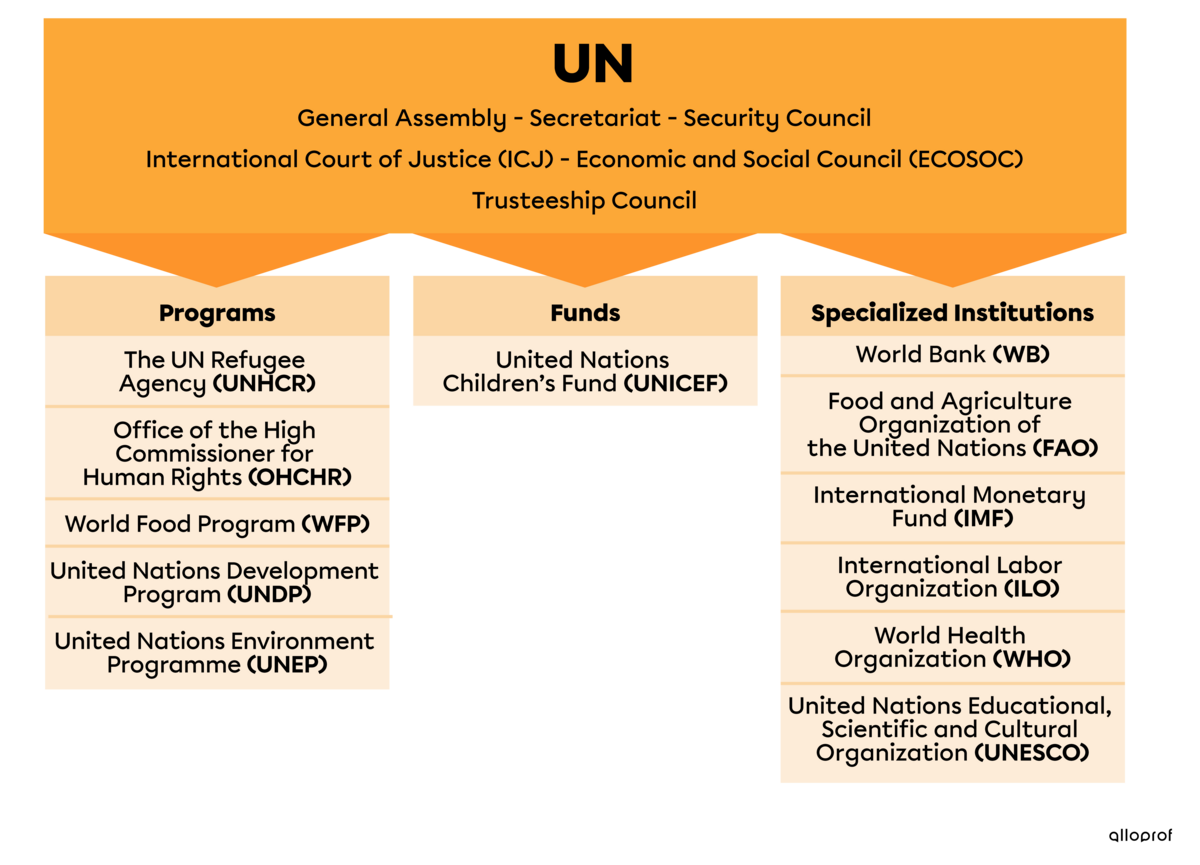
The UN is a single entity divided into specialized agencies, programs and funds (see table). The United Nations also has several bodies to help it make decisions on global issues. Below are the main bodies of the UN.
The General Assembly is the only UN body with universal representation of all 193 member states. Each member state has a vote when it comes to electing members of the Secretariat, the Security Council, the International Court of Justice, the Economic and Social Council and the Trusteeship Council. The General Assembly is a discussion forum where states deliberate and decide how to address global issues.
