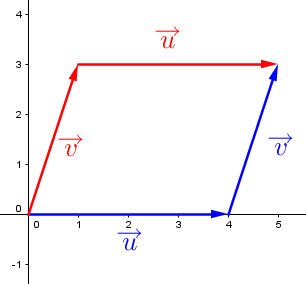
This property can be proven with the following formula. ||\begin{align} \overrightarrow{u} + \overrightarrow{v} &= \overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC} \\
&= \overrightarrow{AD} + \overrightarrow{DC}\\
&=\overrightarrow{v} + \overrightarrow{u}\end{align}||
||\color{Red}{\overrightarrow{u}+(\overrightarrow{v}+\overrightarrow{w}) = (\overrightarrow{u}+\overrightarrow{v})+\overrightarrow{w}}||This property can be proven by using vectors |\overrightarrow{AB}, \overrightarrow{BC}| and |\overrightarrow{CD}| and Chasles' relation. ||\begin{align}(\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC})+\overrightarrow{CD} &= \overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{CD} \\
&= \overrightarrow{AD}\end{align}||A similar calculation can be performed by moving the parentheses.||\begin{align} \overrightarrow{AB} + (\overrightarrow{BC}+\overrightarrow{CD}) &= \overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BD} \\
&= \overrightarrow{AD}\end{align}||Thus, we obtain the associative property.
Additive identity:||\color{Red}{\overrightarrow{u}+\overrightarrow{0}=\overrightarrow{u}}||The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b)| and the components of the |\overrightarrow{0}| vector are |(0,0)|.
Thus: ||\begin{align} \overrightarrow{u} + \overrightarrow{0} &= (a,b)+(0,0)\\
&= (a+0,b+0)\\
&=(a,b) \\
&= \overrightarrow{u}\end{align}||
Multiplicative identity: ||\color{Red}{1\overrightarrow{u}=\overrightarrow{u}}||The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b)|.
Therefore: ||\begin{align}1 \times \overrightarrow{u}&=1 \times (a,b) \\
&= (1a,1b) \\
&=(a,b) \\
&= \overrightarrow{u}\end{align}||
||\color{Red}{\overrightarrow{u}+(-\overrightarrow{u})=\overrightarrow{0}}||
The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b)| and the components of the vector |-\overrightarrow{u}| are |(-a,-b)|.
Then: ||\begin{align}\overrightarrow{u} + (-\overrightarrow{u})&=(a,b)+(-a,-b) \\
&= (a-a,b-b) \\
&= (0,0) \\
&= \overrightarrow{0}\end{align}||
||\color{Red}{k(c\overrightarrow{u})=(kc)\overrightarrow{u}}||
The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b)|.
So: ||\begin{align}k(c \overrightarrow{u}) &= k(c(a,b))\\
&=k(ca,cb)\\
&=(kca,kcb)\\
&=(kc)(a,b) \\
&= (kc)\overrightarrow{u}\end{align}||
||\color{Red}{k(\overrightarrow{u}+\overrightarrow{v})=k\overrightarrow{u}+k\overrightarrow{v}}||
The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b)| and the components of the vector |\overrightarrow{v}| are |(c,d).|
Then:||\begin{align}k(\overrightarrow{u}+\overrightarrow{v}) &= k((a,b)+(c,d)) \\
&= k(a+c,b+d) \\
&= (k(a+c),k(b+d))\\
&=(ka+kc,kb+kd) \\
&= (ka,kb)+(kc,kd)\\
&=k\overrightarrow{u}+k\overrightarrow{v}\end{align}||
||\color{Red}{(k+c)\overrightarrow{u}=k\overrightarrow{u}+c\overrightarrow{u}}||
The components of the vector |\overrightarrow{u}| are |(a,b).|
Thus:||\begin{align} (k+c)\overrightarrow{u} &=(k+c)(a,b) \\
&=((k+c)a,(k+c)b) \\
&= (ka+ca,kb+cb) \\
&= (ka,kb)+(ca+cb)\\
&=k(a,b)+c(a,b) \\
&= k\overrightarrow{u}+c\overrightarrow{u}\end{align}||
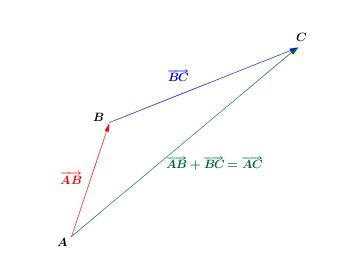
In this relation, |A|, |B|, and |C| represent points in the Cartesian plane.||\color{Red}{\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}=\overrightarrow{AC}}||
||\color{Red}{ \overrightarrow{u} \cdot (\overrightarrow{v} + \overrightarrow{w}) = \overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{v} + \overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{w}}||
Let |\overrightarrow{u}=(a,b)|, |\overrightarrow{v}=(c,d)| et |\overrightarrow{w}=(e,f)|.
Then:
||\begin{align}\overrightarrow{u} \cdot (\overrightarrow{v} + \overrightarrow{w}) &= (a,b) \cdot ((c,d)+(e,f))\\
&= (a,b) \cdot (c+e,d+f) \\
&=(a(c+e)+b(d+f))\\
&=(ac+ae+bd+bf)\\
&=(ac+bd)+(ae+bf) \\
&= (a,b) \cdot (c,d) + (a,b) \cdot (e,f)\\
&= \overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{v} + \overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{w}\end{align}||
Let |\overrightarrow{u}=(a,b)|, |\overrightarrow{v}=(c,d)| be vectors, and |k_1| and |k_2|, scalars.||\color{Red}{k_1 \overrightarrow{u} \cdot k_2 \overrightarrow{v}=(k_1k_2)\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{v}}||
||\begin{align}k_1 \overrightarrow{u} \cdot k_2 \overrightarrow{v} &= k_1(a,b) \cdot k_2(c,d)\\
&= (k_1a,k_1b) \cdot(k_2c,k_2d)\\
&= k_1k_2ac+k_1k_2bd\\
&=(k_1k_2)(ac+bd)\\
&= (k_1k_2)(a,b) \cdot (c,d)\\
&=(k_1k_2)\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{v}\end{align}||
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des vecteurs de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :
