This concept sheet explains the procedures to follow to determine whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral in nature.
There are four ways to determine the nature of a substance.
If the solution is in solid form, it must be dissolved in a small quantity of distilled water (pure water) before testing.
Litmus paper is soaked in litmus dye or lichen powder extract. It is used as a coloured indicator to determine the acidic, basic, or neutral nature of a solution. However, it does not give a precise pH value.

-
Solution to be identified
-
Beaker, test tube, or any suitable container
-
Tweezers
-
Red litmus paper strips
-
Blue litmus paper strips
-
Watch glass
-
Apron or smock
-
Safety glasses

-
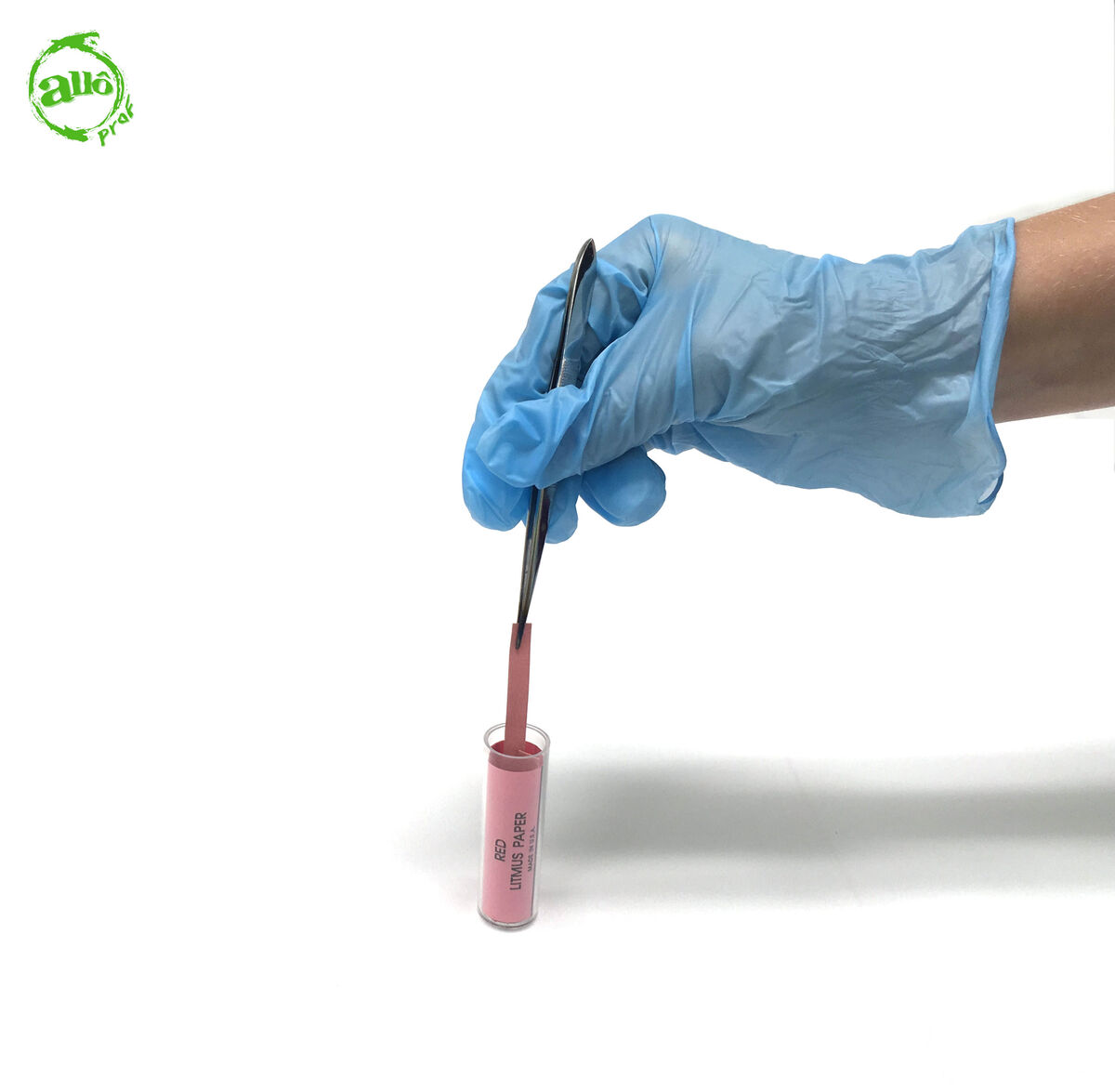
Take a strip of litmus paper with tweezers.

-
Dip the free end of the litmus paper into the unknown liquid.
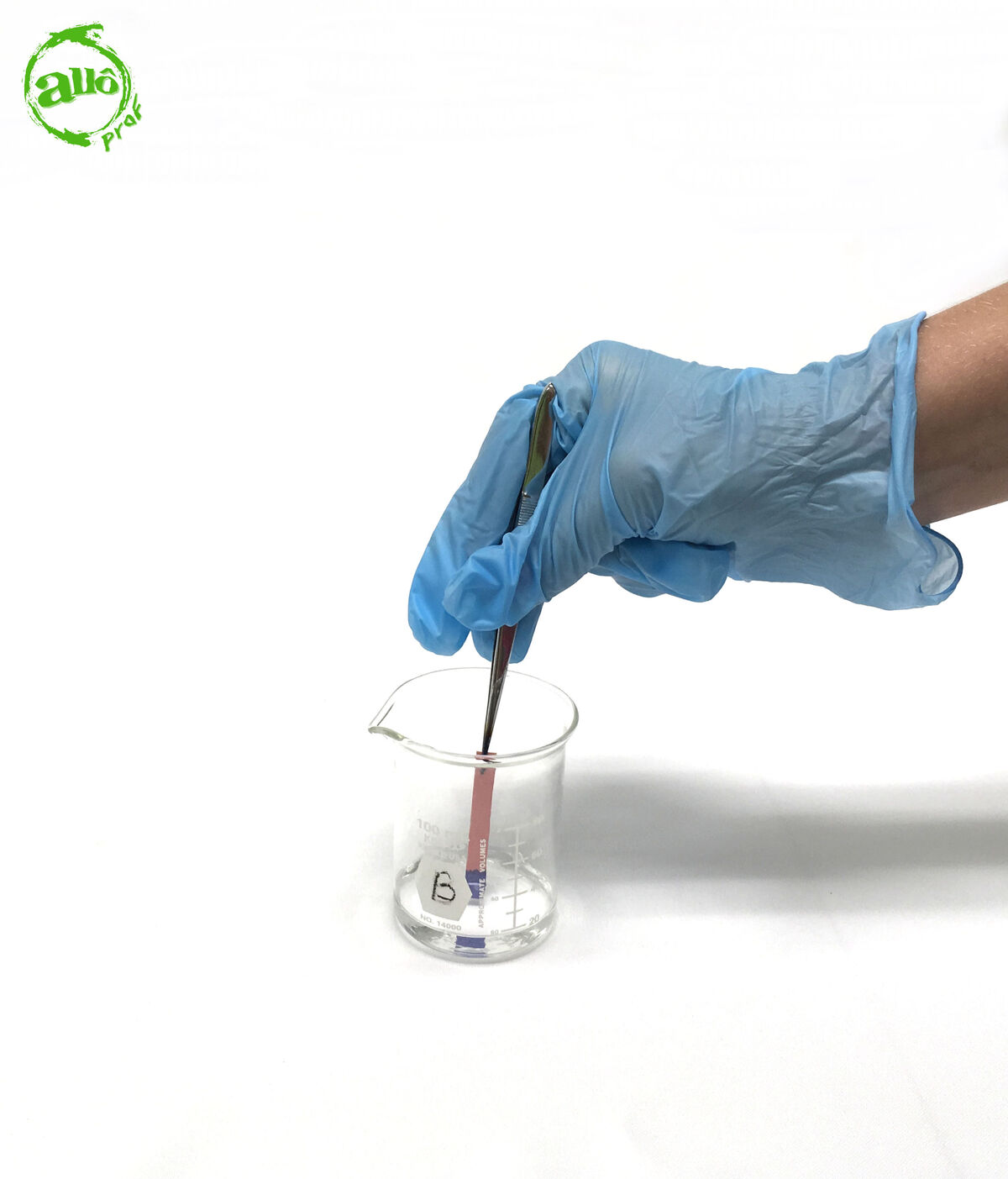

It is not useful to completely soak litmus paper in the liquid. Since the paper is held by the tweezers, they could become contaminated if soaked in the liquid. Should the tweezers come into contact with liquid, they must be washed before reuse.
Also, do not use your hands to dip the litmus paper in the liquid. Since the nature of a substance is unknown, dipping fingers in certain liquids can be dangerous (it might be a liquid that is harmful to human skin). It is, therefore, preferable to work with tweezers at all times.
-
Observe the colour of the litmus paper.

-
Discard used litmus papers and clean the equipment.
In some settings, to avoid cross-contamination, it is preferable to use a dropper to perform the litmus paper test. Simply take a few drops of the unknown solution, and place them on a strip of litmus paper placed in a watch glass.
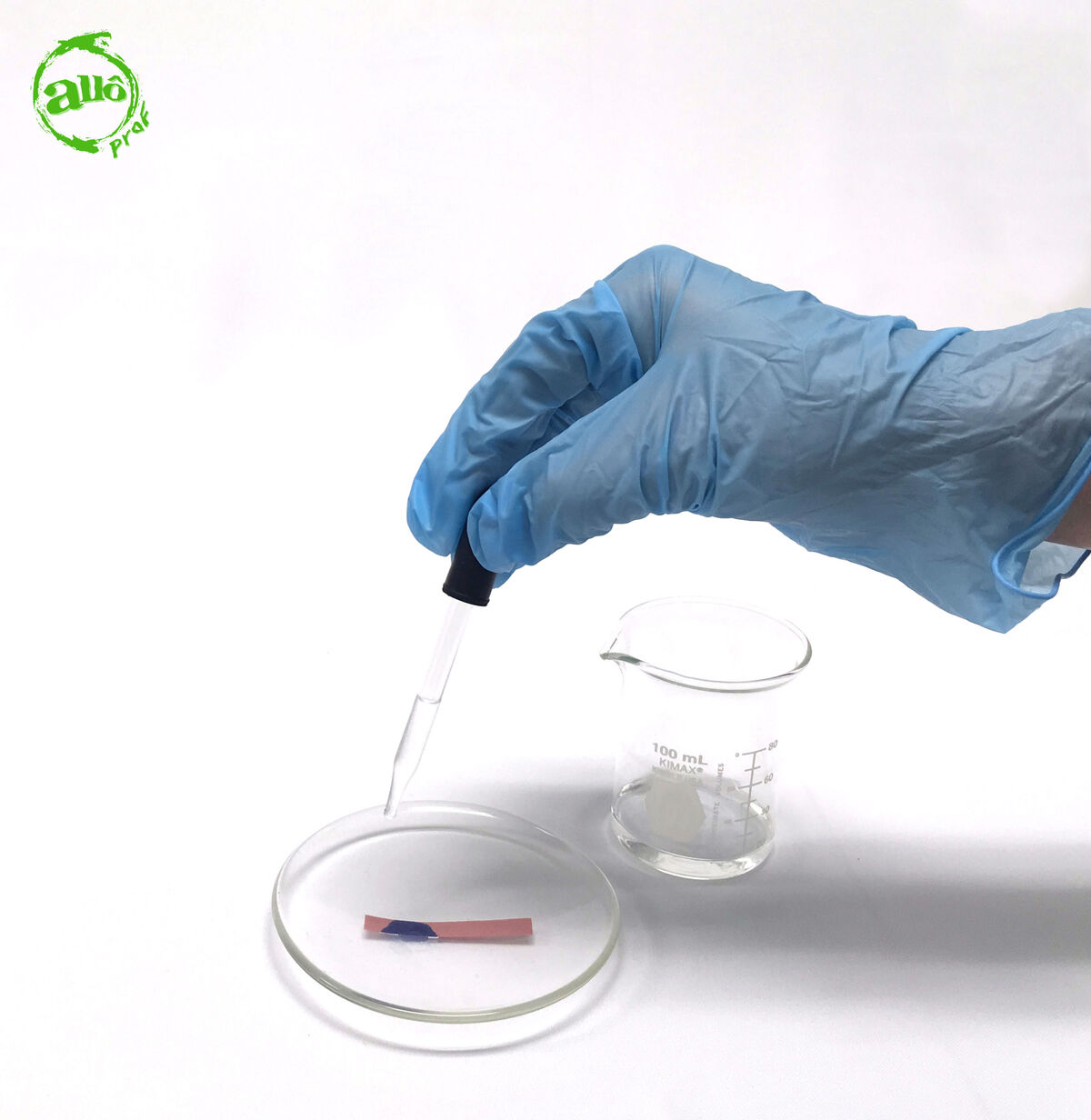

Depending on the colour of litmus paper initially used, different results may be achieved.
-
If the red litmus paper turns blue and the blue litmus paper retains its blue colouring, the solution is basic.
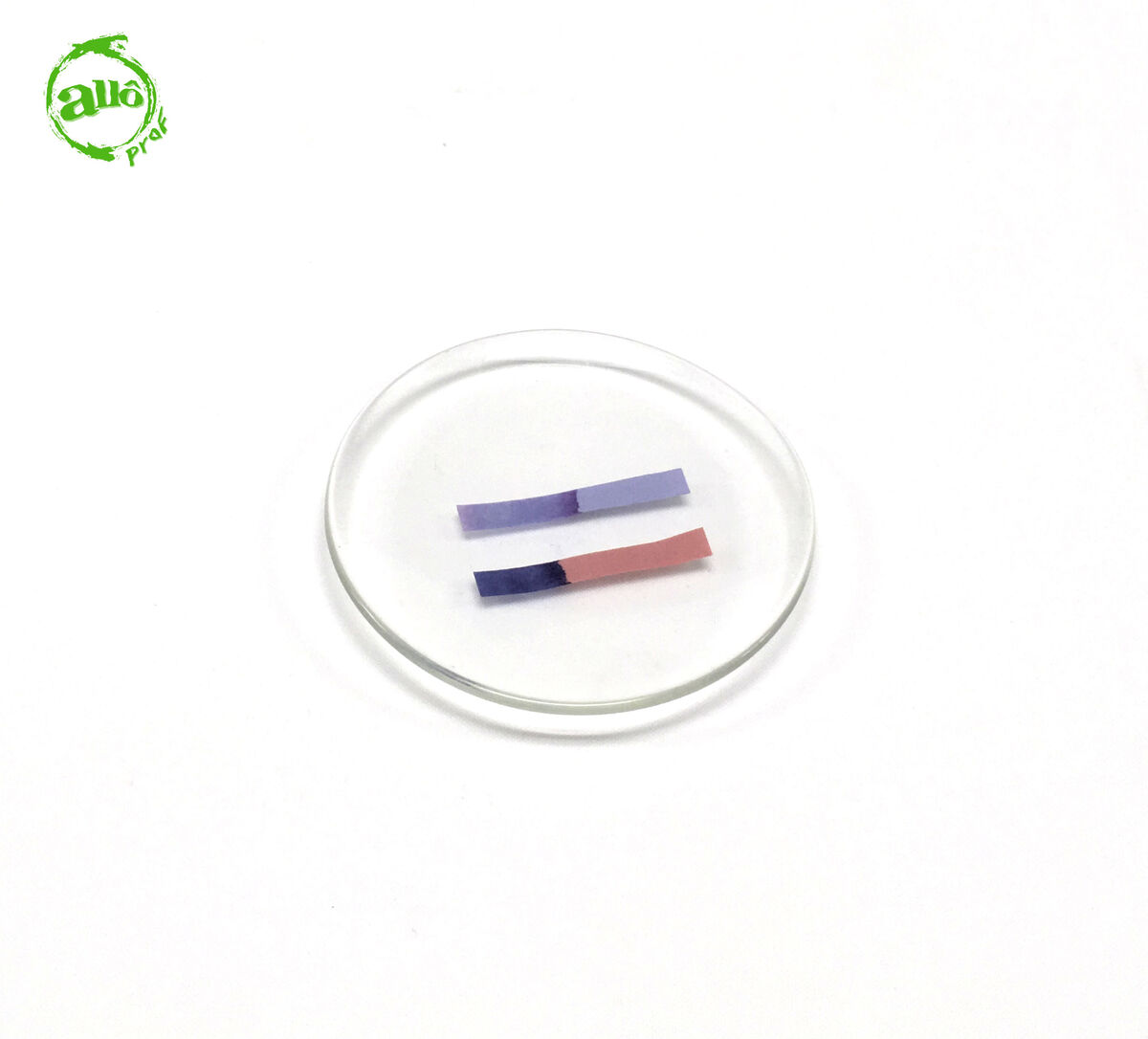
-
If the blue litmus paper turns red and the red litmus paper retains its red colouring, the solution is acidic.
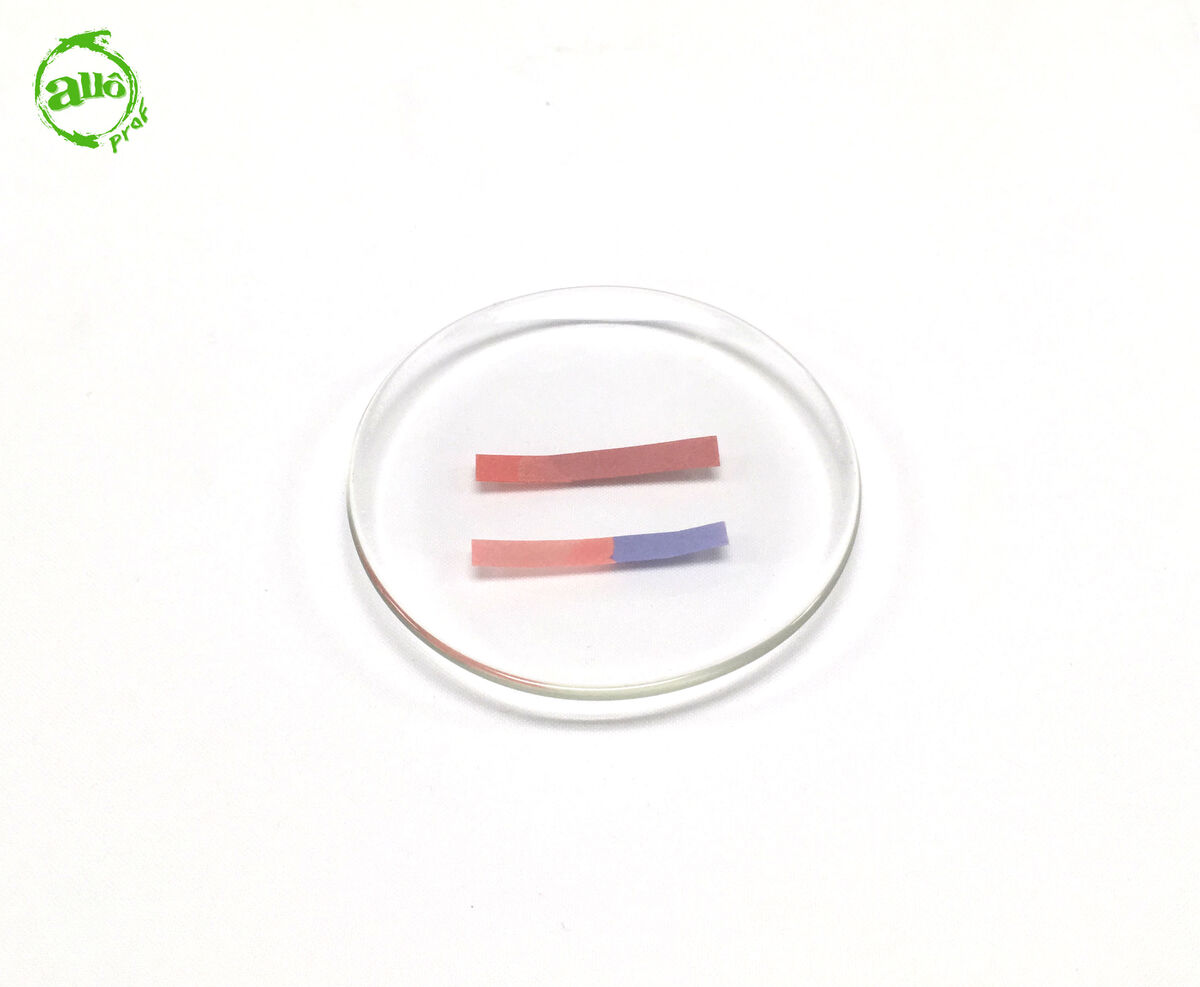
-
If the red litmus paper retains its red colouring and the blue litmus paper retains its blue colouring, the solution is neutral.
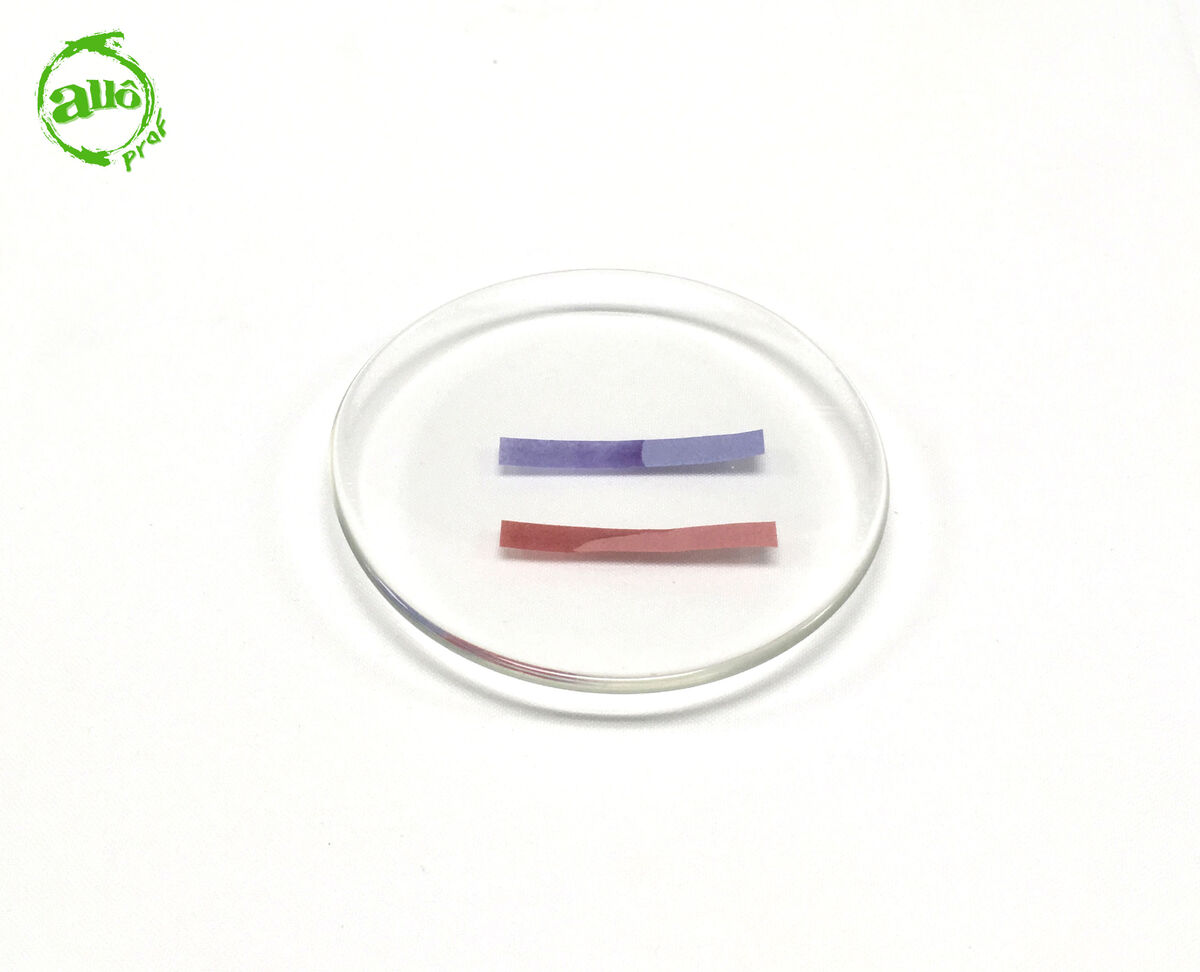
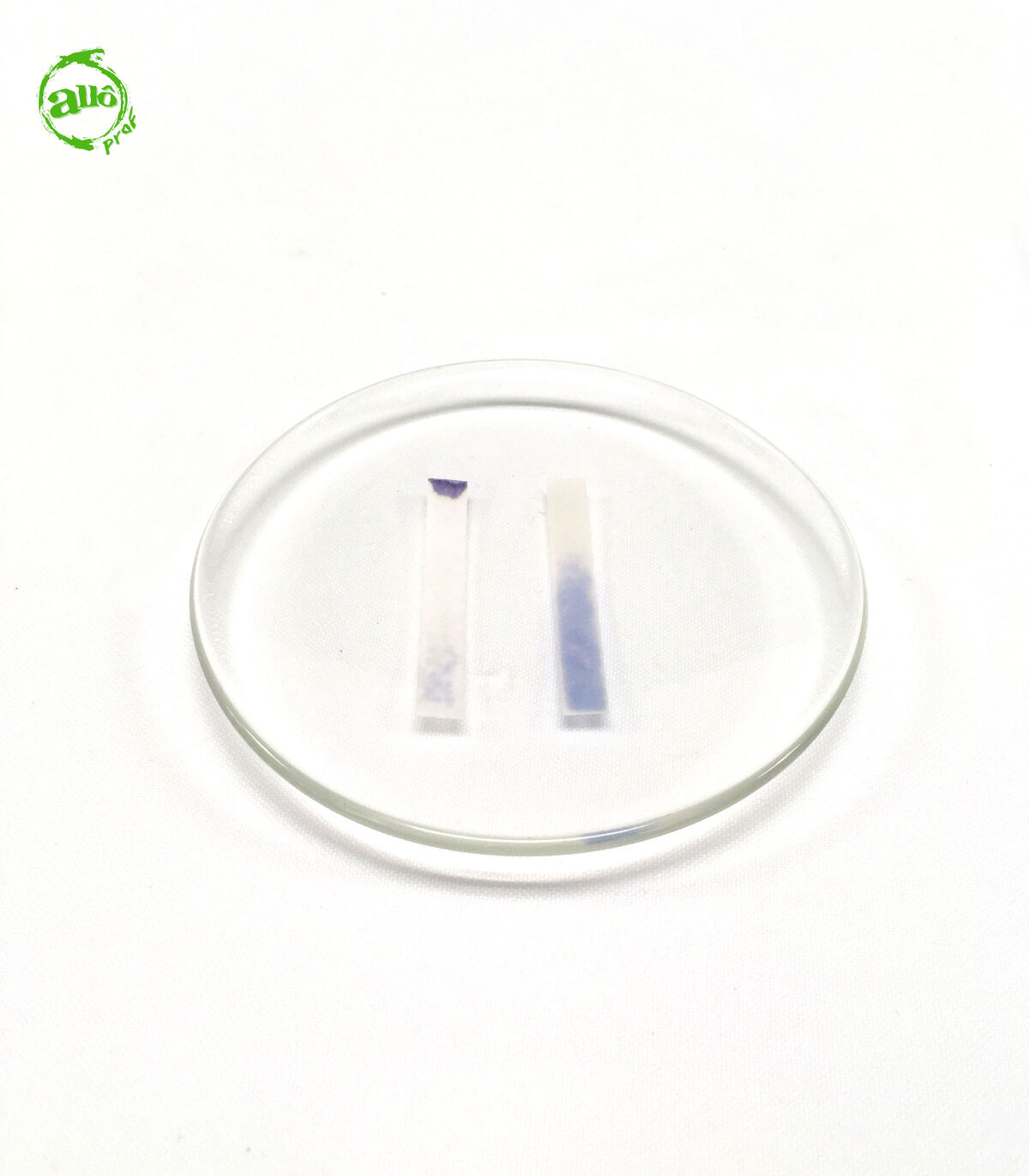
There is a purple litmus paper that can replace red and blue litmus papers. This paper allows both tests to be carried out in one step. The analysis of the results thus obtained is done in the same way.

