Choose your level.
-
The pH, short for potential of hydrogen, is a measure used to determine the acidity, neutrality or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution. The pH has no unit of measurement.
-
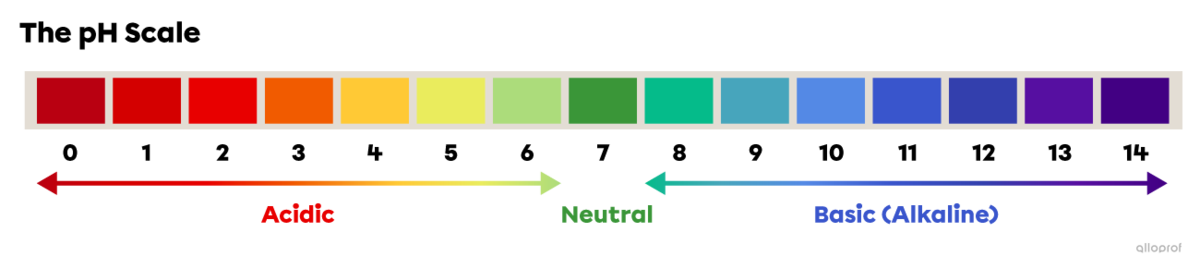
The pH scale is used to compare the acidity, neutrality or basicity (alkalinity) of solutions. The pH scale generally ranges from 0 to 14.
On the pH scale, 0 is the most acidic value, 7 is neutral and 14 is the most basic, or alkaline, value.
An aqueous solution always contains hydrogen ions |(\text{H}^+)| and hydroxide ions |(\text{OH}^-).| The pH value of an aqueous solution depends on the concentration of the |(\text{H}^+)| ions relative to the concentration of the |(\text{OH}^-)| ions.
-
When the concentration of |(\text{H}^+)| ions is higher than the the concentration of |(\text{OH}^-)| ions, the pH is below 7 and the solution is acidic.
-
When the concentration of |(\text{H}^+)| ions is equal to the concentration of |(\text{OH}^-)| ions, the pH is 7 and the solution is neutral.
-
When the concentration of |(\text{H}^+)| ions is lower than the concentration of |(\text{OH}^-)| ions, the pH is above 7 and the solution is basic, or alkaline.
The pH scale can be used to assess the degree of acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of an aqueous solution.
- An acid is a substance that allows the release of |\text{H}^+| ions in an aqueous solution.
- A base is a substance that allows the release of |\text{OH}^-| ions in an aqueous solution. Basic substances are also often called alkaline.
- The pH, short for potential of hydrogen, is a measure used to determine the acidity, neutrality or basicity (alkalinity) of a substance. The pH has no unit of measurement.
- The pH scale is used to compare the acidity, neutrality or basicity (alkalinity) of substances. The pH scale generally ranges from 0 to 14.
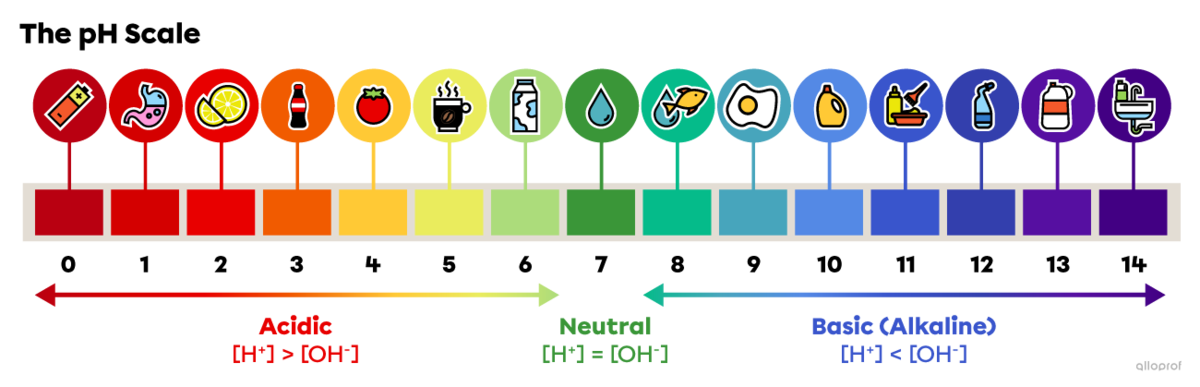
On the pH scale, 0 is the most acidic value, 7 is neutral and 14 is the most basic, or alkaline, value. The following image illustrates the approximate pH values of some common substances.