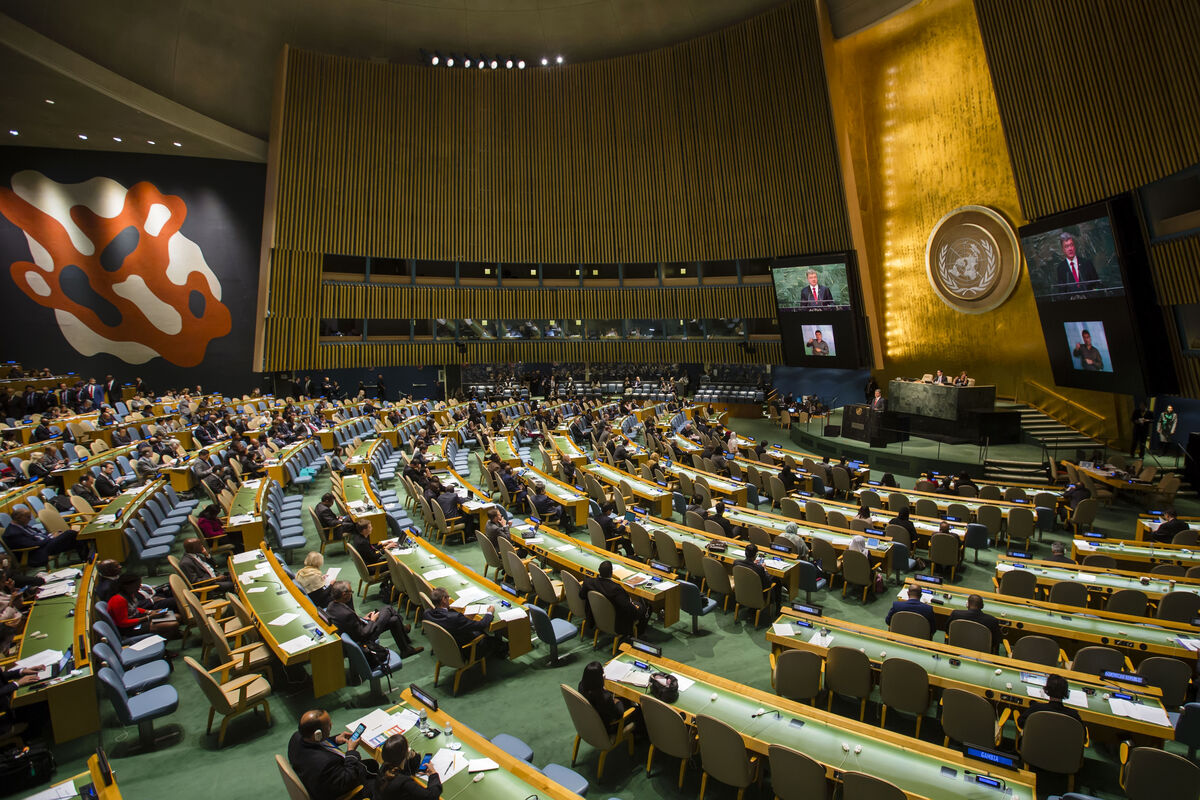

Source: Drop of Light. “NEW YORK, USA - Sep 27, 2015: President of Ukraine Poroshenko Petro delivers his speech at the UN Sustainable Development Summit in New York,” Shutterstock, September 27, 2015.