Certain substances, such as those containing chlorine, can bleach litmus paper. It is, therefore, not possible to identify the nature of these solutions with litmus paper.
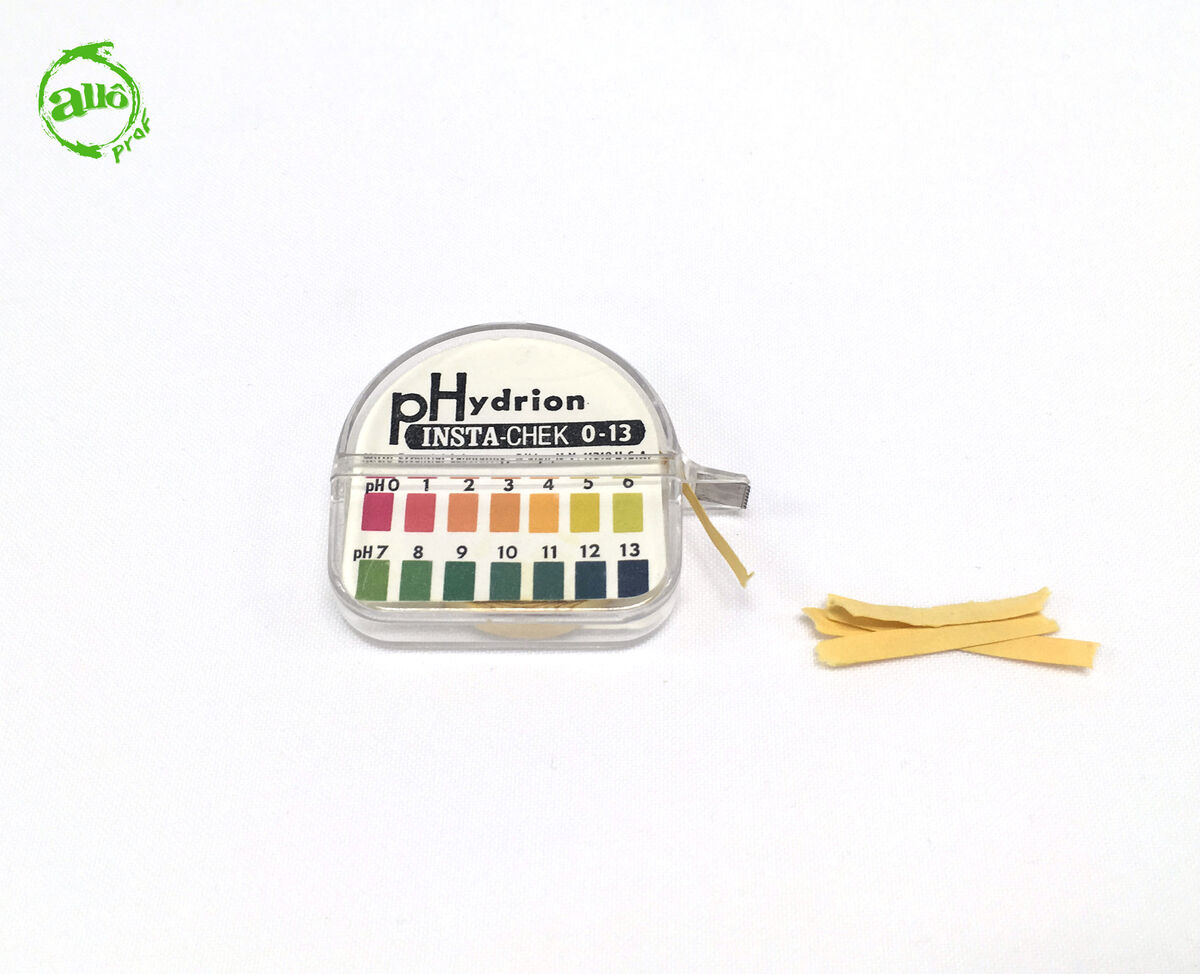
pH paper is actually a paper soaked in a universal indicator, which is a mixture of indicators. When a strip of pH paper is dipped into a solution, the paper changes colour depending on the pH of the medium. pH paper is, therefore, more precise than litmus paper in identifying the nature of the solution, as it can determine the level of acidity or basicity.

