Decimal numbers can be compared in order to place them in relation to each other. They can be placed in ascending or descending order. To fully understand the topics covered in this concept sheet, it is important to remember a few concepts about decimal notation.
Ordered decimal numbers can be represented in a number of ways. Here is one such way:
The Number Line
Like natural numbers and integers, ordered decimal numbers can be represented using a number line.
Once positioned on a number line, the further to the right a number is placed, the larger the number is.
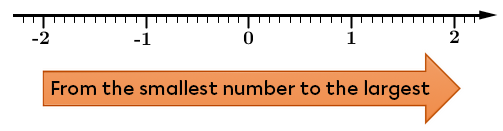
Conversely, the further to the left a number is positioned, the smaller the number.
The difference between the number line used for integers and decimals is that, for decimals, each unit of the line is subdivided into equal parts to position the numbers more accurately.
Each unit of the line above is divided into |10| equal parts. These subdivisions represent the tenths.
The following numbers are represented on a number line.
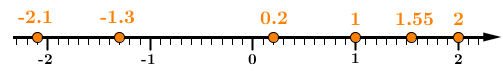
Notice that |-2.1| is the number with the smallest value and is positioned furthest to the left on the number line. On the other hand, the number |2| is the number with the greatest value because it is positioned furthest to the right.
The numbers are listed in ascending order from left to right.||-2.1<-1.3<0.2<1<1.55<2||
Descending order is obtained by listing these numbers from right to left.||2>1.55>1>0.2>-1.3>-2.1||
There are a few different methods used to put decimal numbers in order. Here are two:
This method applies when positive numbers must be placed in order.
To order positive decimal numbers, it is possible to separate them into groups according to the number of digits in their integer part (those to the left of the decimal point). Here are the steps to use this method.
-
Determine if the numbers should be placed in ascending or descending order.
-
Group the numbers to be ordered according to the number of digits in their integer part.
-
Place the numbers of each group in the desired order.
-
Bring the groups together so that the numbers are in the desired order.
The more digits there are in the integer part of a positive decimal number, the larger the number.
In other words, when comparing 2 positive numbers, the one with the most digits in its integer part will be the largest.
Consider the following positive decimal numbers: |3.1562| and |14.2.|
Note that the integer part of |\color{#ec0000}{3}.1562| has only one digit, while the integer part of |\color{#ec0000}{14}.2| has two.
This means that |3.1562\ <\ 14.2.|
When comparing 2 decimal numbers whose decimal parts contain a different number of digits, it can be helpful to add one or more |0|’s to the end of the decimal part. This does not change the value of the number.
||14.2=14.2\color{#ec0000}{0000}||Normally, we avoid using zeros at the end of a decimal number, but they can help when comparing numbers.
If 2 positive numbers have the same number of digits in their integer parts, you can use the following trick to compare them.
To order positive decimal numbers whose integer part has the same number of digits, compare the digits with the same place value from left to right. As soon as a difference is noted, the largest digit belongs to the larger number.
Consider the numbers |16.45| and |16.432,| for example.||\large\bbox[#fa7921]{1}\:\bbox[#ff55c3]{6}\: . \bbox[#efc807]{4}\:\bbox[#51b6c2]{5}\qquad \qquad \bbox[#fa7921]{1}\:\bbox[#ff55c3]{6}\: . \bbox[#efc807]{4}\:\bbox[#51b6c2]{3}\:\bbox[#c58ae1]{2}||
First, compare the digits with the leftmost place value. In this case, it is the tens position. Both numbers have the digit |\bbox[#fa7921]{1},| so move to the digits in the ones position.
Again, both numbers have the same digit, |\bbox[#ff55c3]{6},| in the ones position, and they have the same digit in the tenths position too, |\bbox[#efc807]{4}.|
Moving once more to the right, we finally notice a difference. Since the number |\bbox[#51b6c2]{5}| is greater than the number |\bbox[#51b6c2]{3},| the number |16.4\bbox[#51b6c2]{5}| is greater than the number |16.4\bbox[#51b6c2]{3}2.| This means that:||16.4\bbox[#51b6c2]{3}2\ <\ 16.4\bbox[#51b6c2]{5}||
Place the following numbers in ascending order:
|23.5| |7.25| |102.4| |26.72| |23| |7.523| |100.1|
-
Determine if the numbers should be placed in ascending or descending order.
As mentioned in the problem statement, the numbers must be placed in ascending order, meaning from smallest to largest. -
Group the numbers to be ordered according to the number of digits in their integer part.
Here, there are 3 groups: numbers whose integer part have 1 digit, numbers whose integer part have 2 digits and numbers whose integer part have 3 digits.
|\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#333fb1"]{\color{black}{23.5}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#3a9a38"]{\color{black}{7.25}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#560fa5"]{\color{black}{102.4}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#333fb1"]{\color{black}{26.72}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#333fb1"]{\color{black}{23}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#3a9a38"]{\color{black}{7.523}}| |\enclose{circle}[mathcolor="#560fa5"]{\color{black}{100.1}}|
|\underbrace{\color{3a9a38}{7.523\quad 7.25}}| |\underbrace{\color{#333fb1}{23.5\quad 26.72\quad 23}}||\underbrace{\color{#560fa5}{102.4\quad 100.1}}| -
Place the numbers of each group in the desired order.
Using the trick above, you can place the numbers in each of the three groups in ascending order. To help with this, you can add |\color{#ec0000}{0}|s at the end of the decimal parts.This gives:
|\color{3a9a38}{7.25}\color{#ec0000}{0}\ <\ \color{3a9a38}{7.523}| |\color{#333fb1}{23.}\color{#ec0000}{00}\ <\ \color{#333fb1}{23.5}\color{#ec0000}{0}\ <\ \color{#333fb1}{26.72}| |\color{#560fa5}{100.1}\ <\ \color{#560fa5}{102.4}| -
Bring the groups together so that the numbers are in the desired order.
Since the more digits there are in the integer part of a number, the larger that number is, the following ascending order is obtained:
||\color{3a9a38}{7.25}<\color{3a9a38}{7.523}<\color{#333fb1}{23}<\color{#333fb1}{23.5}<\color{#333fb1}{26.72}<\color{#560fa5}{100.1}<\color{#560fa5}{102.4}||
This method is more versatile than the previous one. It allows you to place both positive and negative decimal numbers in order. Here are the steps to follow.
-
Determine if the numbers should be placed in ascending or descending order.
-
Draw a number line, if one is not already provided.
-
Taking into account the scale, position the numbers to be ordered on the number line.
-
Place the numbers in the desired order, keeping in mind that the further to the right a number is positioned, the larger it is.
Place the following numbers in descending order:
|-0.6| |0.15| |1.5| |-1.9| |-1.3| |1.95|
-
Determine if the numbers should be placed in ascending or descending order.
As mentioned in the problem statement, the numbers must be placed in descending order, meaning from largest to smallest. -
Draw a number line, if one is not already provided.
Below is a number line with increments of |0.1.|
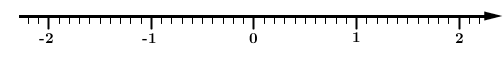
-
Position the numbers to be ordered on the number line.
Taking into account the scale, position the numbers as accurately as possible.
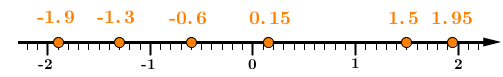
-
Place the numbers in the desired order.
Since the largest numbers are those positioned furthest to the right, the following descending order is obtained:
||1.95>1.5>0.15>-0.6>-1.3>-1.9||