A difference of one unit on the pH scale causes the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution to change by a factor of 10.
-
A decrease by one unit on the pH scale means that the acidity is increased by a factor of 10.
-
An increase of one unit on the pH scale means that the basicity (alkalinity) is increased by a factor of 10.
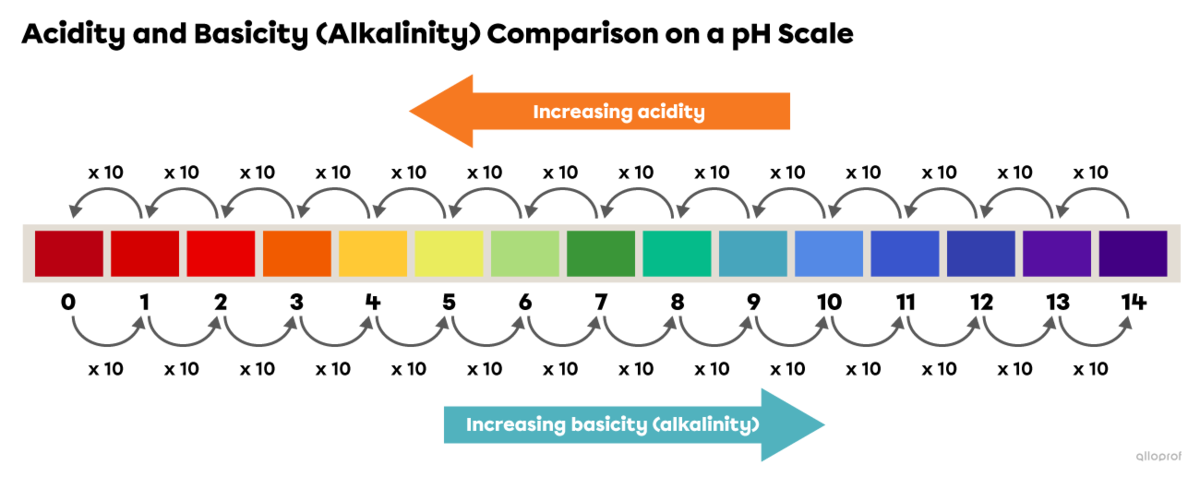
Tomato juice (pH 4) is 1 unit below coffee (pH 5) on the pH scale. Therefore, tomato juice is 10 times more acidic than coffee.
Tomato juice (pH 4) is 2 units below milk (pH 6) on the pH scale. Therefore, tomato juice is 100 times more acidic than milk |(10\ \times 10=100).|
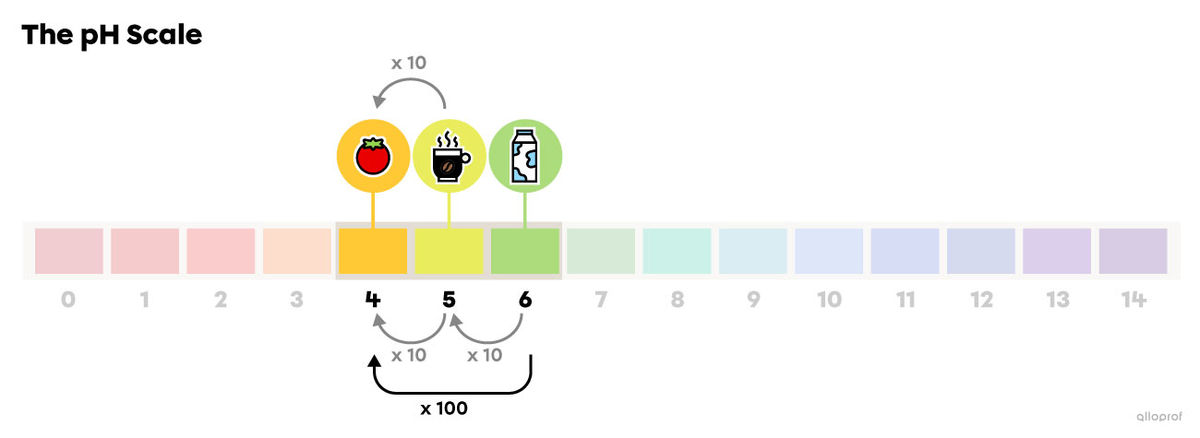
Answer the following questions to compare laundry detergent (pH 10) and bleach (pH 13).
