A variable is a letter that can be assigned different values.
In algebra, calculations are often generalized by replacing numbers with letters. These letters are called variables. A variable can be denoted by any letter of the alphabet.
||\begin{gather}a^2\\4b^4-3c\\ y+z\end{gather}||
In the preceding algebraic expressions, the letters |a,b,c,y,| and |z| are variables.
A quantitative variable is a variable that can be expressed by a number, or a quantity.
-
The number of legs of a grasshopper;
-
a person's age rounded off to the year;
-
the body mass;
-
the number of women who voted in the last election;
-
the time it takes to complete a road trip.
Quantitative variables can be divided into two subcategories: continuous variables and discrete variables.
A continuous variable is one whose value can be all the possible real numbers in an interval.
In the list of examples above, there are two continuous variables:
-
the body mass can involve each division of kilograms and grams;
-
a road trip is not counted only in hours. It also involves minutes and seconds.
Dans la liste précédente, on retrouve 3 variables discrètes.
-
L’âge exacte d'une personne (si on n'arrondit pas à l'année)
-
La masse corporelle
-
Le temps pris pour effectuer un trajet en voiture
A discrete variable is one whose value can only be some of the real numbers in an interval. Usually, the only admissible values are whole numbers.
In the list of examples above, there are three discrete variables:
-
the number of legs on a grasshopper can only involve whole numbers as a value;
-
a person’s age rounded off to the year can only involve whole numbers as a value;
-
the number of women who voted in the last election can only involve whole numbers as a value.
A qualitative variable is a value that does not represent a quantity.
Instead of quantifying a quantity as in the case of a quantitative variable, a qualitative variable involves a characteristic, or an attribute.
-
The eye colour;
-
the civil status;
-
a person’s gender.
-
An independent variable is the parameter in a problem that varies without being influenced by the other parameters of the problem. In general, the independent variable is denoted by the letter |"x".|
-
A dependent variable is a parameter in a problem that varies under the influence of the independent variable. In general, the dependent variable is denoted by the letter |"y".|
The link between a dependent variable and an independent variable is called a relationship. The relationship can be illustrated in various ways. For example, in a Cartesian plane, the independent variable is associated with the |x|-axis while the dependent variable is associated with the |y|-axis.
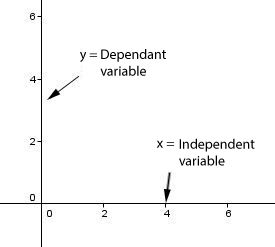
The relationship between dependent and independent variables can also be represented by forming an algebraic function. Since several types of relationships exist, there are many different types of functions.
To confirm you understand of functions, including dependent and independent variables, see the following interactive CrashLesson:
