- The solar system is made up of the Sun and all the celestial bodies orbiting it.
- A celestial body is a natural object located in space, such as a planet, natural satellite or meteorite.
- Orbiting a celestial body means “following a curved path around it due to gravity.”
The solar system is located in a galaxy called the “Milky Way.”
Adapted from Triff, Shutterstock.com
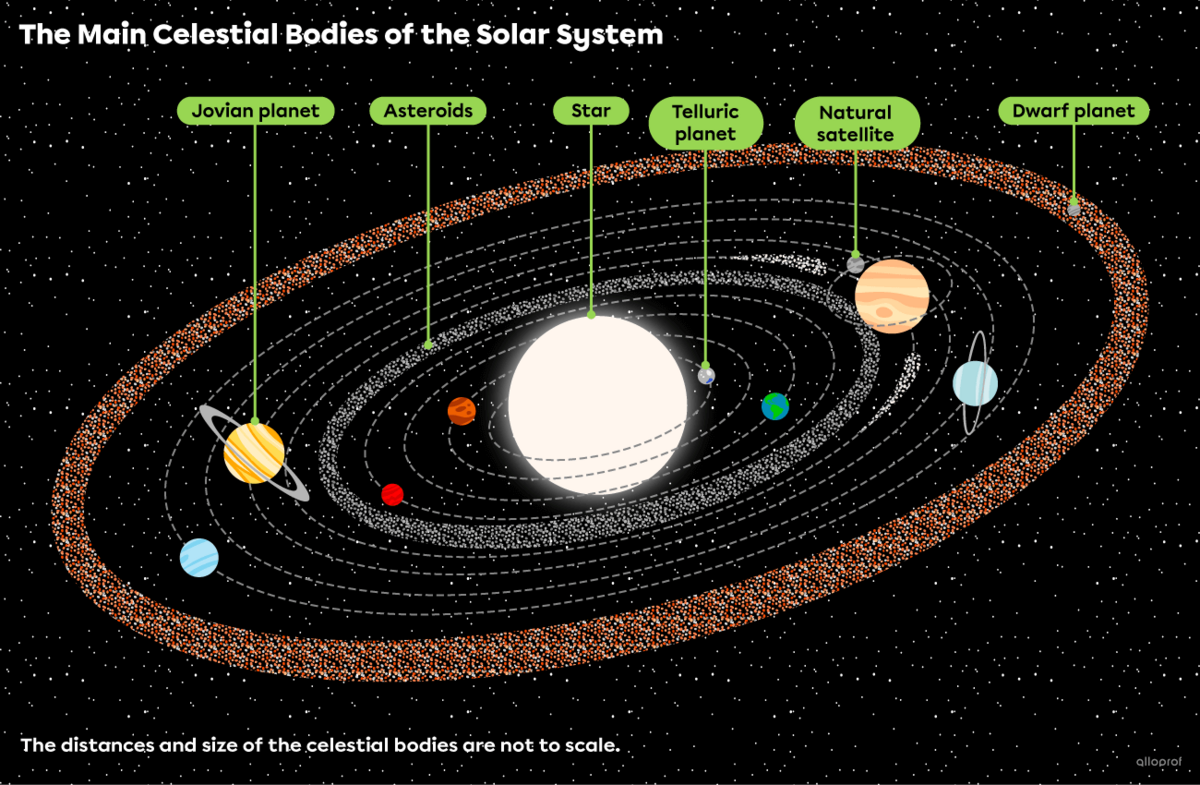
In our solar system, there are several different types of celestial bodies:
- One star (the Sun)
- The telluric planets, also known as “terrestrial planets” (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars)
- The Jovian planets, also known as “gas giants” (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune)
- Natural satellites (e.g., the Moon)
- Other celestial bodies (dwarf planets, asteroids, etc.)
The Sun is at the centre of our solar system, and most other celestial bodies in the solar system orbit it directly. When a celestial body has completed a full orbit around the Sun, it is said to have completed a revolution.
The solar system has two belts: the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt.
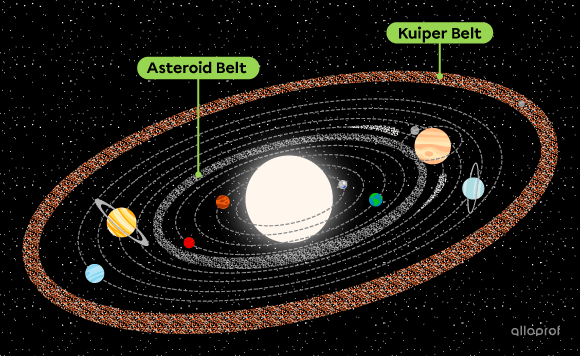
The asteroid belt is a collection of asteroids scattered between the telluric planets and the Jovian planets. Although they appear to be close together, the asteroids are actually separated by an average of one million kilometres!
The Kuiper belt includes many different types of celestial bodies: rocks, comets, dwarf planets, icy bodies, etc.
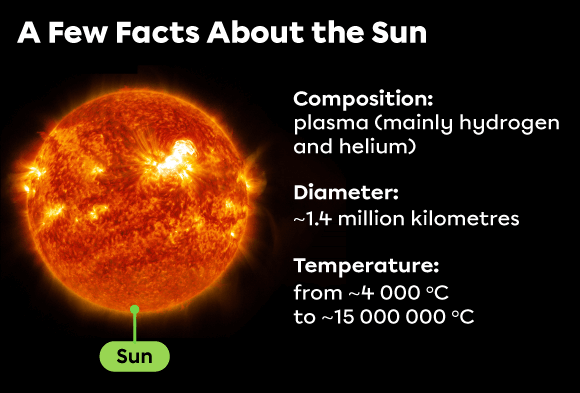
- A star is a celestial body made up of plasma that produces heat and light.
- A body in the plasma state is composed of gases and particles called “electrons.”
The Sun is a star. The plasma that makes up the Sun is mainly composed of particles called “hydrogen” and “helium.”
In the Sun, hydrogen particles fuse to form helium particles. This fusion reaction releases a great deal of energy in the form of heat and light.
This heat and light played a major role in the emergence of life on Earth.
The Sun is often depicted as yellow to red. However, these colours come from the instruments used to observe it. In reality, the Sun is white.
Adapted from Artsiom P, Shutterstock.com
The Sun’s diameter is about 109 times greater than the Earth’s!
The Sun rotates on its own axis and revolves around the centre of the galaxy.

A planet is a spherical celestial body that orbits around a star.
Planets do not emit light, and their orbits are clear. In other words, they do not have other celestial bodies of comparable size in their orbital zones, except for their natural satellites.
The planets in the solar system fall into two categories: telluric (or terrestrial) planets and Jovian planets (or gas giants).
The following table compares the Jovian and telluric planets.
| Telluric Planets | Jovian Planets |
|---|---|
| Surface mainly composed of rock | Surface mainly composed of gas |
| Smaller size | Larger size |
| Closer to the Sun | Farther from the Sun |
| Warmer (between approximately -175℃ and 430℃) | Cooler (between approx. -220℃ and -110℃) |
| Shorter revolution* (88 days to 2 years) | Longer revolution* (12 years to 165 years) |
*Revolution: Number of Earth days or years required to complete one orbit around the Sun.