-
Which of the two substances is more basic?
-
What is the variation in basicity between the two substances?
-
According to the pH scale, the higher the pH, the more basic the substance. Bleach is more basic than laundry detergent because the pH of 13 is greater than the pH of 10.
-
To go from pH 10 to pH 13, it takes three jumps on the pH scale. Since |(10\ \times 10\ \times10= 10^3 =1\ 000),| bleach is 1 000 times more basic than laundry detergent. It can also be said that laundry detergent is 1 000 times less basic than bleach.

The pH of an aqueous solution can be used to determine the molar concentration of the |\text{H}^+| ions present. The following formula is used.
|[\text{H}^+]=10^\text{-pH}|
where
|[\text{H}^+]:| concentration of |\text{H}^+| ions in moles per litre |(\text{mol/L})|
|\text{pH}:| pH value
An aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid |(\text{HCl})| has a pH value of |2.5.| Here is the dissociation equation of hydrochloric acid in water.
||\text{HCl}_\text{(aq)}\rightarrow\text{H}^+_\text{(aq)}+\text{Cl}^-_\text{(aq)}||
What is the molar concentration of |\text{H}^+| ions in this solution?
First, let’s identify the given values.
|\begin{align} \text{pH} &=\ 2.5\\ [\text{H}^+] &=\ ?\ \text{mol/L}\end{align}|
Write down the formula to be used in this problem.
|[\text{H}^+]=10^\text{-pH}|
Replace the variables with the given values.
|[\text{H}^+]=10^{-2.5}|
Finally, solve the equation to obtain the final answer.
|[\text{H}^+]\approx0.0032\ \text{mol/L}|
The molar concentration of |\text{H}^+| ions in the hydrochloric acid solution is approximately |0.0032\ \text{mol/L}.|
When the concentration of |\text{H}^+| ions in a solution is expressed in scientific notation where the coefficient is 1, the pH of that solution can be determined by identifying the exponent.
| |\bf[\text{H}^+]| in |\bf\text{mol/L}| | pH |
|---|---|
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{1}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}1| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{2}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}2| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{3}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}3| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{4}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}4| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{5}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}5| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{6}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}6| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{7}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}7| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{8}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}8| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{9}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}9| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{10}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}{10}| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{11}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}{11}| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{12}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}{12}| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{13}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}{13}| |
| |1\ \times\ 10^{-\color{#7CCA51}{14}}| | |\color{#7CCA51}{14}| |
This tip reflects the fact that the pH is a logarithmic function. To find out more about calculating the pH, you can consult the following concept sheet.
Acid-base indicators, commonly referred to as pH indicators, are substances that change colours depending on the pH.
Some of the application of acid-base indicators in laboratories are:
-
To determine the acidity, neutrality or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution.
-
To determine the pH value of a solution.
