The cell is the basic unit of all living organisms. In this concept sheet, we distinguish two types of cells: animal cells and plant cells.
These types of cells have many similarities. However, due to their different functions, they also have some differences in their composition. Although animal and plant cells have common components and organelles, some are specific to one type of cell.
Organelles are the components of the cell that are immersed in cytoplasm.
There are several types of animal cells. These cells are given different names depending on the function they perform in the body. Here are some examples of animal cells.
-
White blood cells
-
Red blood cells
-
Muscle cells
-
Epithelial cells
Each of these cells has its own characteristics in terms of structure and function.
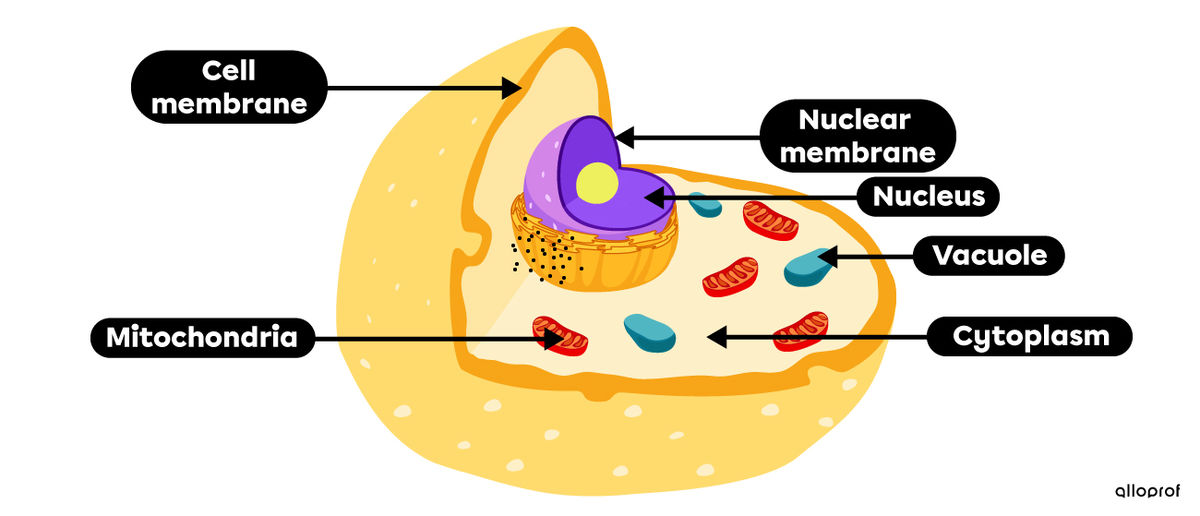
|
Component |
Description and role of the component |
|---|---|
|
Nucleus |
|
|
Nuclear membrane |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Vacuole |
|
|
Mitochondria |
|
|
Cell membrane |
|
The plant cell is the basis of all plant organisms. It differs from the animal cell by 3 characteristics.
-
It has a cellulose wall (cell wall), a rigid outer membrane made of cellulose.
-
It has a single large vacuole used to store substances and allow cell growth by storing water in it through osmosis.
-
It has chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll, a pigment that gives plants their green colour and helps in the photosynthesis process.

|
Components |
Description and role of component |
|---|---|
|
Nucleus |
|
|
Nuclear membrane |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Vacuole |
|
|
Mitochondria |
|
|
Chloroplast |
|
|
Cell membrane |
|
|
Cell wall |
|
|
Component |
Animal cell |
Plant cell |
|---|---|---|
|
Nucleus |
X |
X |
|
Nuclear membrane |
X |
X |
|
Cytoplasm |
X |
X |
|
Vacuole |
X |
X |
|
Mitochondria |
X |
X |
|
Chloroplast |
|
X |
|
Cell membrane |
X |
X |
|
Cell wall |
|
X |
To validate your understanding of the cell in an interactive way, consult the following MiniRecup:

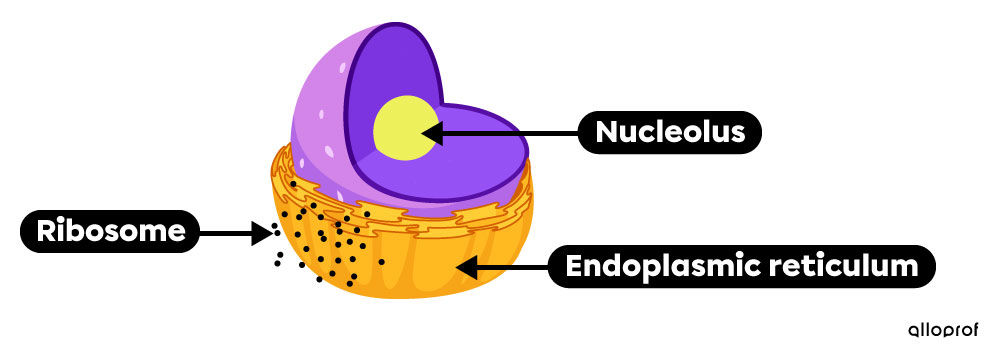
The nucleolus is located at the centre of the nucleus of animal and plant cells. This is where the transcription of DNA into RNA takes place during cell division.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a labyrinth of sacs and tubes connected to the nuclear membrane. It is found in both animal and plant cells. It is responsible for several metabolic functions such as lipid synthesis, detoxification, and storage of certain substances. Two types of reticulum can be distinguished: the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which carries ribosomes on its membrane, and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, which has none.
Ribosomes are the organelles that produce proteins. They either lie on the rough endoplasmic reticulum or move freely in the cytoplasm. They are found in both animal and plant cells.