-
Solution to be identified
-
Beaker, test tube, or any suitable container
-
Tweezers
-
PH paper strips
-
Watch glass
-
Apron or smock
-
Safety glasses

-
Take a strip of pH paper with tweezers.
-
Dip the free end of the pH paper into the unknown liquid.
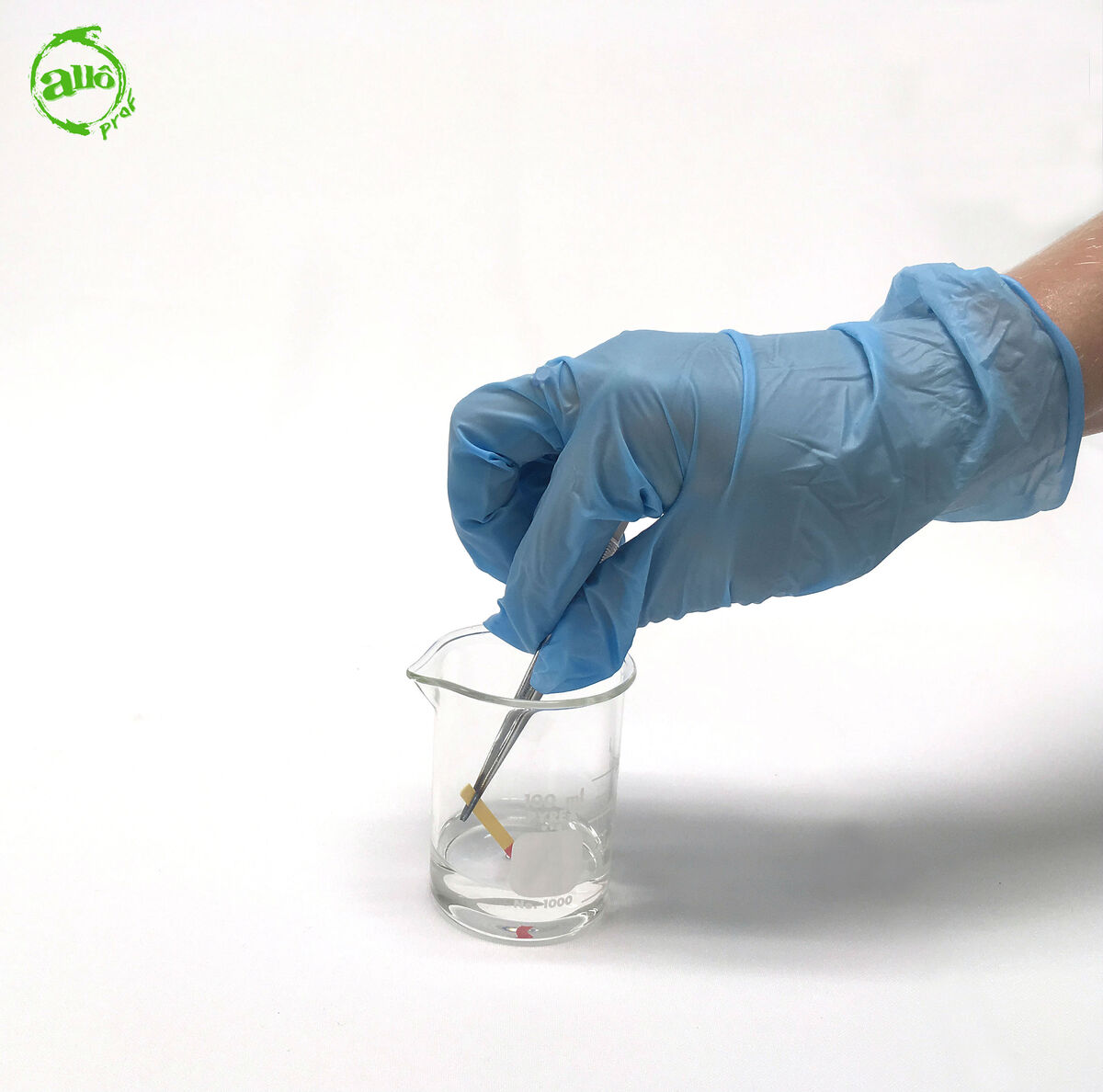

It is not useful to completely soak the pH paper in the liquid. Since the paper is held by the tweezers, it could become contaminated if soaked in the liquid. Should the tweezers come into contact with liquid, they must be washed before reuse.
Also, do not pick up the pH paper with your hands and dip it in the liquid. Since the nature of a substance is unknown, dipping your fingers in certain liquids can be dangerous (it might be a liquid that is harmful to human skin). It is, therefore, preferable to work with tweezers at all times.
-
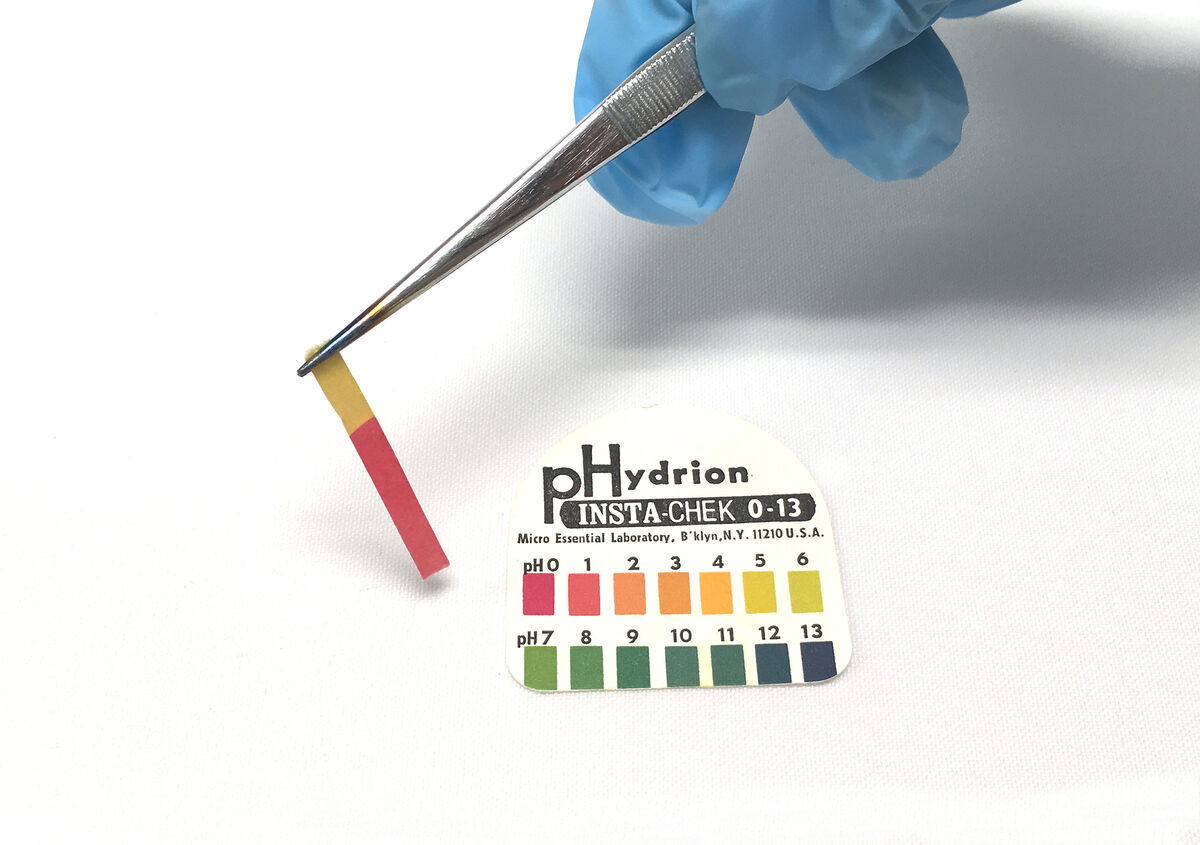
Compare the colour of the pH paper with the universal standard supplied by the manufacturer.
-
Discard the used pH paper and clean the equipment.
In some contexts, to avoid cross contamination, it is preferable to use a dropper to perform the pH paper test. Simply take a few drops of the unknown solution and place them on a strip of pH paper placed in a watch glass.
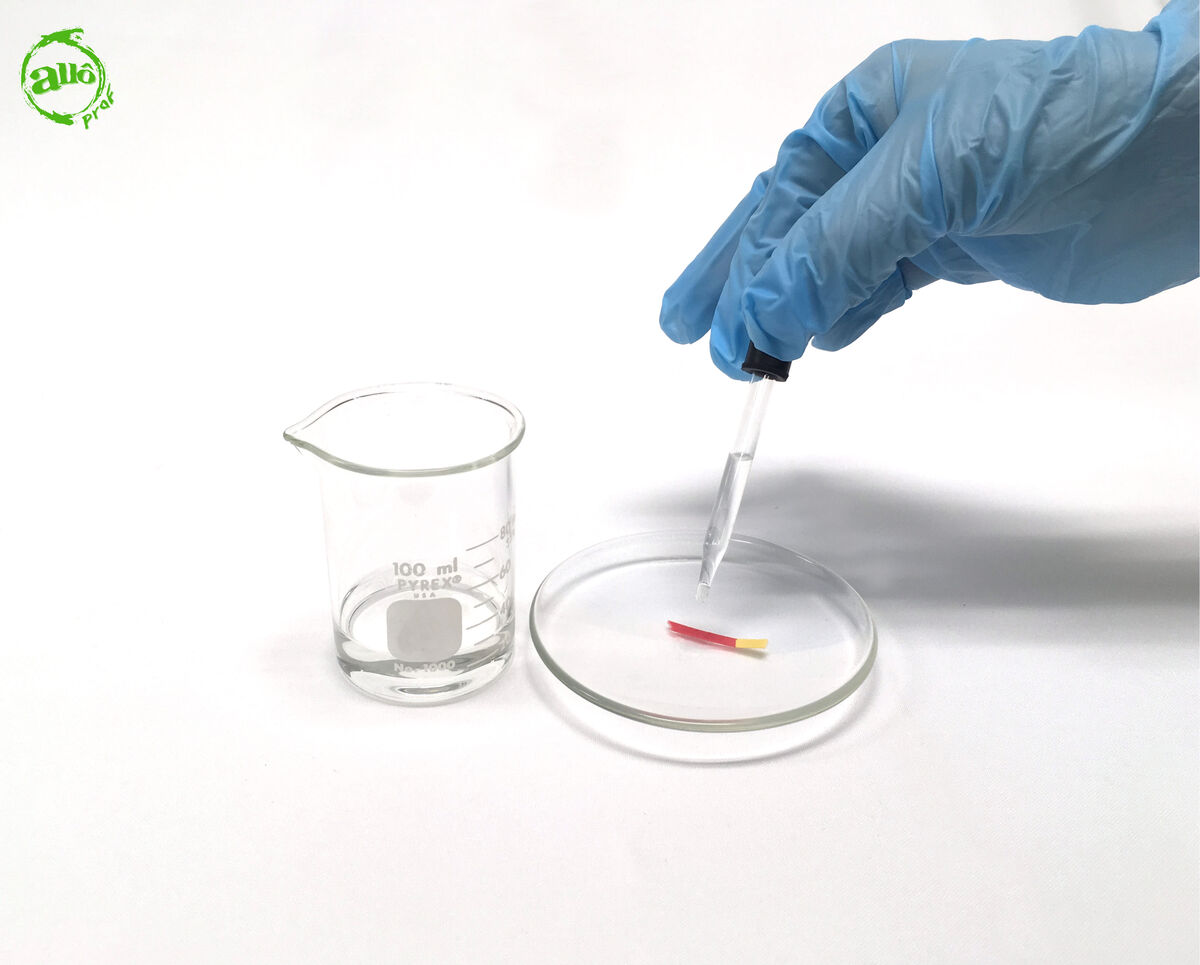

