The distance between two parallel lines is the length of the shortest perpendicular line segment that separates them.
The distance between two parallel lines is denoted by the length of the segment, which is perpendicular to and connects them. Depending on the information provided, its length can be determined in three different ways:
-
Given the coordinates of a point on one of the lines and the equation of the other line, the formula for the distance between a point and a straight line can be used to determine the distance.
-
If the coordinates of a point on one of the lines are not known, they can be determined from the equation by choosing a value of |x| and calculating the value of the corresponding |y|. Next, we use the formula for the distance between a point and a straight line to determine the desired distance.
-
If the coordinates of a point on one of the lines are not known, the following formula can also be applied:
||\text{dist}=\dfrac{\mid b_1-b_2\mid}{\sqrt{a^2+1}}||The formula uses the parameters of the equations of the following lines:
|y_1=ax+b_1| and |y_2=ax+b_2.|
What is the distance between the following lines:
|d_1:y=3x-4| and |d_2:y=3x-2|?
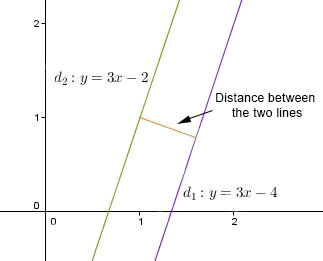
Use the following formula for the distance between two straight lines:||\begin{align}\text{dist}&=\dfrac{\mid b_1-b_2\mid}{\sqrt{a^2+1}}\\[3pt]&=\dfrac{\mid(-4)-(-2)\mid}{\sqrt{3^2+1}}\\[3pt]&=\dfrac{\mid-2\mid}{\sqrt{10}}\\[3pt]&\approx0.63\end{align}||The distance is approximately |0.63| units.
If the coordinates of a point are known, or if they can be determined, use the formula for the distance between a point and a straight line.