Gerunds are verb forms that end in -ing and function as nouns in a sentence.
Infinitives are verb forms in their base form and function as nouns, adjectives or adverbs in a sentence.
|
Gerund in a sentence |
Conjugated verb |
Infinitive in a sentence |
|
Reading is one of my favourite hobbies. |
I am reading a good book right now. |
Thriller stories are great to read. |
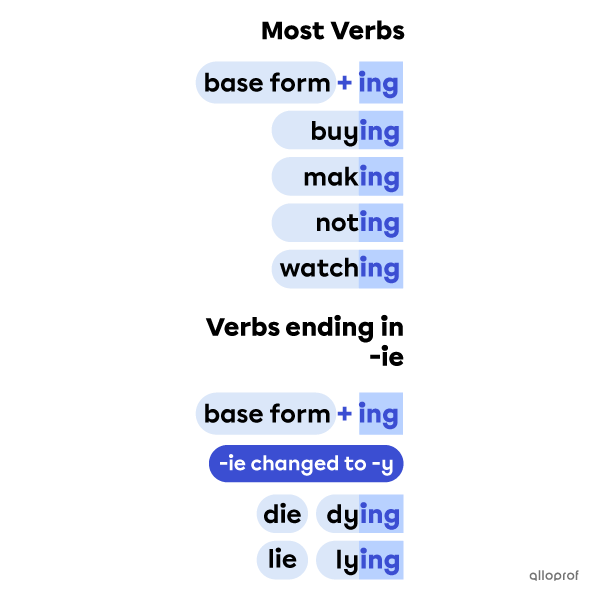
Forming Gerunds
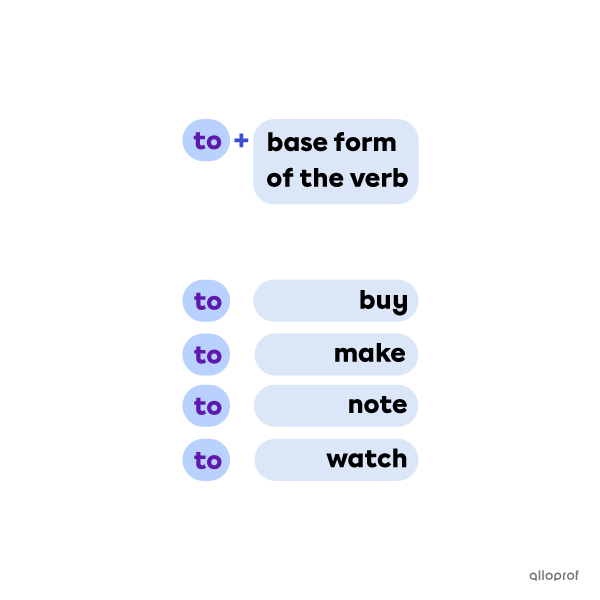