Results
When comparing the coloured pH paper with the supplied standard, the pH value of the solution can be identified. According to this value, the nature of the substance can be determined.
-
A solution with a pH between |0| and |6| will be acidic in nature.
-
A solution with a pH of |7| will be neutral.
-
A solution with a pH between |8| and |14| will be basic in nature.
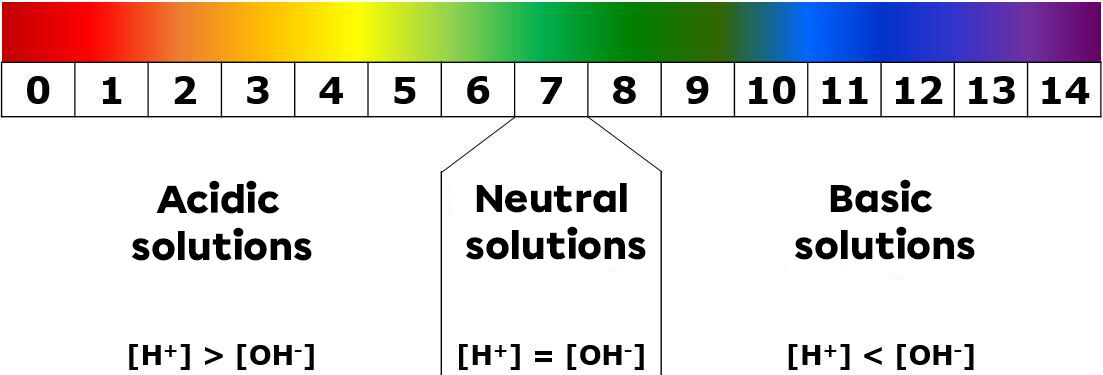
The colours shown in the image above are indicative.
Acid-base indicators are substances that change colour depending on the pH of a solution. Each indicator provides a pH interval according to the colour obtained when the indicator is mixed with the solution.

Acid-base indicators are often used in the laboratory during acid-base neutralization.
-
Solution to be identified
-
Test tube
-
Rubber stopper
-
Acid-base indicator (for this example, bromothymol blue will be used)
-
Dropper
-
Apron or smock
-
Safety glasses

-
Pour a few drops of acid-base indicator using the dropper into the solution to be identified.
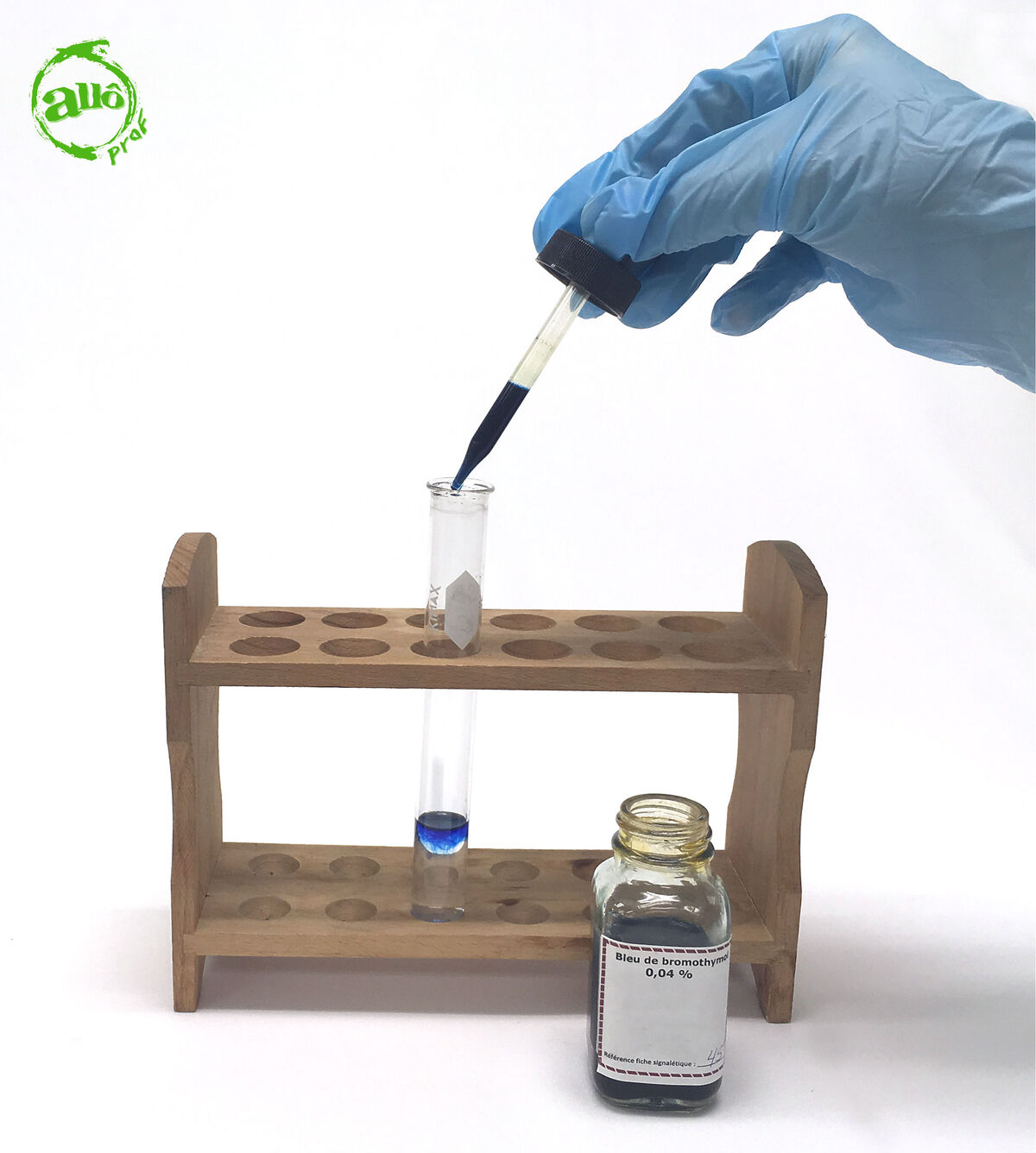

-
Put the rubber stopper on the test tube.
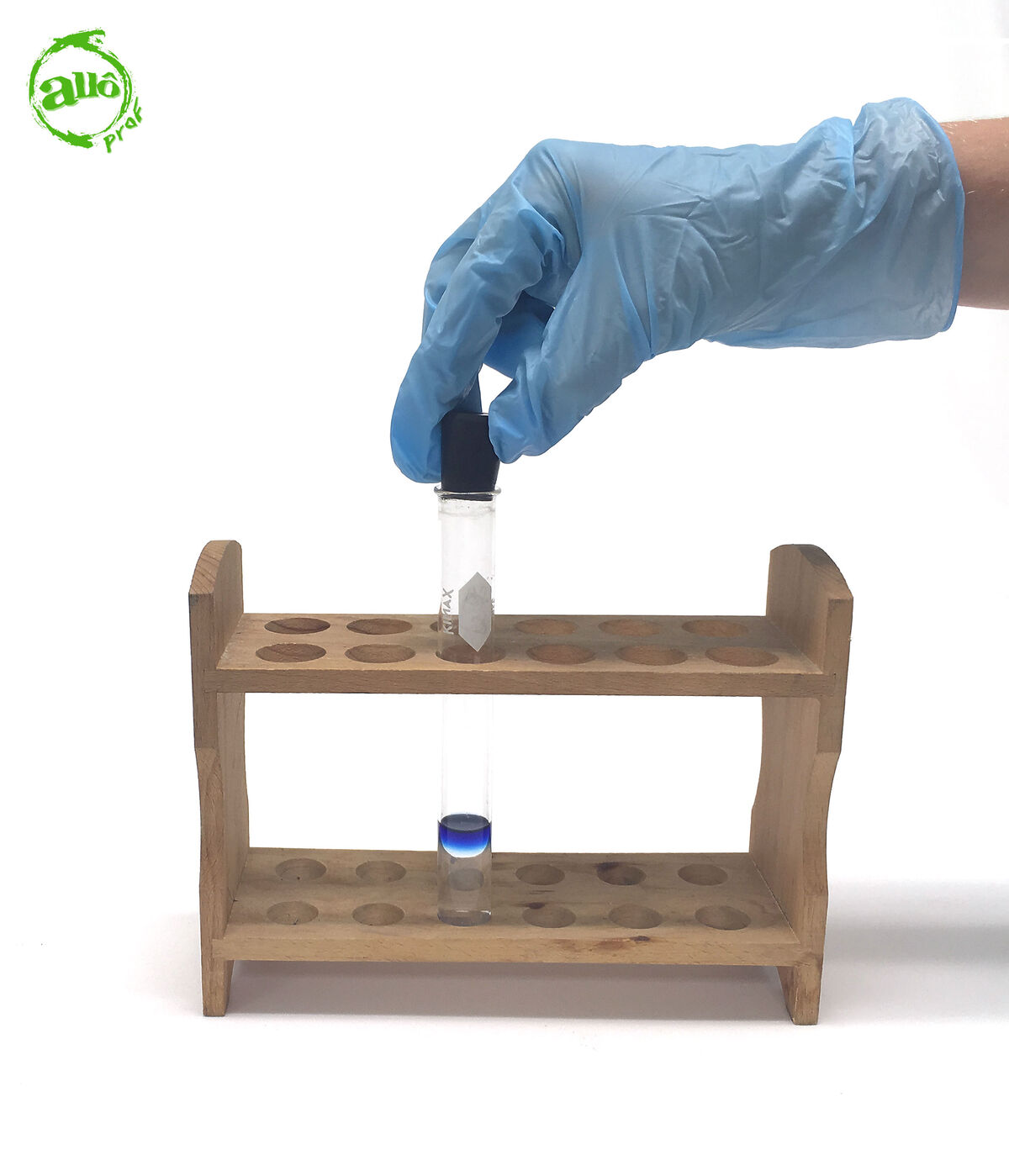

