A sequence is a list of elements placed in a specific order.
A sequence is a series of elements in the form of an ordered list. In order for a list to be a sequence, there must be a repeating pattern that explains the order of the elements in the list. There are many sorts of sequences. Some sequences are numerical (involving numbers) and others are non-numerical.
A non-numerical sequence is a list of elements – other than numbers – placed in a specific order.
A non-numerical sequence can be formed using colours, sounds, geometric shapes, or gestures. A sequence is produced when a specific pattern is repeated throughout the whole list.
The following is a sequence of circles in two different colours. There is a repeating colour pattern because two blue circles are followed by two orange circles and so on. Therefore, it is a colour sequence.
All of the designs below are gray. However, the first three shapes are repeated a second time in the same order, making it a sequence of geometric shapes.
What letter will follow the second m in this sequence of letters?
j, f, m, a, m, ...
To find this letter, you must first identify the logic of the sequence. The letters correspond to the first letters of the months of the year: January, February, March, April, May...
The next month to follow is June. The letter we are looking for is therefore j, the first letter of the word.
A numerical sequence is an ordered list of numbers.
Certain vocabulary is important to learn in order to fully understand numerical sequences.
-
The numbers in a sequence are called terms.
-
In a numerical sequence, each term occupies a precise position called rank.
-
A pattern is the mathematical relationship that is repeated between each of the terms of the sequence.
Each of the numbers in a sequence is called a term. Each term is associated with a rank which indicates its position in the sequence.
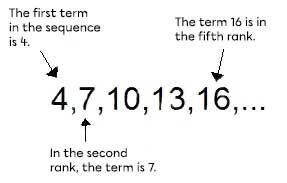
Sequences are very important in mathematics. Instead of studying sequences of words or letters, mathematicians study number sequences. Depending on the pattern that is present, a sequence can be defined as either arithmetic or geometric.
When a pattern is not constant, its numerical sequence is non-arithmetic.
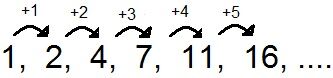
This sequence is non-arithmetic since the pattern between each term of the sequence is not identical.
A pattern is the relationship that exists between terms in a numerical sequence.
A sequence is made from elements whose order depends on a pattern. This pattern can be the addition or subtraction of a number, or the multiplication or division of a term by a number. So, from any given term, the other terms in a sequence can be determined by continuing the pattern with the last term in the sequence.
We make a distinction between the arithmetic sequence and the geometric sequence.
An arithmetic sequence is a number pattern created using an addition or a subtraction of a number.
An arithmetic sequence occurs when a number is added to or subtracted from each term. The process is repeated from one term to another so that the difference between two consecutive terms remains constant.
-
The pattern of this sequence is |-8.|
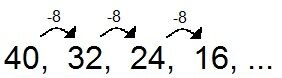
It is possible to find the next term in the sequence: |16 - 8 = 8.|
The next term will be |8.|
-
The pattern of this sequence is |+12.|
It is possible to find the next term in the sequence: |52+12=64.| The next term will be |64.|
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des situations de proportionnalité, des situations inversement proportionnelles et des suites arithmétiques, consulte la MiniRécup suivante.

A geometric sequence is a sequence where the pattern is created using a multiplication or a division.
A geometric sequence is produced when the same number is either multiplied by or divided into each term. The process is repeated from one term to another so that the ratio between two terms remains constant.
-
The pattern of this sequence is |\times 2.|
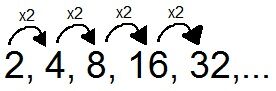
It is possible to find the next term in the sequence: |32 \times 2=64.|
The next term will be |64.|
-
The pattern of this sequence is |\div 3.|
It is possible to determine the next term in the sequence: |6 \div 3=2.|
The next term will be |2.|
There are several ways to represent a numerical sequence. In each one, the relationship between the rank of a term and its value is illustrated. So, a sequence can be described in 5 ways: using a word description, a table of values, an illustration, a graph, or a rule.
To describe a sequence in words, take the first term and identify its relationship to the next term(s) in the sequence.