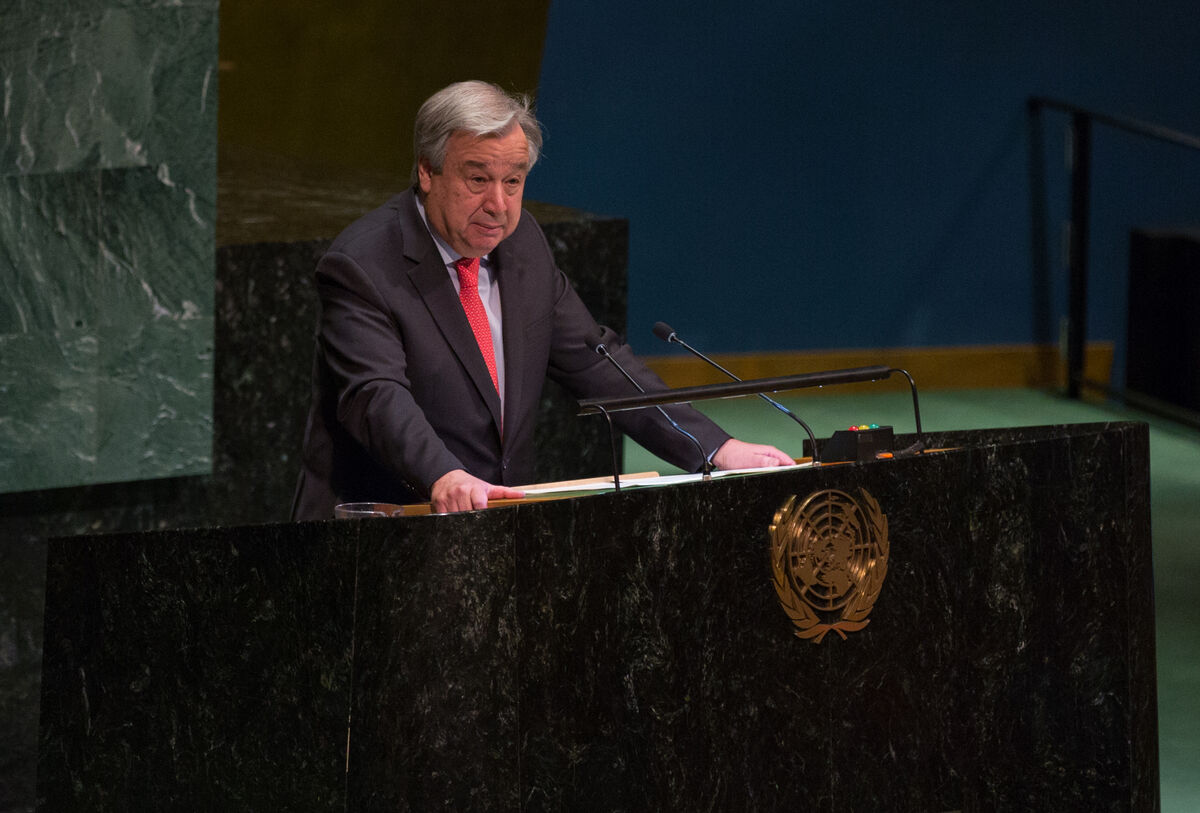

António Guterres, Secretary-General of the United Nations
Source: orhan akkurt. “Secretary-General António Guterres makes remarks at the opening of the high-level event on ‘Women in Power,’ hosted by María Fernanda Garcés, President of the seventy-third session on March 12 2019,” Shutterstock, March 19, 2019.
The Secretariat is one of the UN’s main bodies and consists of the Secretary-General and hundreds of staff members. According to the UN Charter, in addition to being responsible for the UN’s overall administration, the Secretariat performs other functions that may be assigned to it by other UN bodies. The Secretariat is responsible for responding to their requests.
The Security Council is extremely concerned about threats and attacks against their military force called “Peacekeepers.” On March 30, 2020, the Security Council asked the Secretary-General to review the UN’s standards for the training and performance of peacekeepers to ensure their safety. This was to help them better restore and maintain international peace and security.
The Security Council maintains international peace and security. When it sees a threat to peace, it proposes peaceful means for the parties concerned to settle their dispute. If the states engaged in a conflict fail to reach an agreement, the Security Council can impose sanctions and even authorize military intervention by sending peacekeepers to the territory in question. It is the only organ with the power to take action within the territory of a member state.