-
Stir the solution.
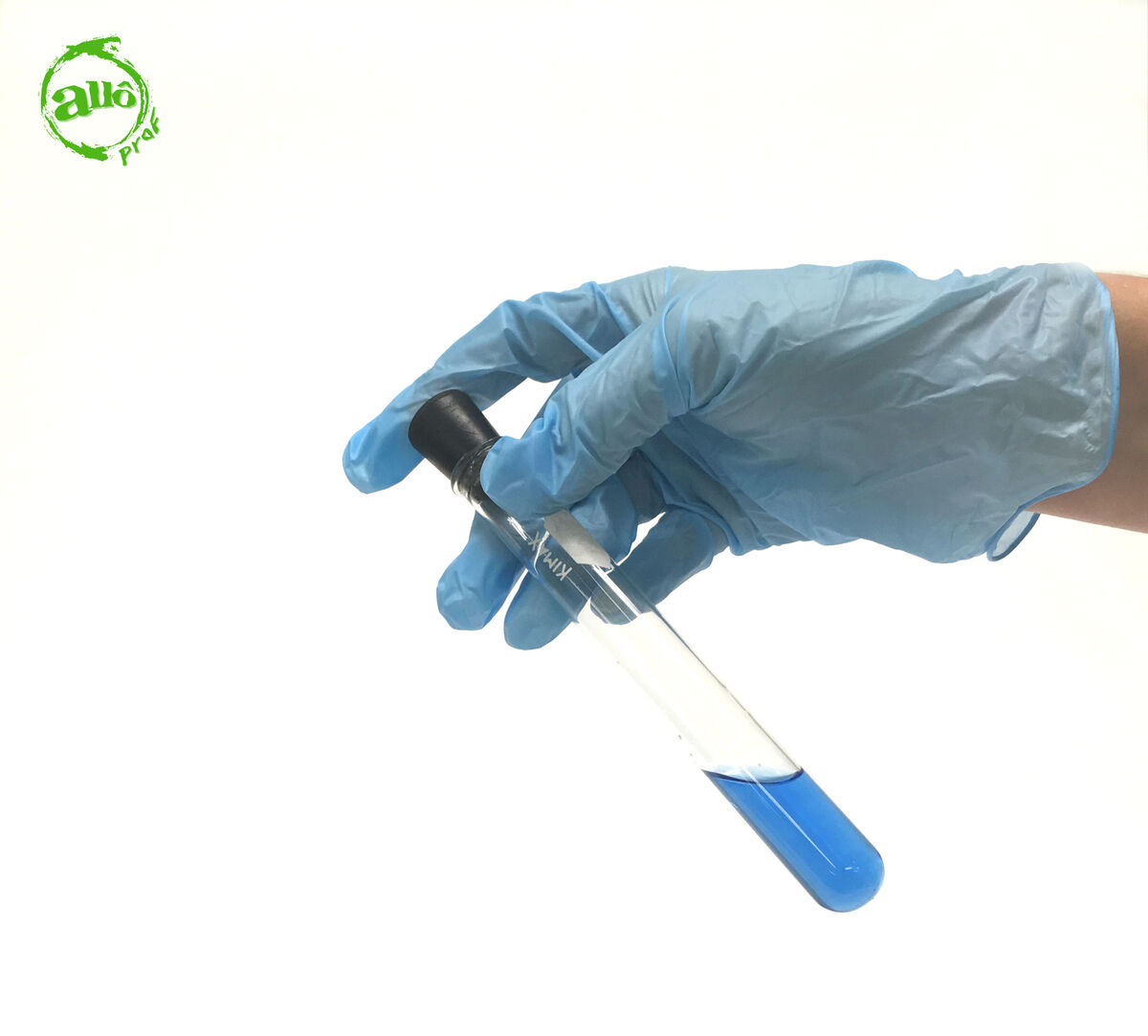

-
Compare the colour of the solution with the known colours of the endpoint.
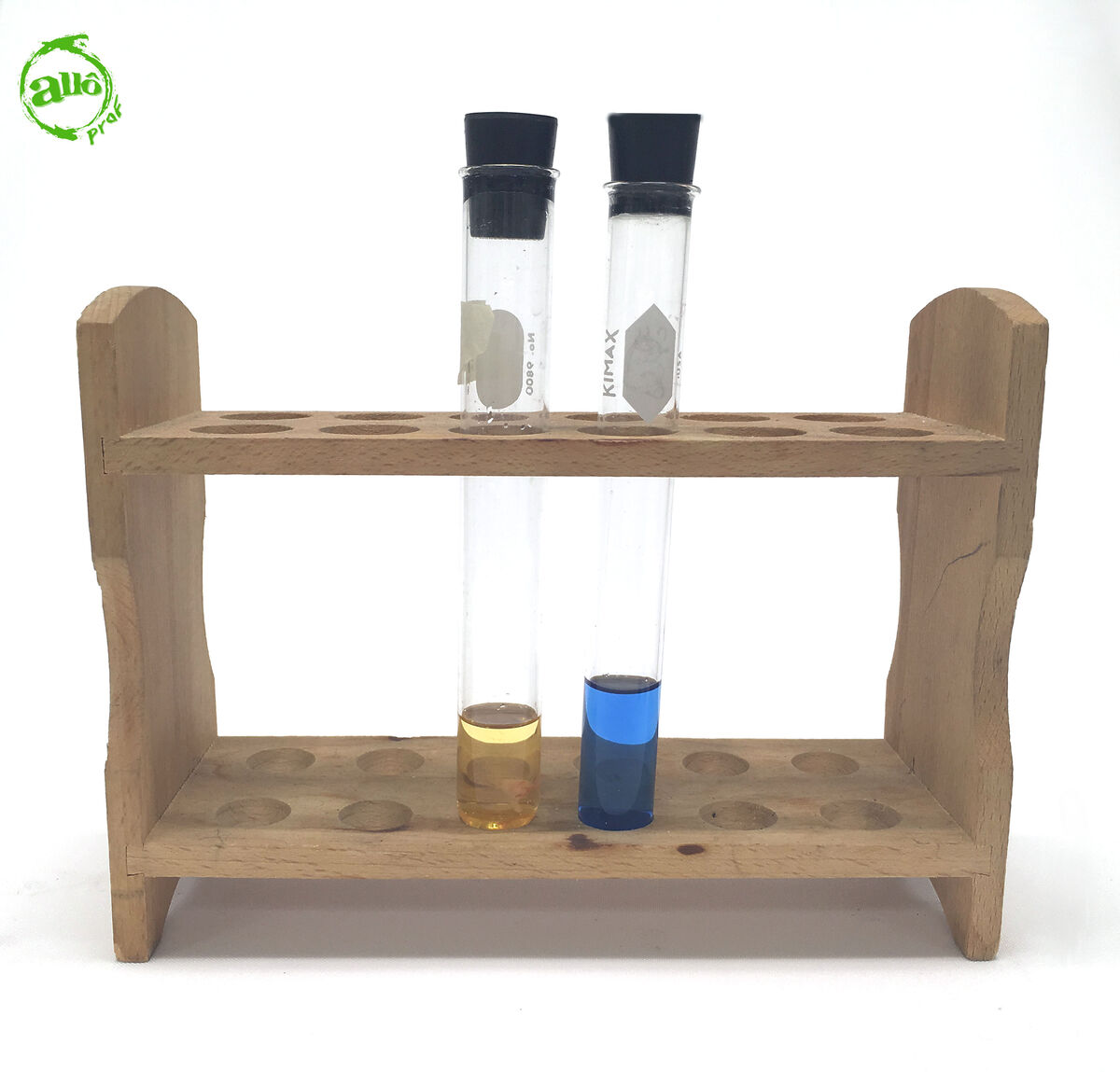

-
Discard the solution according to the required standards.
To determine the pH of the solution, it is necessary to know its endpoint. For bromothymol blue, the endpoint is as follows.
|
|
End point |
Acidic tint |
Basic tint |
|
Bromothymol blue |
|6.0| – |7.6| |
Yellow |
Blue |
In this context, we can therefore deduce that:
-
a solution with a yellow colour has a pH between |0| and |6.0;|
-
a solution with a blue colour has a pH between |7.6| and |14;|
-
a solution with a green colour (between yellow and blue) has a pH between |6.0| and |7.6.|
In the example shown above, the solution is basic (pH between |7.6| and |14|).
The pH meter is an electronic device used to determine the pH of a solution. There are many models of pH meters. However, they all have the same operating principle: a pH meter consists of two electrodes, one standard called a reference electrode, and another that varies with pH, called a glass electrode. These two electrodes can be combined or separated.

-
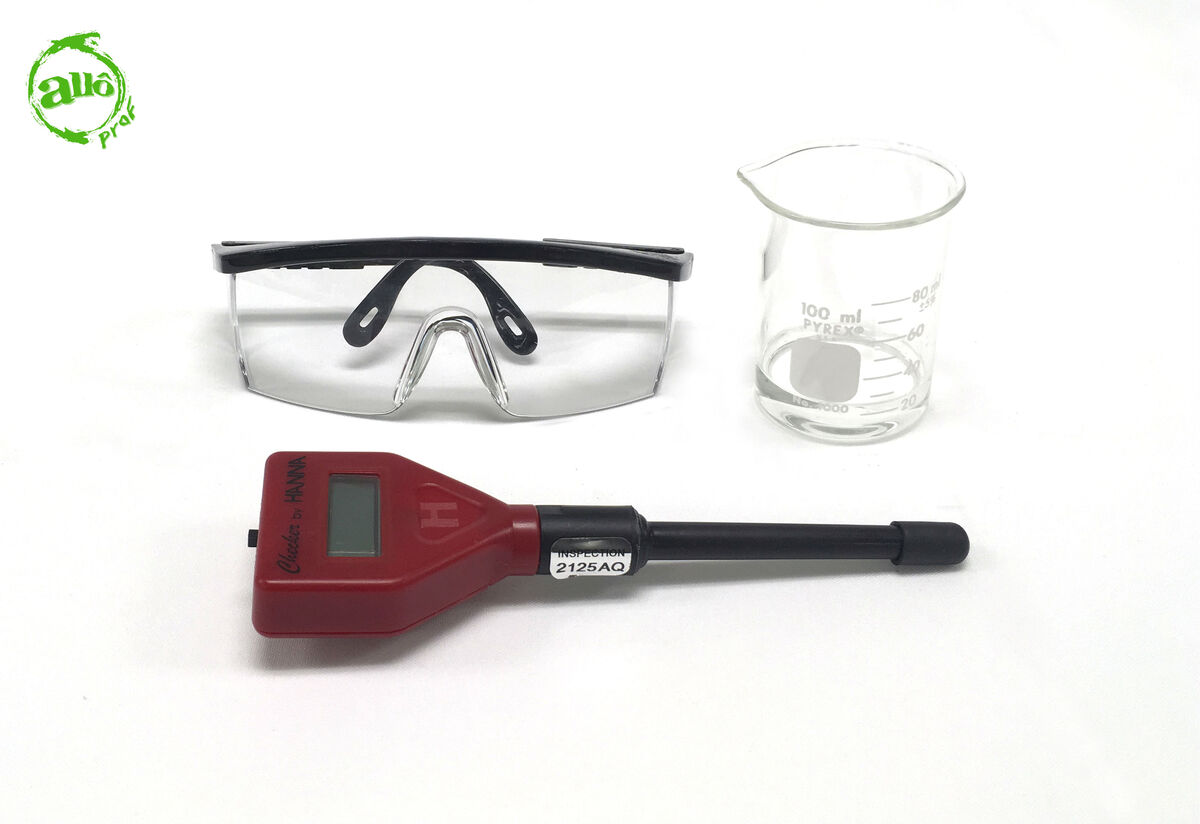
Solution to be identified
-
pH meter
-
Apron or smock
-
Safety glasses

-
Switch on the device.