Sequence: |1, 3, 5, 7, ...|
The first term in the sequence is |1| and the pattern is |+2.|
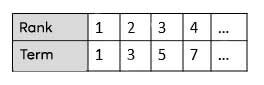
A table of values is used to represent the relationship between two values. In a sequence, the table of values will indicate the rank and the related term.
Sequence: |1, 3, 5, 7, ...|
An illustration can be used for sequences associated with different geometric constructions.
Sequence: |1, 3, 5, 7, ...|
A graph relates pairs of values using points placed in a Cartesian plane. A pair of values can be formed by a term (in |y|) and its rank (in |x|).
Sequence: |1, 3, 5, 7, ...|
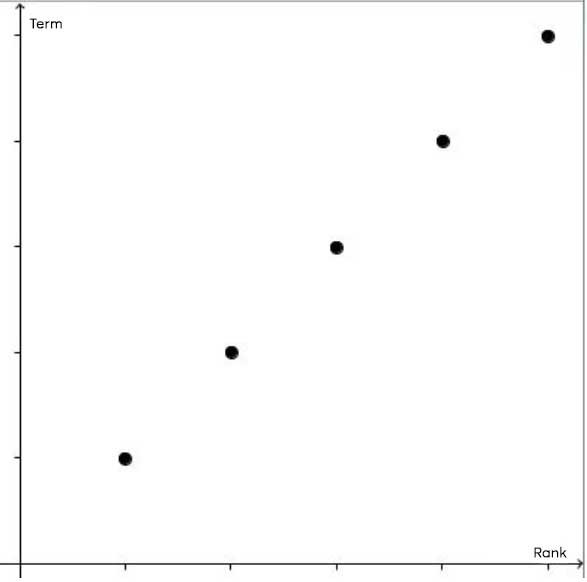
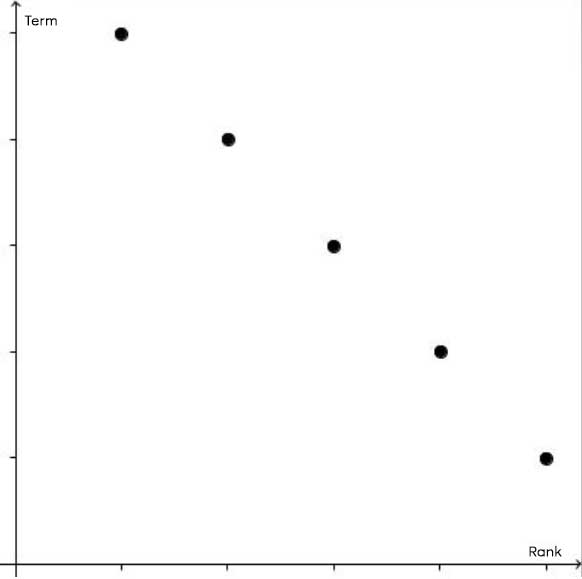
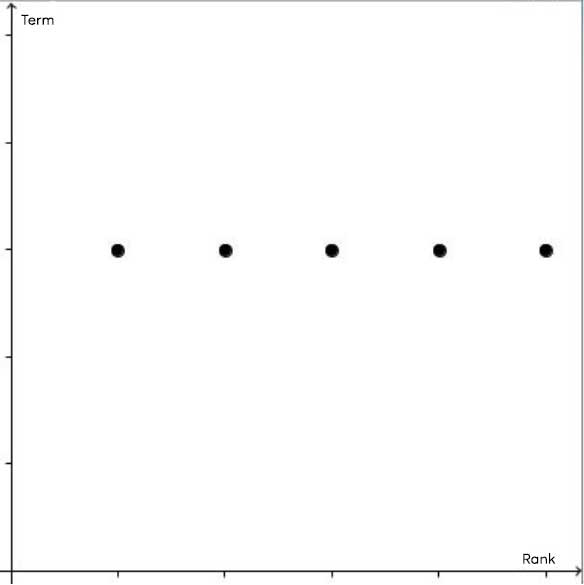
In a graph, an arithmetic sequence is characterized by a sequence of aligned points. There are three forms of alignment.
|
Increasing arithmetic |
Decreasing arithmetic |
Non-arithmetic |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
A rule implies equality between the terms and ranks.
-
|t=2n+5|
-
|y=3x−1|