Data source: Canadian Space Agency, 2020.[1]
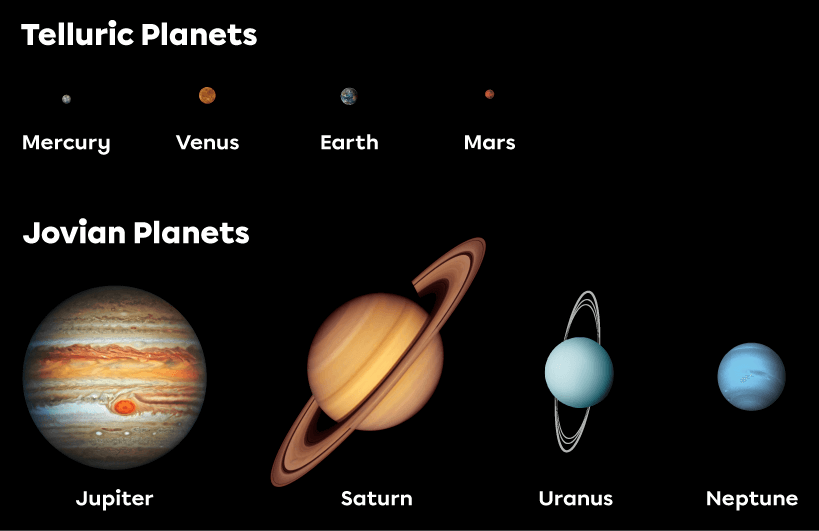
Adapted from 24k-Production, Elena11, 24k-Production, Artsiom P, buradaki, Shutterstock.com
At the time of their discovery, the celestial bodies Ceres and Pluto were considered planets. In 2006, astronomers defined a new category of celestial bodies: the dwarf planets. Ceres and Pluto now fall into this new category.
A dwarf planet is a celestial body that orbits a star.
Dwarf planets emit no light, and their orbits are not clear. In other words, they have other celestial bodies of comparable size in their orbital zones. For example, several asteroids lie relatively close to the dwarf planet Ceres.
There are five officially recognized dwarf planets in our solar system: Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake and Eris.

Adapted from Nostalgia for Infinity, NASA images, OverAnimated, Meletios Verras et Larich D, Shutterstock.com
A natural satellite is a naturally occurring celestial body that orbits a more massive celestial body.
In astronomy, we distinguish between natural satellites and artificial satellites. Artificial satellites are made by humans. For example, the International Space Station is an artificial satellite placed in orbit around our planet to carry out scientific experiments.
The Moon is a natural satellite orbiting the Earth. It is a naturally occurring celestial body that orbits the Earth, a more massive celestial body.
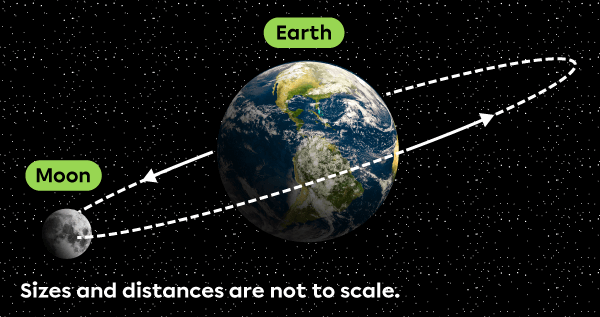
Adapted from 19 Studio, Shutterstock.com
The planets Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune have several natural satellites.
In our solar system, the natural satellites of telluric planets have a surface made up mainly of rock, while the satellites of the Jovian planets have a surface made up of a mixture of rock and ice.
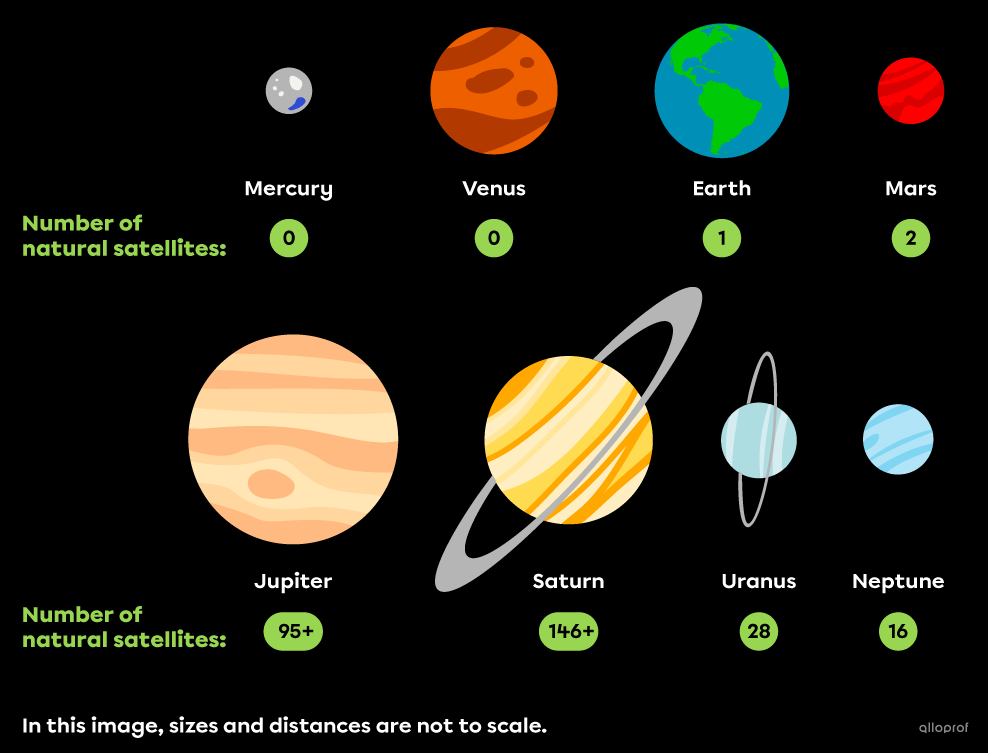
Note that although planets and stars orbit a heavier celestial body, they are not considered natural satellites.