-
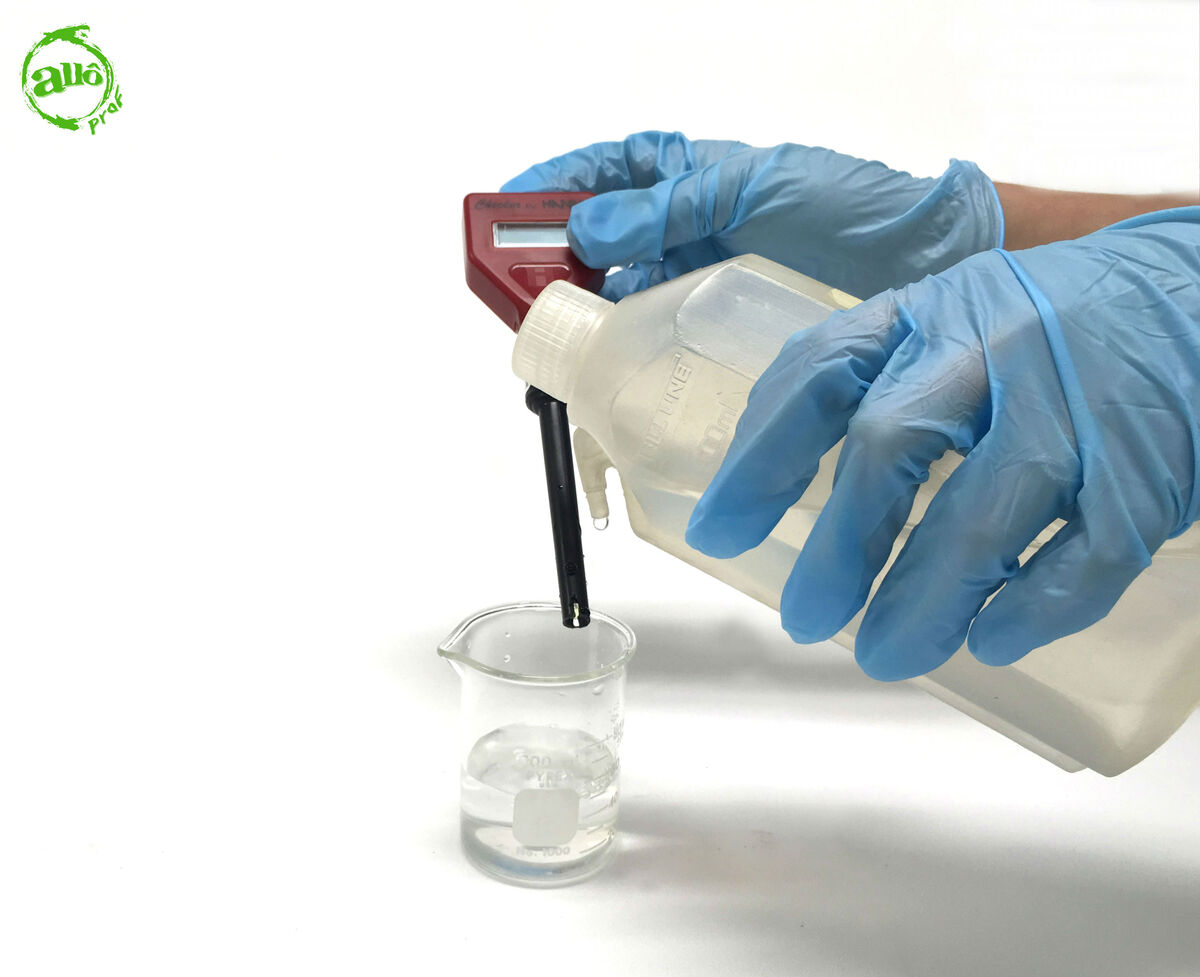
Rinse the electrode with distilled water.

-
Calibrate the pH meter by dipping the electrode in a substance of known pH (standard solution).

-
Remove the electrode from the standard solution and rinse it again with distilled water.

-
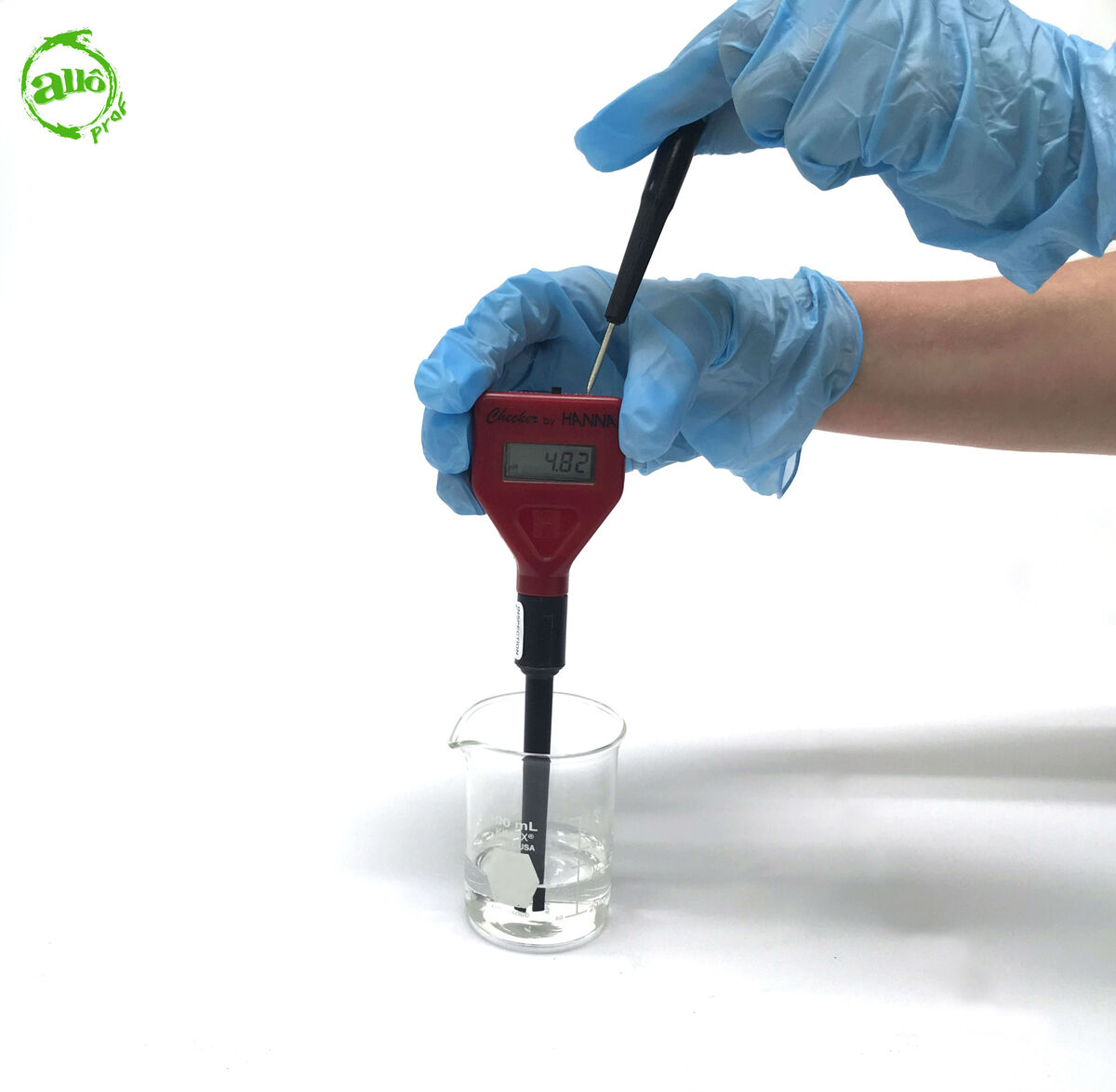
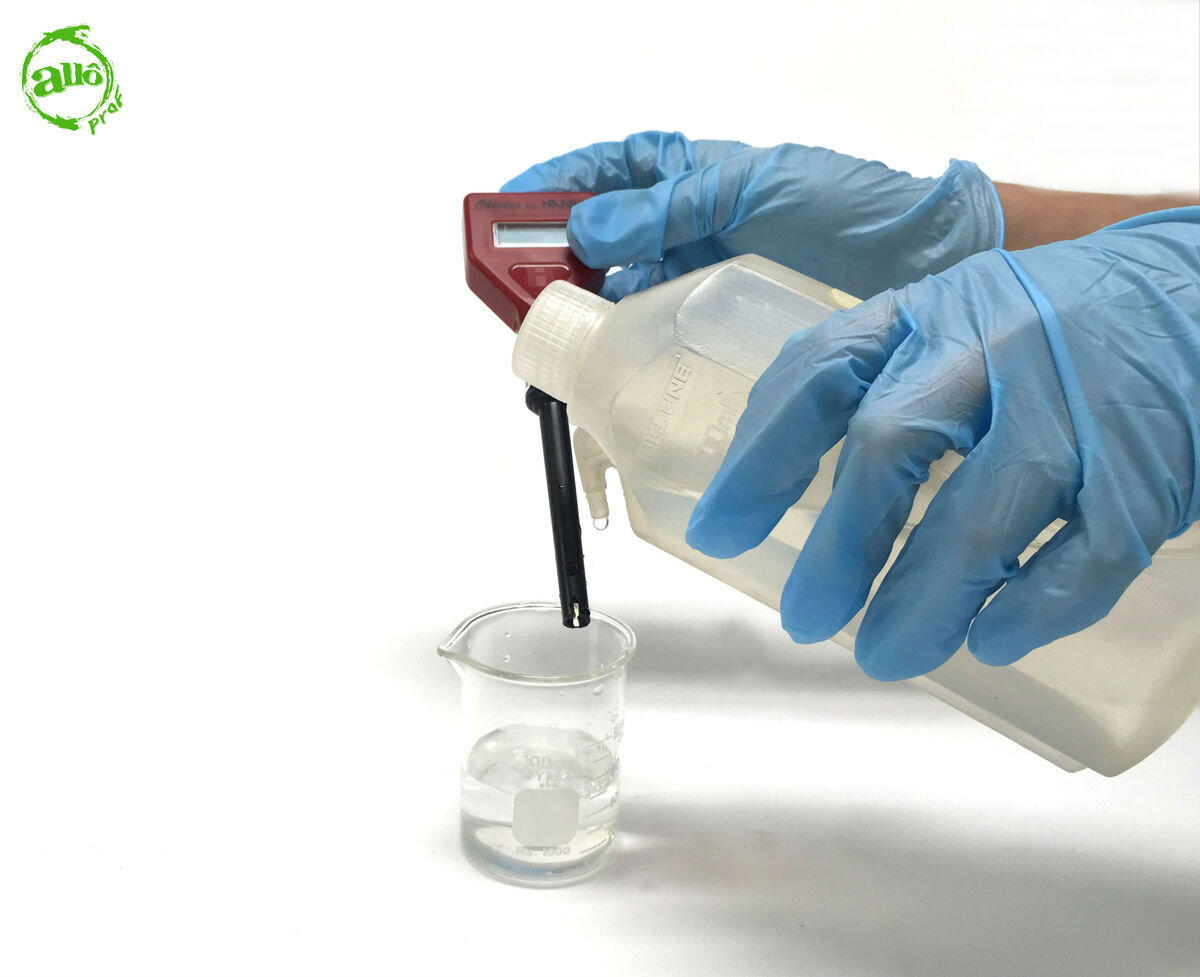
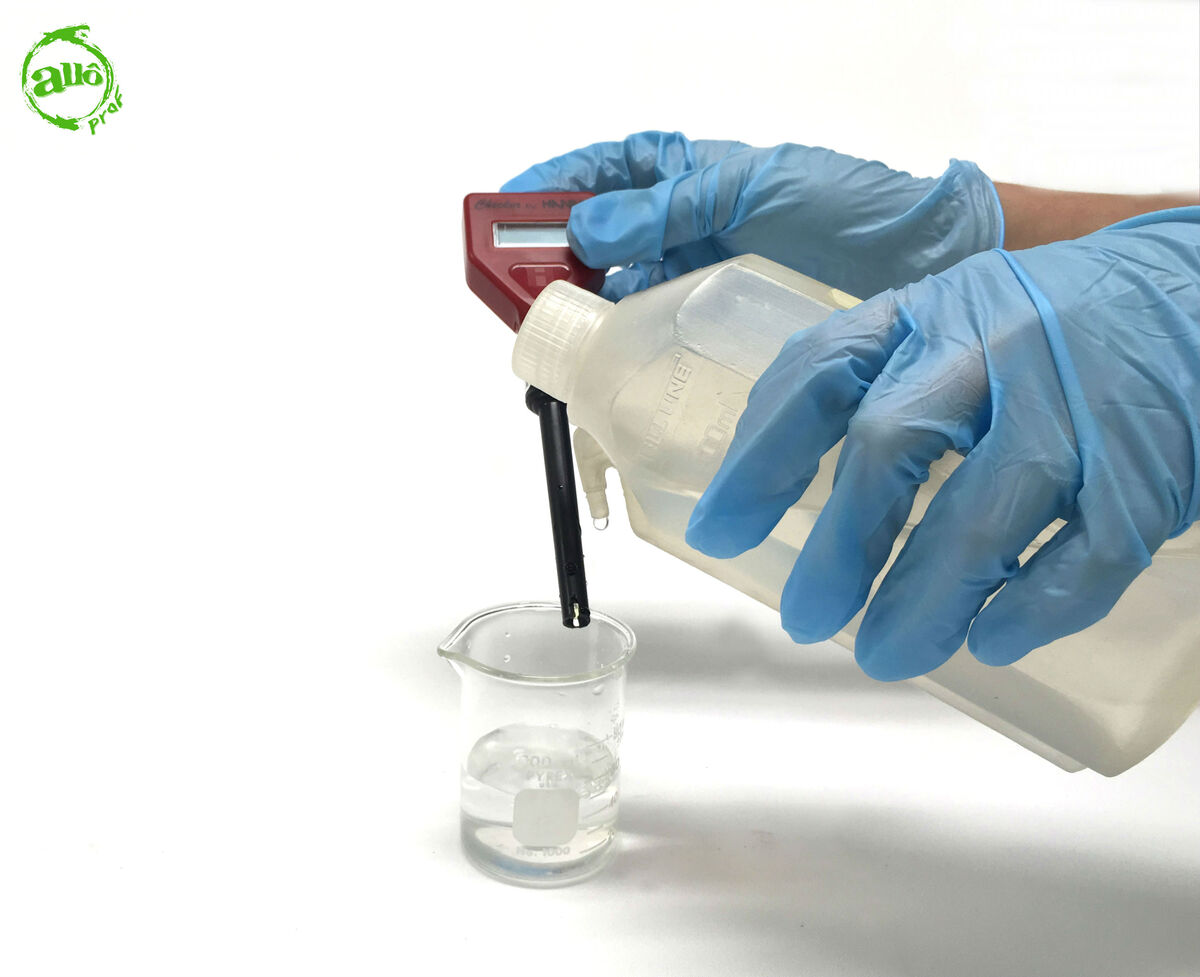
Dip the electrode in the solution to be identified.

