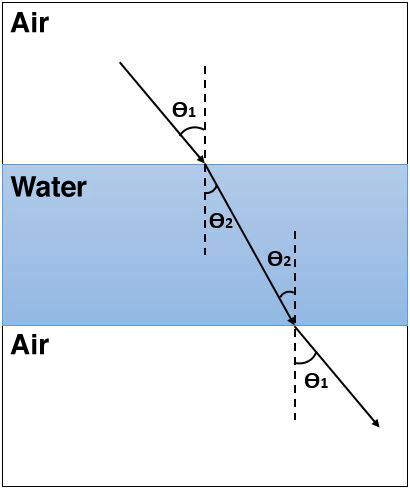
Refraction is the phenomenon of light in which light deviates from its rectilinear path, changing its speed when it passes from one transparent medium to another.
If a sprinter is running in a gym, his speed is very high. However, if he had to do the same run in water, his speed would necessarily be slower, because the water would slow down his movement. Light acts similarly: when it changes medium, it decreases its speed and deviates from its trajectory.
The image below illustrates the phenomenon accurately.
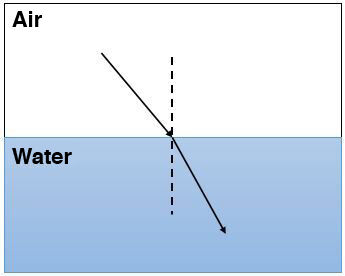
This deviation is due to the change in the velocity of light, as the velocity of light varies from one transparent medium to another. These transparent media are said to have different indices of refraction.
The index of refraction is a value that measures the ability of a substance to slow or deviate a ray of light.
To determine a index of refraction, the transparent substance must be compared to a reference medium. The vacuum was chosen as the reference medium, since it is the medium where light travels the fastest. It was determined that the absolute refractive index of the vacuum would be 1. This velocity is compared to the velocity in the second medium to find the index of refraction.
The equation for determining the index of refraction of a given medium is:
|n= \displaystyle \frac{c}{v}|
where
|n| is the index of refraction,
|c| is the speed of light in a vacuum |(c = 3.00 \times 10^{8} \text { m/s})|,
|v| is the speed of light in the given medium.
The index of refraction has no unit of measurement: it represents a factor indicating the slowing down of light in the medium compared to that of a vacuum.
What is the index of refraction of glycerin, if that the speed of light in this medium is |2.04 \times 10^{8} \text {m/s}?|
Using the formula, the index of refraction can be calculated as follows:
||\begin{align} n=\dfrac{c}{v} \quad \Rightarrow \quad n &=
\dfrac{3.00 \times 10^{8}\: \text {m/s}}{2.04 \times 10^{8}\: \text {m/s}} \\ \\
&=1.47 \end{align}||
The index of refraction of glycerin is therefore |1.47,| which means that the light travels |1.47| times slower in glycerin than in a vacuum.
Here are the indices of refraction of some mediums.
Indices of Refraction and the Speed of Light in Different Mediums
|
Media |
Index of Refraction |
Speed of light |
|---|---|---|
|
Ice |
|1.31| |
|2.29 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Water |
|1.33| |
|2.25 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Ethanol |
|1.36| |
|2.20 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Glycerin |
|1.47| |
|2.04 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Mineral oil |
|1.48| |
|2.02 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Pyrex |
|1.48| |
|2.02 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Crown glass |
|1.52| |
|1.97 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Light flint glass |
|1.58| |
|1.90 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Flint glass |
|1.63| |
|1.84 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Heavy flint glass |
|1.66| |
|1.81 \times 10^{8}| |
|
Diamond |
|2.42| |
|1.24 \times 10^{8}| |
The faster light travels through a medium, the smaller the index of refraction of that medium. Therefore, light travels faster through ice than through a diamond.
When light passes through different media, the deviation is greater if the difference between the indices of refraction is large. As shown in the diagram below, the light deflection is greater between air and crown glass than between crown glass and water.
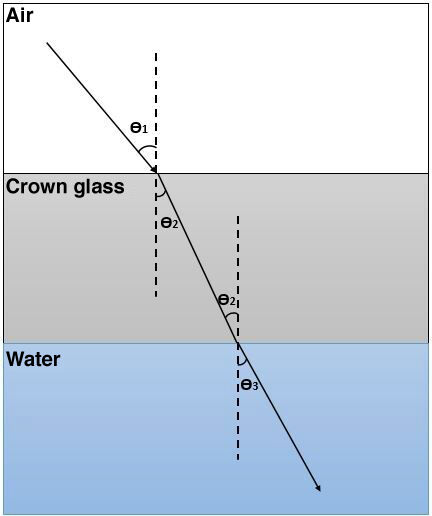
Furthermore, it can be seen that when light passes from a less refractive medium (having a smaller index of refraction) to a more refractive medium (having a greater index of refraction), the refracted ray moves towards the normal, like when light passes from air to crown glass in the image above.
Similarly, when light moves from a more refractive medium to a less refractive medium, the refracted ray moves away from normal, as when light passes from crown glass to water in the image above.
If the indices of refraction of two media are similar, the light acts as if it were passing through only one medium.
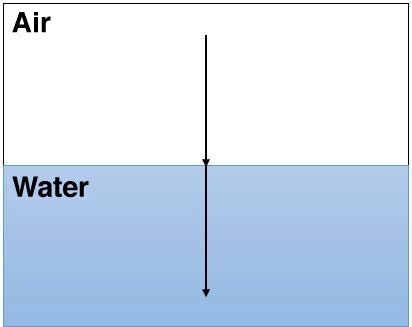
A ray which travels towards a transparent medium perpendicular to the surface of the medium will not be deflected. It will travel through the second medium without changing its angle. However, the speed of light still decreases although no deviation has been observed.
A ray which passes from a first medium into a second medium with a different refractive index will deviate from its trajectory. However, if this ray leaves the second medium to return to the initial medium, it will resume the same angle as the one it had at the beginning, provided that the surfaces separating the mediums are parallel.