To access the other sheets in the Tools in Geography module, consult the See Also section.
-
The legal time is the time determined by the governments of the countries according to the time zone in which we are.
-
The solar time is the time determined by the Sun's position in the sky. Therefore, noon is the moment when the Sun reaches the highest point in the sky (zenith).
In 1880, Greenwich time in London was recognized as the world’s legal time, known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Greenwich Mean Time is the name given to the time zone of the meridian of origin. Today, the term Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) is used instead.
In 1884, at an international conference held in Washington, the Greenwich meridian was adopted as the prime meridian. It was also during this conference that time zones were created. The Greenwich meridian is used as the starting point for time zones.
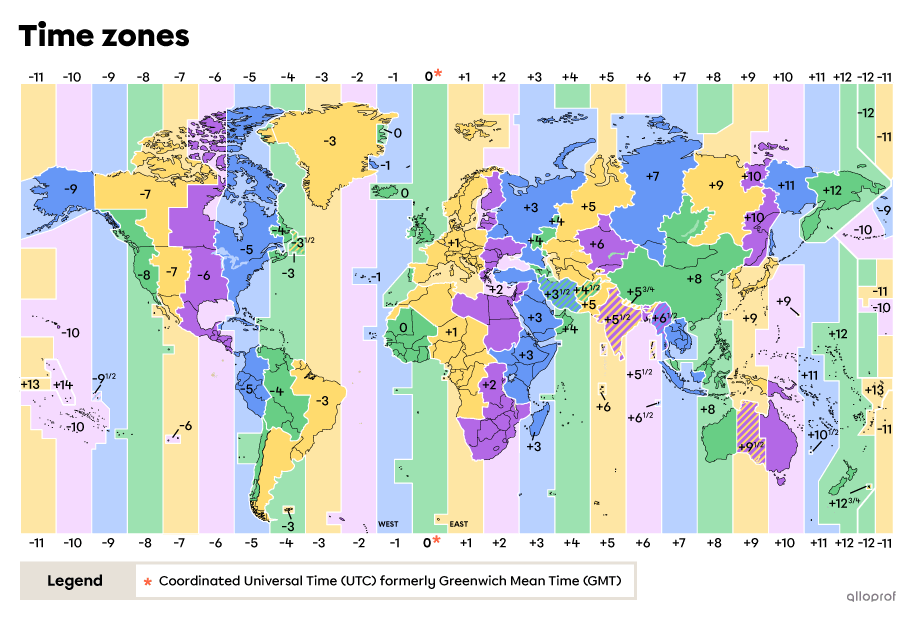
The Earth is divided into 24 different time zones. This number is linked to the fact that there are 24 hours in a day. Indeed, one of the reasons why there are several time zones is to avoid too great a difference between the legal time and solar time. For example, if there were only one world (legal) time, in some places in the world, at noon, it would be dark and at midnight, it would be sunny.
Furthermore, since the Earth is divided into 360 degrees, each time zone has about 15 degrees of longitude. With the Greenwich meridian as the starting point for Coordinated Universal Time, UTC time changes by one hour in each time zone, both east and west of the prime meridian. The offset is expressed in UTC- or UTC+. Time zones west of the 0 meridian move back one hour (UTC-), while time zones east of the 0 meridian move forward one hour (UTC+).
So, when it's 12:00 (noon) in London, UK (UTC), it's...
-
... 9 a.m. (UTC-3) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
-
... 7 a.m. (UTC-5) in Montreal, Canada
-
... 6 a.m. (UTC-6) in Mexico City, Mexico
-
... 4 a.m. (UTC-8) in Los Angeles, USA
-
... 3 p.m. (UTC+3) in Nairobi, Kenya
-
... 8 p.m. (UTC+8) in Shanghai, China
-
... 10 p.m .(UTC+10) in Sydney, Australia
-
... midnight (UTC+12) in Auckland, New Zealand
Source: Adapted from ShustrikS, Shutterstock.com
There are 24 time zones, since there are 24 hours in a day. However, a country's government has the power to decide the time used in its country. Indeed, some governments have added or removed 30 or even 45 minutes from the time zone that crossed their territory. Among others, this is the case in India (UTC+5:30) and Myanmar (UTC+6:30).
Therefore, as can be seen on the map, many time zones do not correspond to the longitudes of 15 degrees. Time zone boundaries are often modified to match certain international borders. Here are a few examples:
- Some countries may decide to ignore one or more time zones, even if part of their territory is technically part of one, in order to uniformize the time used in their country. This is the case for several European countries, such as Finland, Norway and Germany.
- Some countries may also decide to use a different time zone, such as France and Spain, which use UTC+1 instead of UTC.
- Countries larger in area may decide to use a single time zone, like China, while others, like Russia, Canada, Australia and the USA use several time zones to avoid too great a difference between legal time and solar time.
Canada is crossed by six time zones. In total, there is a four-and-a-half-hour difference between the two time zones at the extremes of the country. From east to west, there are the Newfoundland, Atlantic, Eastern (in which most of the province of Quebec is located), Central, Rocky Mountain and Pacific time zones.
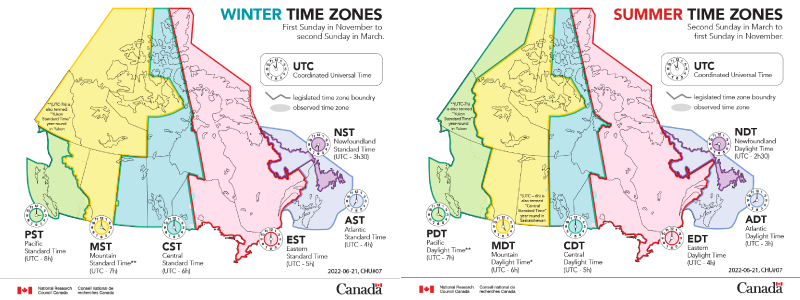
Source: National Research Council Canada, 2022[1].
In Canada, official time is set by the National Research Council of Canada (NRC).
- From the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March, the country follows standard time.
- From the second Sunday in March to the first Sunday in November, the country switches to daylight saving time (summer time), with the exception of Yukon and Saskatchewan.
When this happens, the time zone abbreviations are adjusted.
| Time zone | Standard time | Daylight saving time |
|---|---|---|
| Newfoundland Time | NST | NDT |
| Atlantic Time | AST | ADT |
| Eastern Time | EST | EDT |
| Central Time | CST | CDT |
| Rocky Mountain Hour | MST | MDT |
| Pacific Time | PST | PDT |
To access the rest of the module, consult the Tools in Geography sheet.
1. National Research Council of Canada (2022). Time Zones and Daylight Saving Time. [Map] Government of Canada. https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/canadas-official-time/time-zones-daylight-saving-time