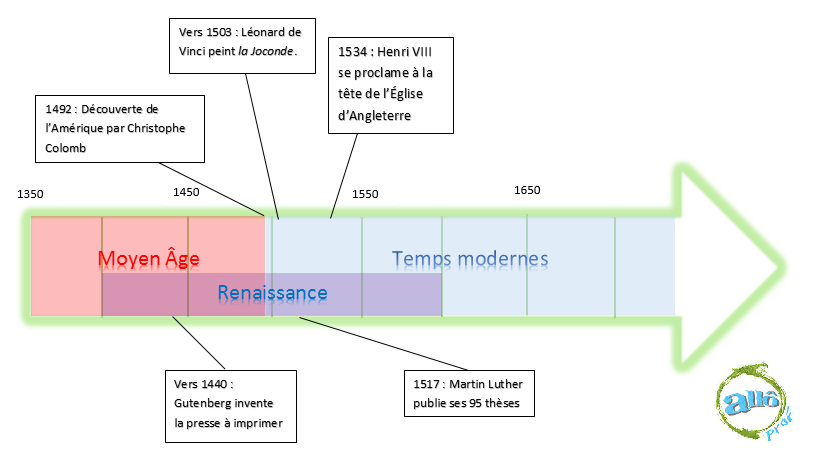
The Renaissance is a moment in history representing the transition between two historical periods: the Middle Ages and Modern Times. The Renaissance is thought to have taken place between 1400 and 1600. It was during this period that man renewed his vision of humanity and began to question the importance of God.
The Renaissance is not a historical period, but most historians consider it to be a period bridging the Middle Ages and Modern Times. This transition was so named because there was a renaissance in the scientific and artistic fields following the darkness left by the Middle Ages. It was during this period that several major works of art appeared, as well as a number of scientific discoveries that would leave their mark on history.
Note: English image coming soon
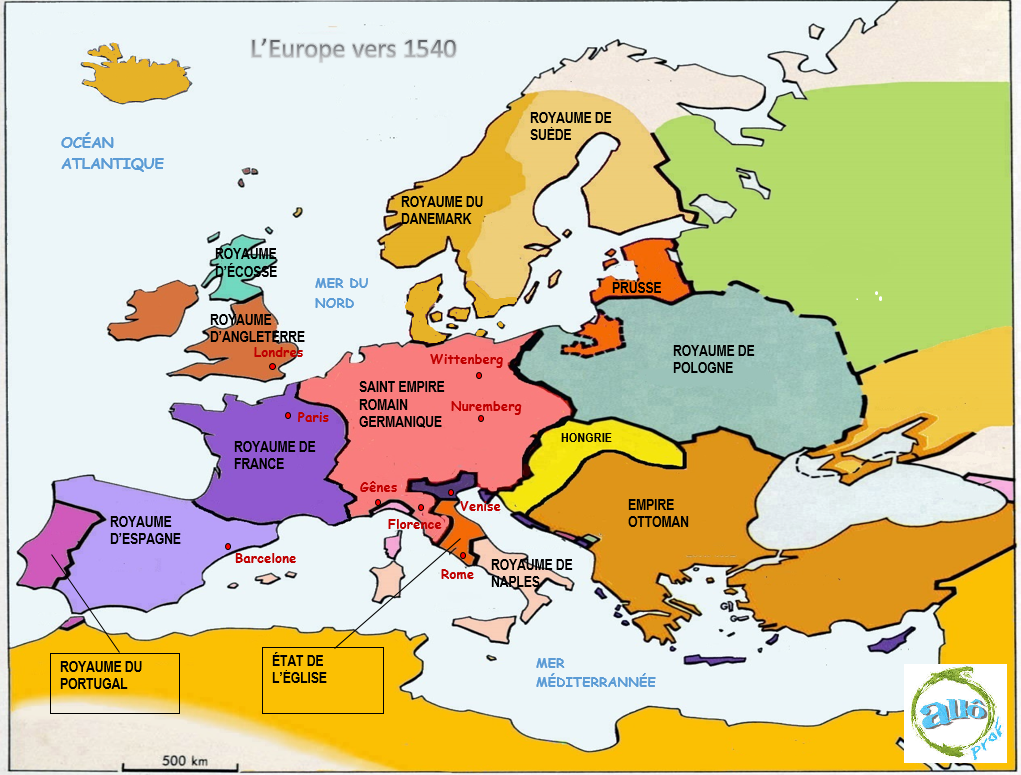
We associate the Renaissance with Europe. In fact, the movement began in Italy. With the years and the means of the time, it spread to the rest of the European continent. At the time, the aim of each kingdom was to expand its territorial holdings. As a result, borders were constantly shifting and Europe was practically always at war. The map below shows that the borders separating the kingdoms in 1540 were very different from those of today. However, if you look closely, you can still see some elements of continuity: the positioning of the kingdoms is very similar to the location of today's countries.
Note: English image coming soon
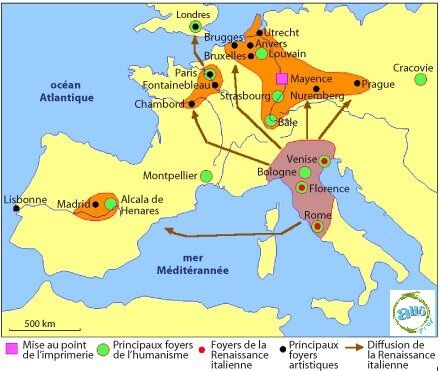
Before making its presence felt across the whole of Europe, the first Renaissance ideas were born in Italy. Subsequently, thanks to various means of dissemination, the ideas of the Italian Renaissance spread throughout Europe. This spread of new ideas took place thanks to the various journeys made by intellectuals of the time and the invention of printing (around 1440), which made it easier to circulate humanist works.
Note: English image coming soon
Education was also an important factor in the sharing of Renaissance ideas. Universities, which had based their teaching on the interpretation of religious texts, now focused on developing students' critical judgement and became centres for the dissemination of humanist thought.