Forming Infinitives
Gerunds and infinitives can be used as:
-
the subject of the sentence
-
the object of the sentence
-
Subject of the sentence
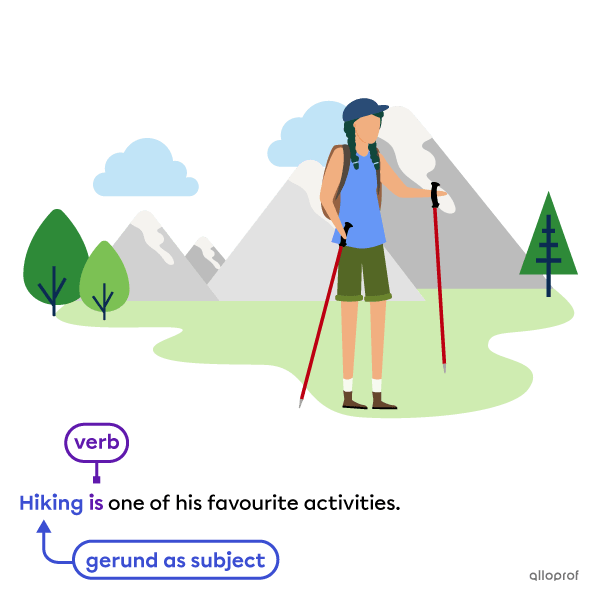
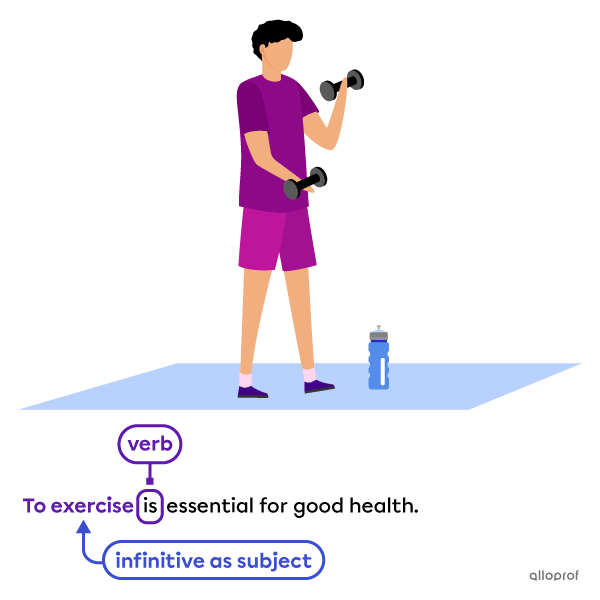
-
Object of the sentence
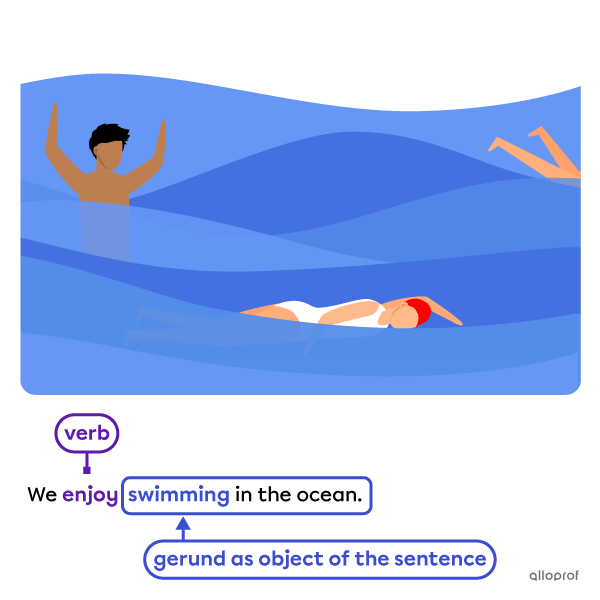
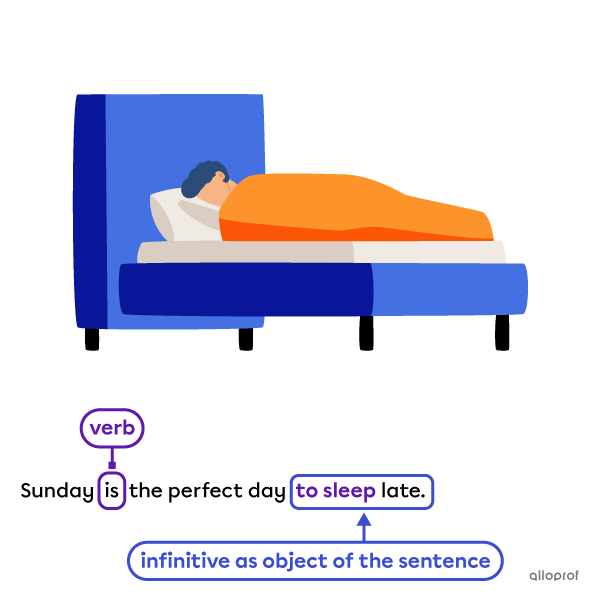
Both gerunds and infinitives can be the object of a sentence.
When the object follows a preposition, a gerund is generally used.