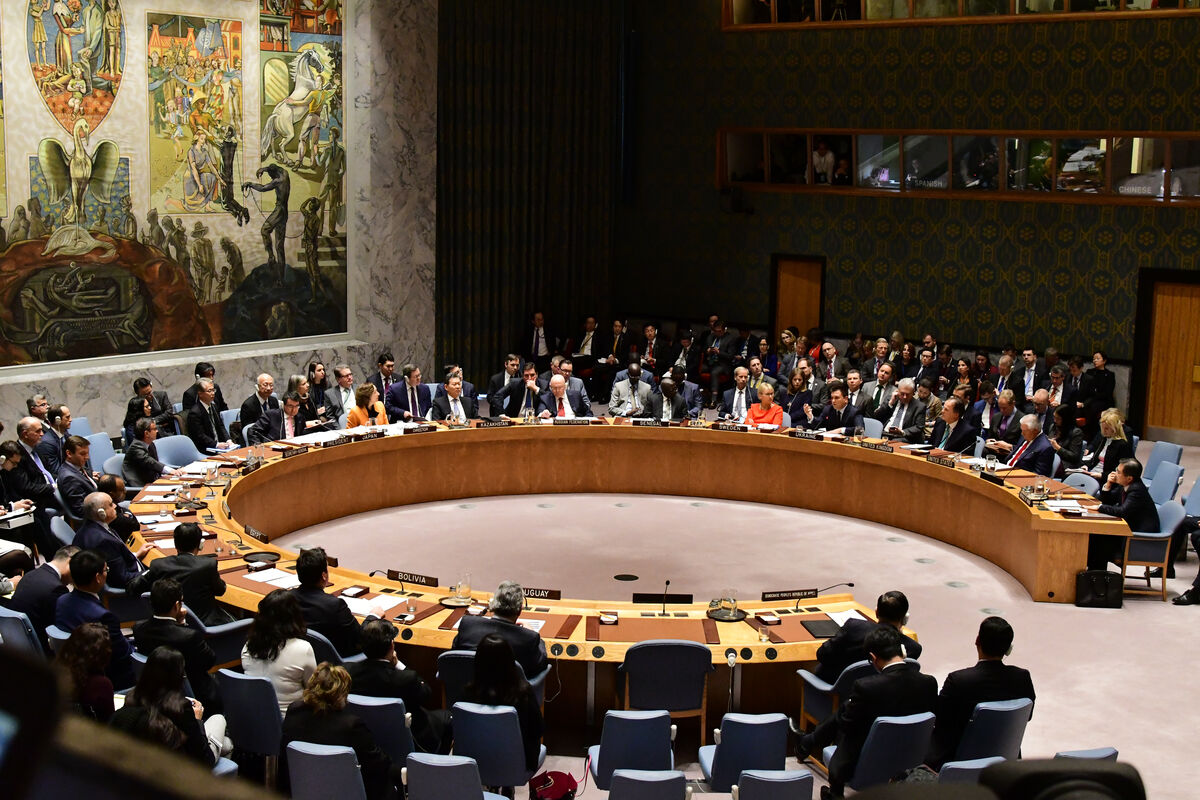

Source: a katz. “NEW YORK CITY - DECEMBER 15, 2017: The United Nations Security Council met in special session to debate alleged North Korean Nuclear proliferation,” Shutterstock, December 15, 2017.
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) resolves tension and conflict between different states. The ICJ settles disputes between states only when they call upon it to do so. These disputes are often over boundary issues. The Court may also give advisory opinions on legal matters.
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) makes recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues. It is the central forum for discussion, reflection, debate and innovation on sustainable development issues.
The Trusteeship Council managed territories that were governed by any of the member states. The Council helped these territories gain their independence. The last trust territory was Palau. When it gained independence from the United States in 1994, the Trusteeship Council ceased operations.
In summary, the UN is made up of several bodies, programs, funds and specialized agencies.
The UN Charter clearly states that the UN is not a world government and that each member state remains sovereign. This means that each state governs itself by establishing its own laws and enforcing them on its territory and its population. This sovereignty limits the UN’s ability to act in a member state’s domestic affairs.
The UN provides recommendations but cannot force the states to follow them. It is a course of action rather than an obligation. However, if a state takes actions that threaten global peace and security, the UN can impose sanctions, such as an arms embargo (prohibiting exports), travel bans or financial restrictions that often affect the oil industry.
Sovereignty is the absolute power of a state to govern itself by making its own laws and enforcing them within its territory. A sovereign state is independent, meaning that it cannot be controlled by any other state or institution.
To better understand what sovereignty is, you can watch the video Sovereignty and Interference.