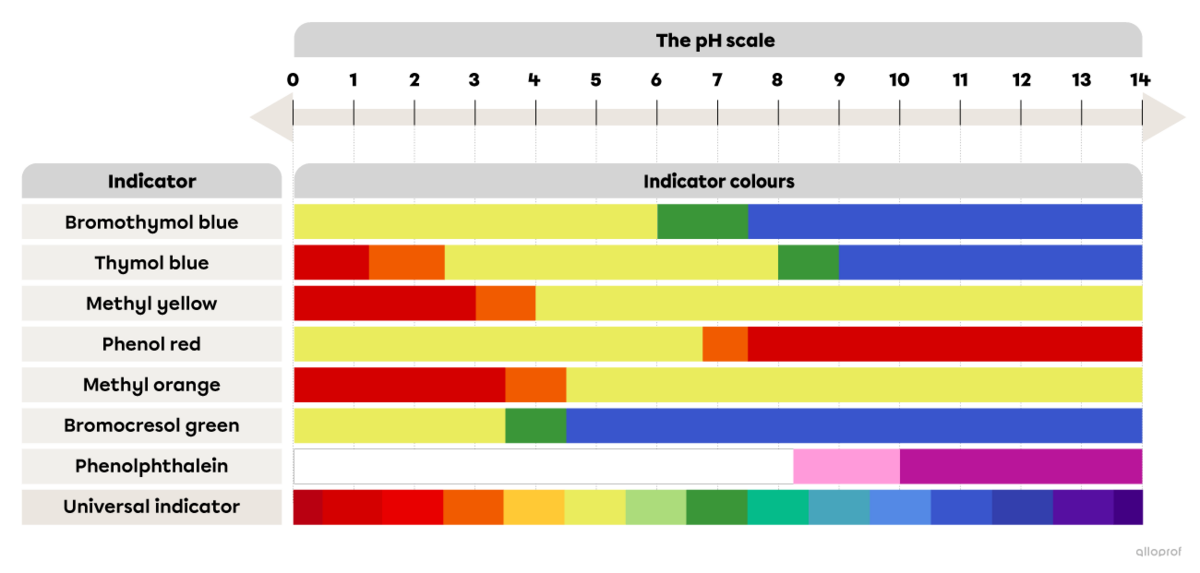
The following image shows the colours of acid-base indicators depending on the pH.
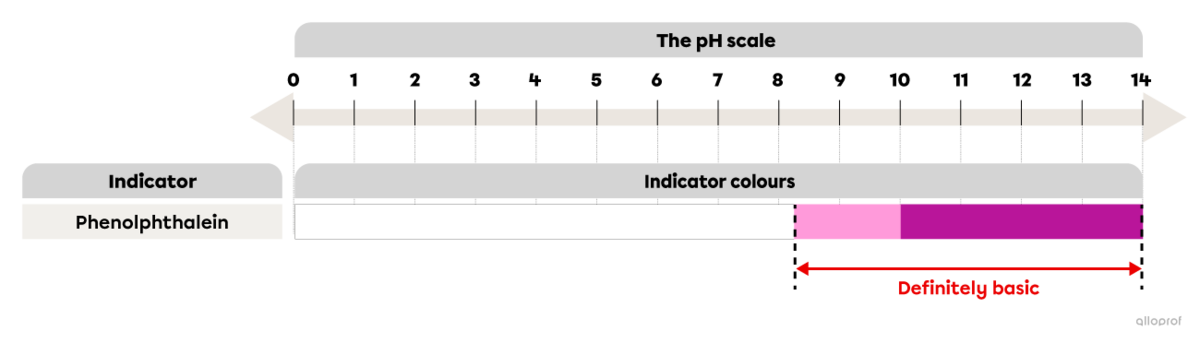
Phenolphthalein is an indicator that can be used to determine if the solution is basic. When a few drops of phenolphthalein are added to the solution in question, a colour change may occur.
-
If phenolphthalein remains colourless, the solution is either acidic (pH below 7), neutral (pH 7), or basic (pH 7-8.2).
-
If the indicator turns pink, the solution is basic with a pH between 8.2 and 10.
-
If the indicator turns fuchsia, the solution is basic with a pH above 10.
In short, if phenolphthalein turns pink or fuchsia when mixed with a solution, the solution is definitely basic.