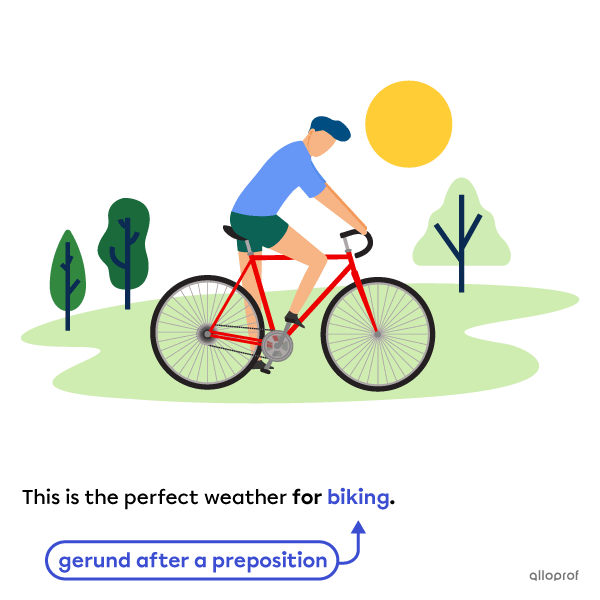
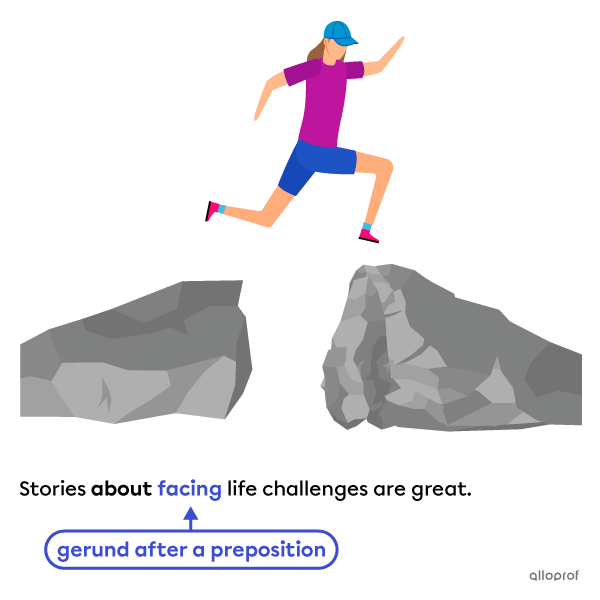
Gerunds are used after prepositions except the prepositions but and except.
For these two prepositions, we use an infinitive after.
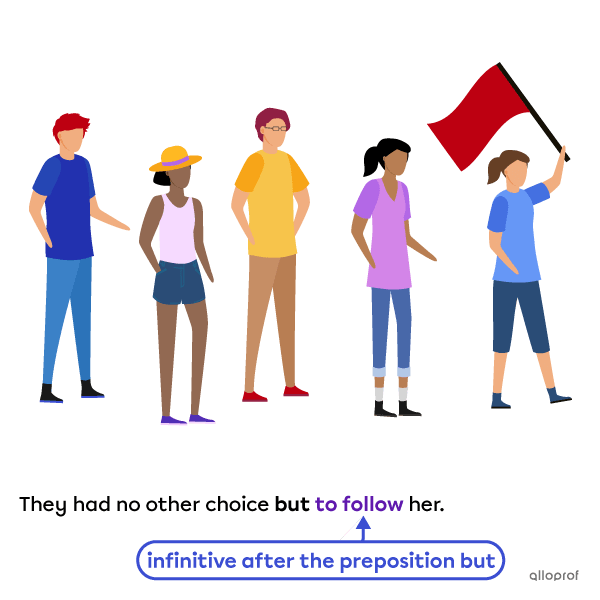
Infinitives can also be used as:
-
Adjectives
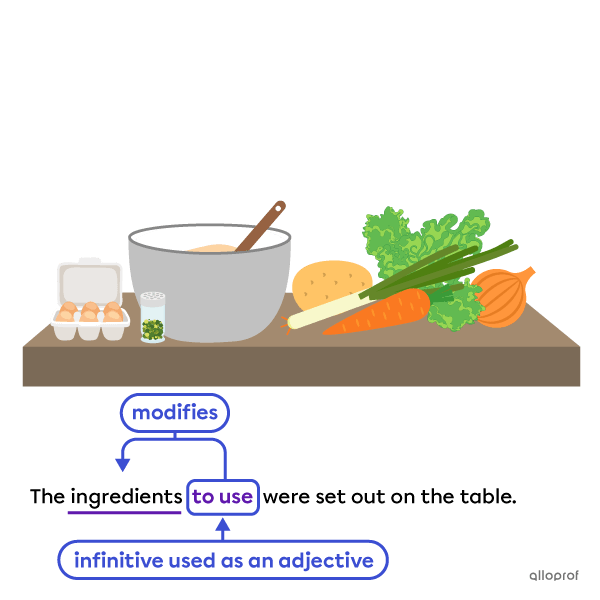
The infinitive to use modifies the noun ingredients, acting as an adjective.
