There are many important new terms to master in order to understand the concept of a vector in mathematics.
A vector (also called a geometric vector), usually denoted |\overrightarrow{u},| is a mathematical object which possesses both a magnitude (norm) and a direction (orientation).
However, this is not the only way to identify a vector.
If |A| represents the origin (starting point) of a vector and |B| represents its extremity (end point), the notation |\overrightarrow{AB}| can be used to refer to it.
As its symbol indicates, a vector is actually a line segment with a starting point and an arrow to indicate its end point and direction.

A scalar quantity, generally called a scalar, is a quantity defined by a real number.
In other words, it is a coefficient which is applied to a vector and its components.
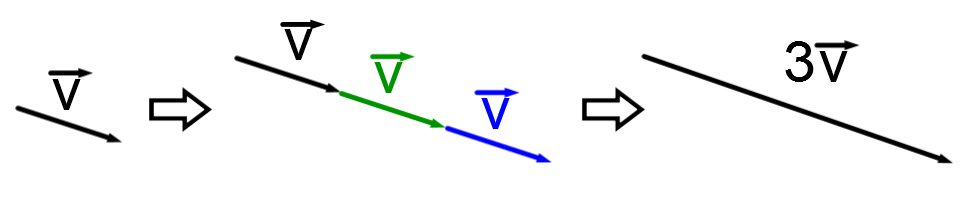
Here, the value of the scalar is |3.|
A vector quantity is defined by a number and a direction.
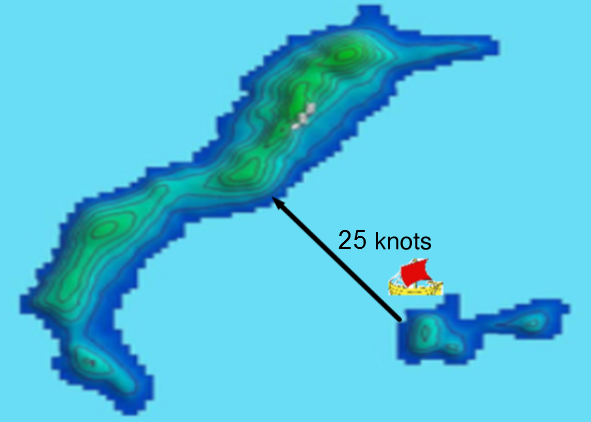
A vector quantity can be summarized using vectors found in everyday life.
A cruise ship stops to visit several small islands. The captain must hold a course of north-west at a speed of 25 knots to get to the second island on schedule.
The orientation of a vector refers to its direction (vector arrow that illustrates the vector).
Let’s compare the following vectors:
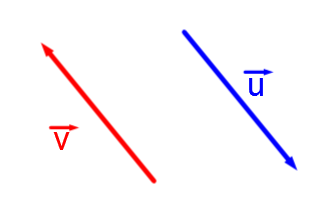
According to the inclination of the lines depicting each vector, we see that vector |\color{red}{\overrightarrow{v}}| is parallel to vector |\color{blue}{\overrightarrow{u}}.|
However, their orientations are opposite since the arrows point in opposite directions.
Identifying a vector using its starting point and end point makes it easy to recognize parallel vectors that have opposite directions.
|\overrightarrow{AB}| starts at point |A| and ends at point |B,| while |\overrightarrow {BA}| starts at point |B| and ends at point |A.|
The magnitude of a vector, also called the norm, is a real number that defines the size of a vector. It is denoted by |\mid\mid\overrightarrow{v}\mid\mid.|
A vector with a magnitude of |1| is called a unit vector.
A vector with a magnitude of |0| is called a null vector (zero vector) and is denoted as |\overrightarrow{0}.|
In terms of analytic geometry, it is the distance from the starting point of the vector to its end point.
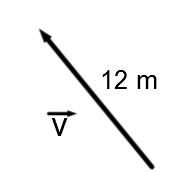
So, |\mid\mid\overrightarrow{v}\mid\mid=12\text{m}.|
Vectors are not only found in mathematics.
Vectors are also used in Physics. However, the approach and concepts are slightly different.
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des vecteurs de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :