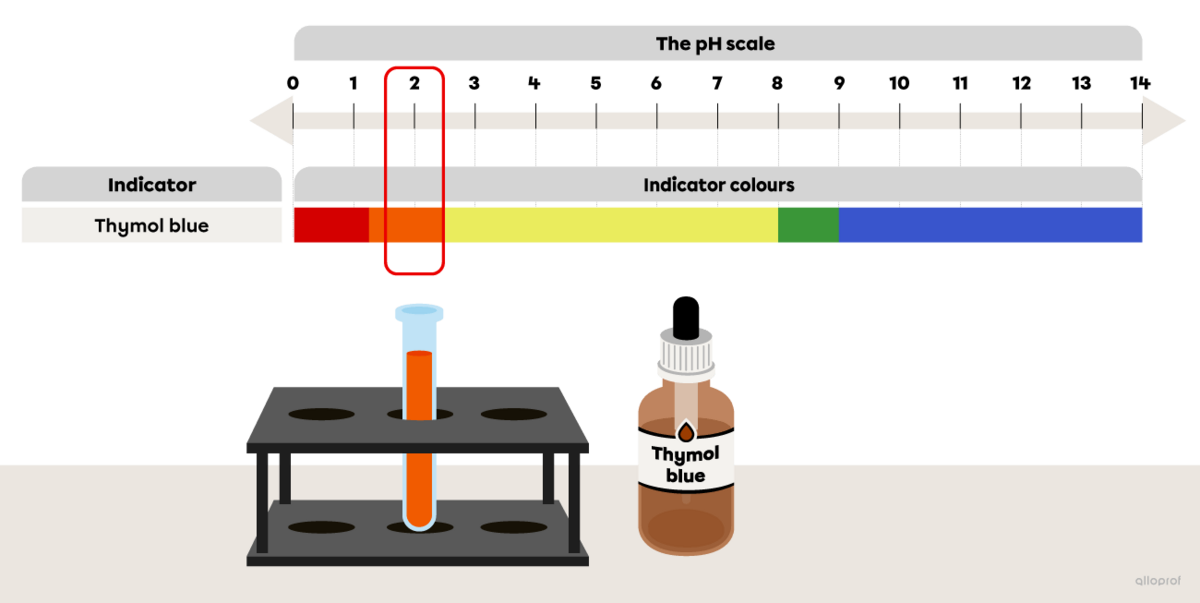
A few drops of an acid-base indicator thymol blue are added to a test tube filled with lemon juice (pH 2). Thymol blue is thoroughly mixed with lemon juice and a colour change occurs.
Referring to the image The colour range of some acid-base indicators depending on the pH, determine the colour of thymol blue after it is mixed with lemon juice.
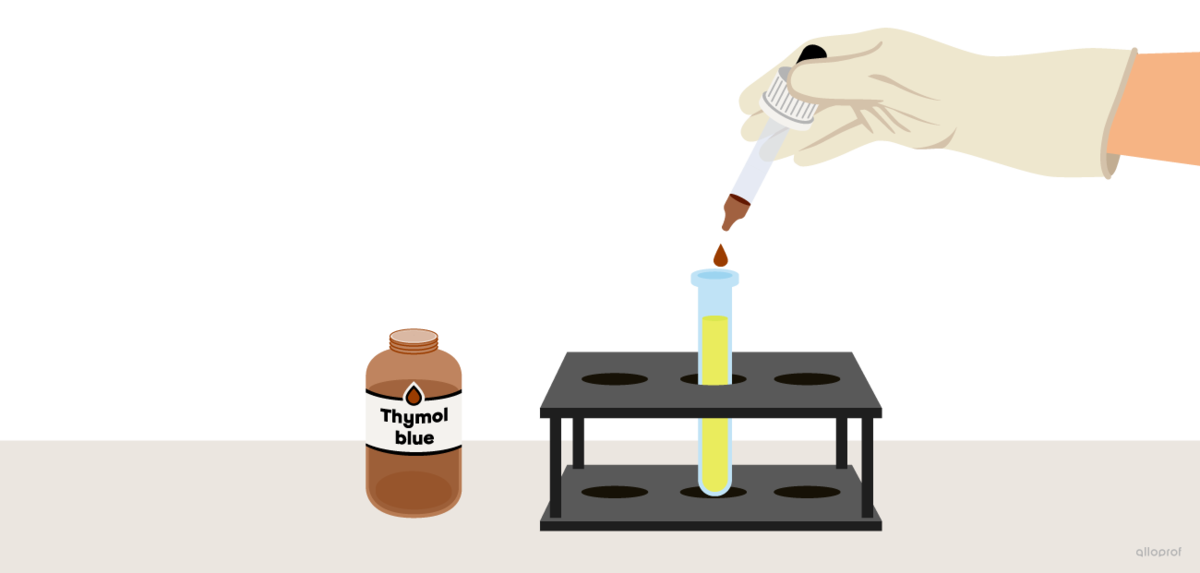
To answer the question, identify the colour of thymol blue that corresponds to a pH value of 2. This colour is the colour of the lemon juice sample mixed with the indicator.