Phobos and Deimos are the two natural satellites of Mars. Their irregular shape suggests that they are asteroids captured by the orbit of Mars.
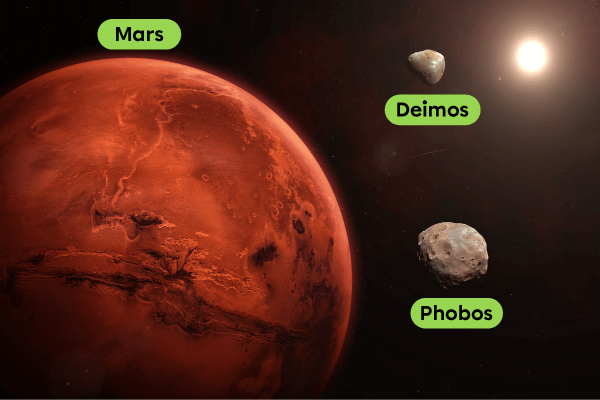

Adapted from buradaki, Shutterstock.com
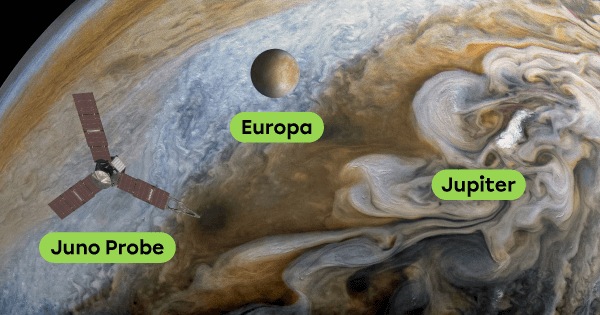
Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa are Jupiter’s largest natural satellites. They are very different from one another: One has a magnetic field, another has very high volcanic activity, and others are thought to hide an ocean beneath their crust.
In 2011, the Juno space probe was sent to study Jupiter and its natural satellites. This mission has revealed a wealth of information about the activity of Jupiter and its satellites. It has also enabled us to capture some magnificent images.
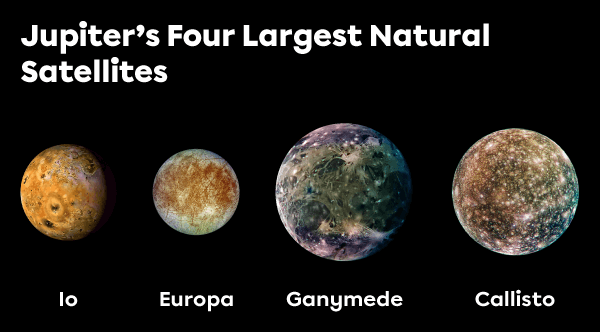
Adapted from Antony McAulay, Shutterstock.com
Adapted from muratart, Shutterstock.com
1. Agence spatiale canadienne. (2020). Le système solaire. https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/fra/astronomie/systeme-solaire/