-
Adverbs
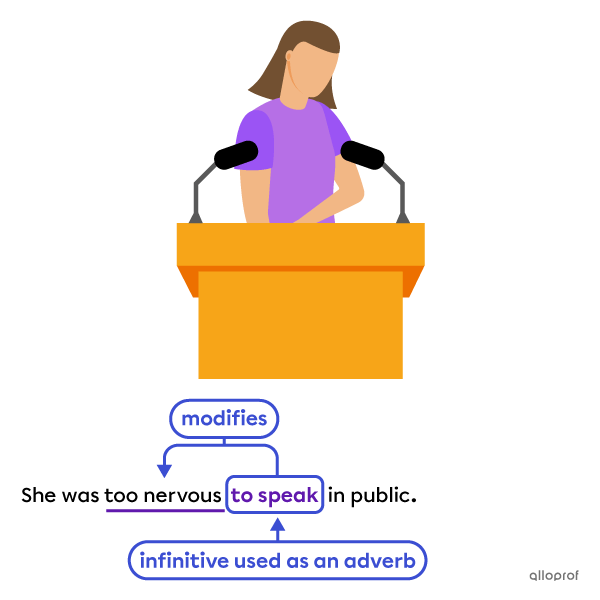
The infinitive to speak modifies the adjective nervous, acting as an adverb.
In most cases, gerunds and infinitives can be interchanged since the meaning is similar.
|
Gerund in a sentence |
Infinitive in a sentence |
|
He started collecting scissors. |
He started to collect scissors. |
Follow these guidelines as a general rule when deciding to use a gerund or an infinitive:
-
Use a gerund when discussing something specific, real or that has already happened.
-
Use infinitives when discussing something abstract, not real or that only might happen.
Something specific, real or that has already happened
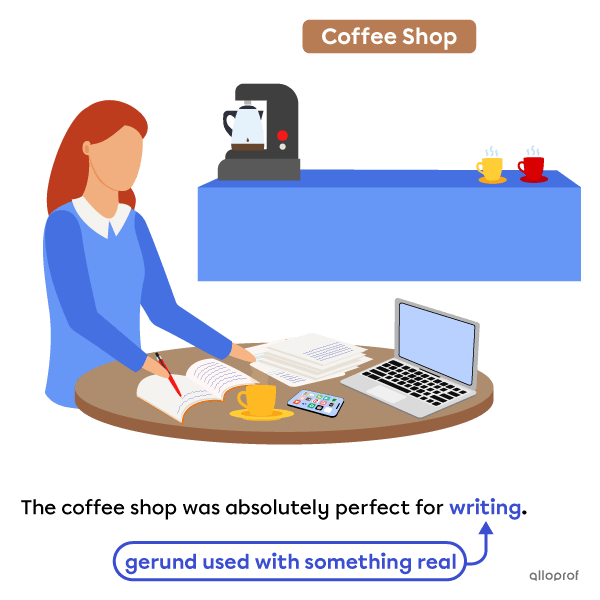
The coffee shop is real and offers a specific place to write.
Something abstract, not real or that only might happen

The location is abstract and the proposal only might happen.
Some verbs should be followed by gerunds, and other verbs by infinitives.
Examples of Verbs That Should Be Followed by a Gerund:
|
Main verb |
Example with a gerund in a sentence |
|
admit |
They admitted committing the crime. |
|
advise |
He advised returning to the entrance gate. |
|
avoid |
You should avoid transmitting private information to random people online. |
|
consider |
They considered moving away, but they decided to stay. |
|
deny |
I deny knowing anything about this situation. |
|
involve |
The project involved developing three new apps. |
|
mention |
You mentioned meeting my father earlier for a job interview. |
|
recommend |
Teachers recommend using gerunds and infinitives. |
|
risk |
“Don’t risk injuring yourself!” |
|
suggest |
They suggest exploring the area. |
Examples of Verbs That Should Be Followed by an Infinitive:
|
Main verb |
Example with an infinitive in a sentence |
|
agree |
I agreed to buy new equipment for my friend. |
|
decide |
I decided to go to the party tonight. |
|
deserve |
Everyone deserves to be respected. |
|
expect |
You should expect to hear from the coach today. |
|
hope |
We were hoping to see progress this week. |
|
learn |
They learned to trust their teammates. |
|
need |
We need to search for a new research subject. |
|
offer |
I offered to pay for the meal. |
|
plan |
They are planning to travel to Norway in June. |
|
promise |
She promised to help me with my science homework. |
|
seem |
It seems to be a problem. |
|
wait |
I can’t wait to participate in the next competition. |
|
want |
We don’t want to make any mistakes. |