In lemon juice, the thymol blue indicator turns orange.
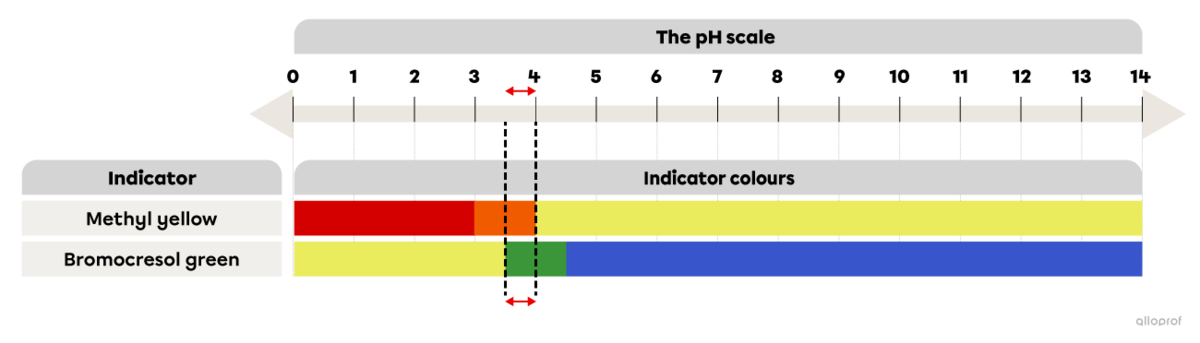
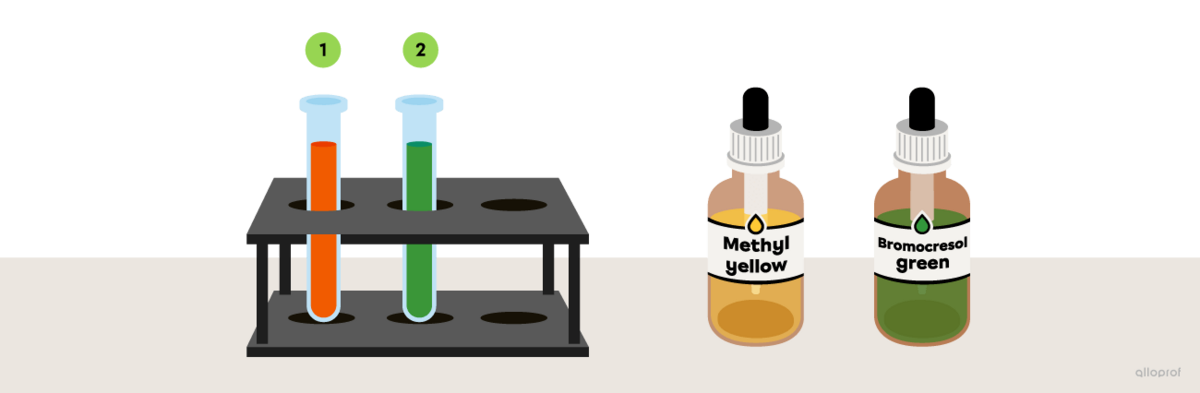
A few drops of methyl yellow are added to an unidentified substance and the solution turns orange. In a second test tube, bromocresol green is added to the same unidentified substance and it turns green.
Referring to the image The colour range of some acid-base indicators depending on the pH, determine the pH interval of the unidentified substance.
-
Since methyl yellow turns orange when mixed with the unidentified substance, its pH must be between 3.0 and 4.0.
-
Since bromocresol green turns green when mixed with the unidentified substance, its pH must be between 3.5 and 4.5.
Taking into account the reaction of both acid-base indicators, it can be concluded that the pH of the unidentified substance is approximately between 3.5 and 4.0.