-
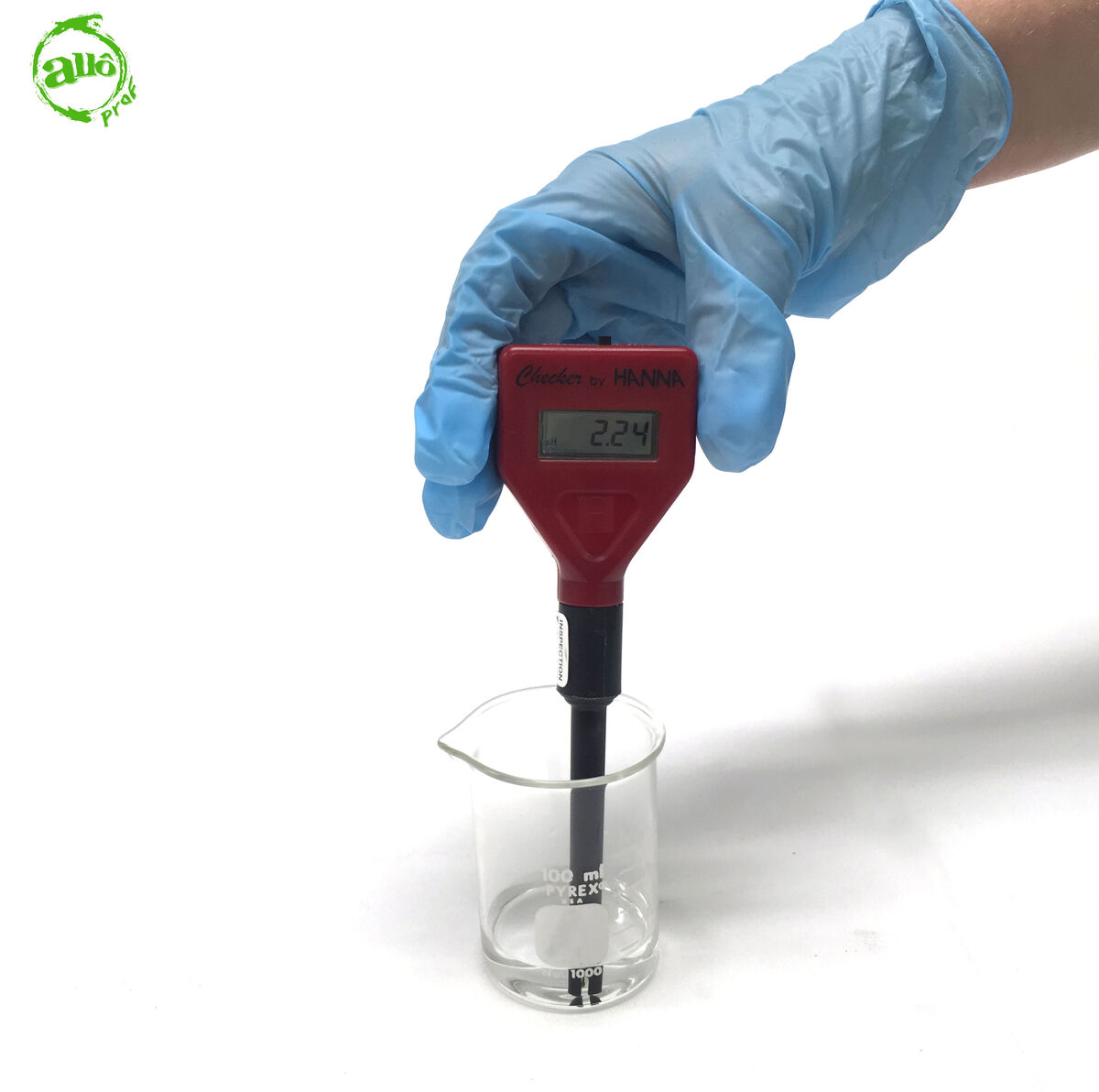
Read the pH measurement.
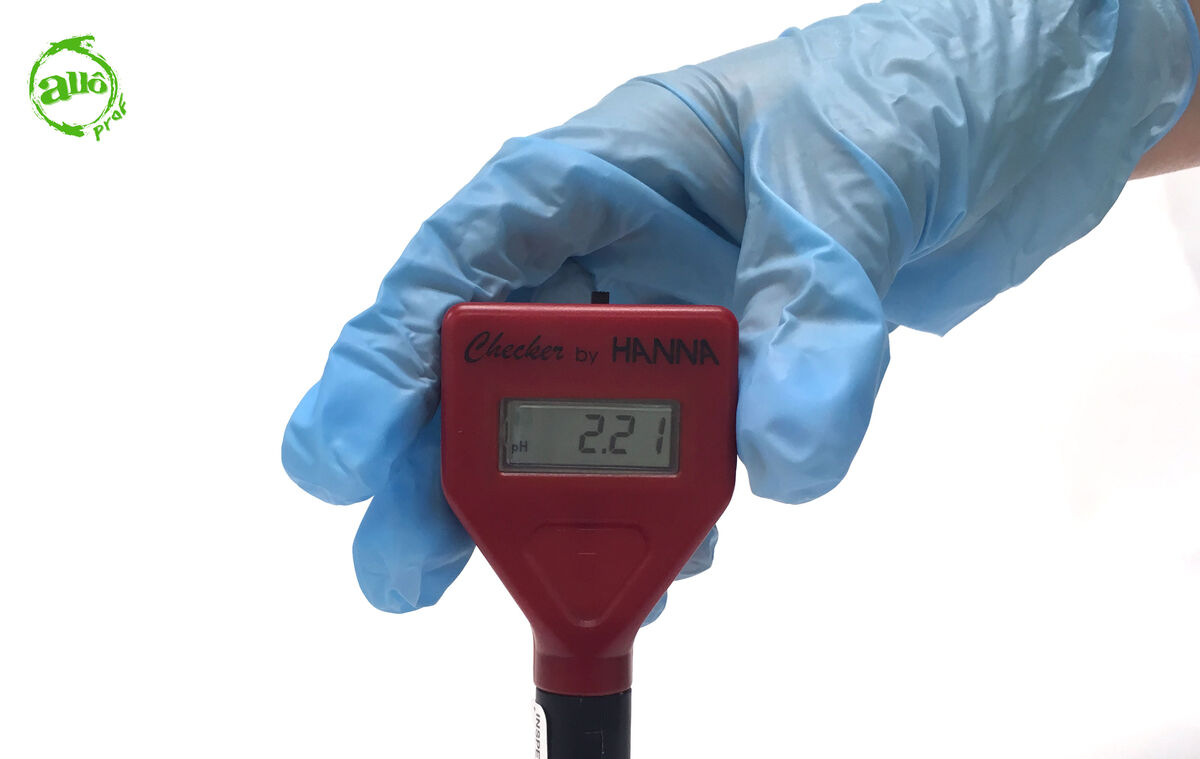

-
Remove the electrode from the solution to be identified and rinse it again with distilled water.

The advantage of the pH meter is that it gives a direct measurement of the nature of the substance. In our example, the nature of the substance is acidic, as the pH value indicated by the pH meter is below |7.|