Tides are the daily change of water levels.
Tides are caused by the combined effects of the following two forces :
-
the gravitational force exerted by the Moon and Sun on the Earth;
-
the centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the Earth and Moon around each other.
Universal gravitation is a force of mutual attraction between two bodies. Its strength varies depending on the mass of the bodies and the distance between them.
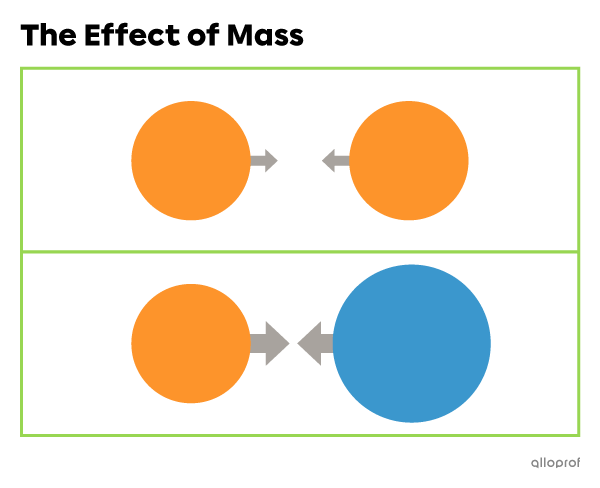
The greater the mass of the bodies, the stronger the force of attraction.
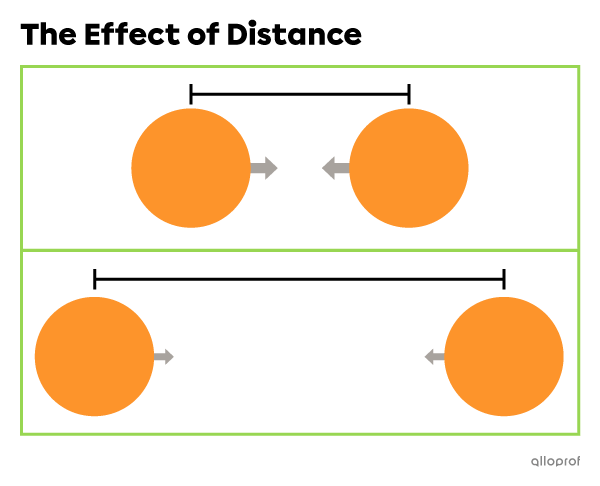
The greater the distance between two bodies, the weaker the force of attraction.
The Moon and Sun exert a gravitational force on the Earth’s surface. This attraction causes water masses to swell.
Tides are mostly caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon.
The Sun may be much heavier than the Moon (about 27 million times heavier!). However, the Moon’s proximity to the Earth causes its gravitational pull to be about twice as strong as the Sun’s.
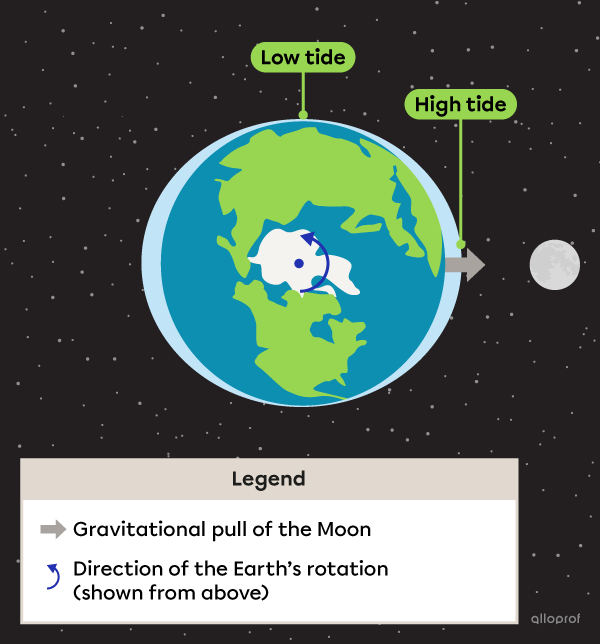
Water masses facing the Moon are attracted, causing water levels to rise. This is known as high tide.
At the same time, another high tide occurs on the opposite side of the Earth. This one is caused by the effect of centrifugal force.
Water levels perpendicular to the high tides are lower. This is known as low tide.
High tides and low tides alternate due to the Earth’s rotation. On the same day, a given region will experience two high tides and two low tides.
The position of the Moon and the Sun in relation to the Earth influences the tidal range.
When the Earth is aligned with the Moon and Sun, their gravitational forces are also aligned.
Under these conditions, high tides reach higher-than-average levels and low tides reach lower-than-average levels. These tides are called spring tides. This alignment occurs at the new moon and at the full moon.
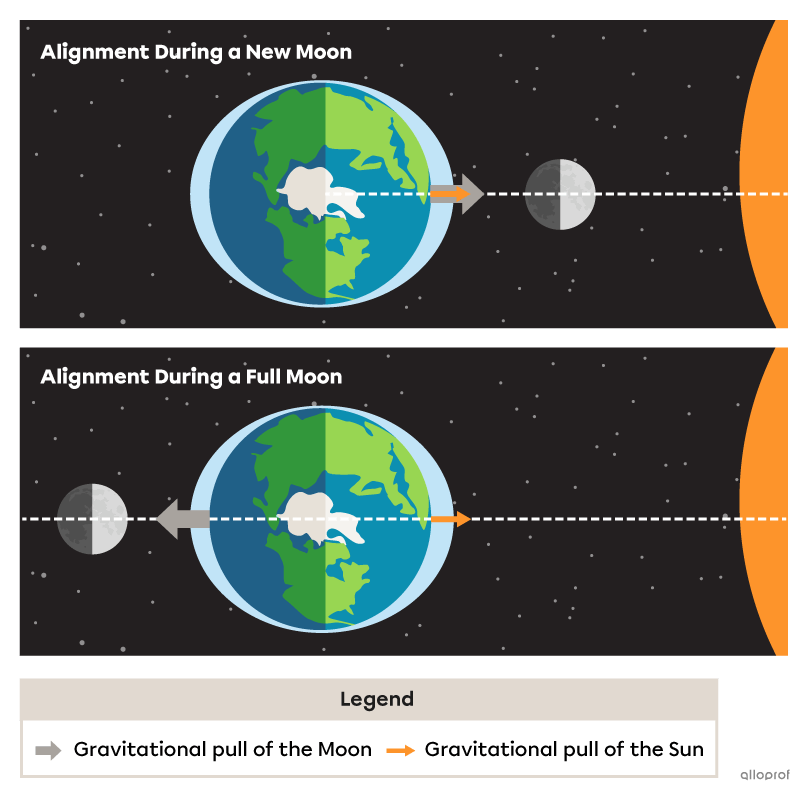
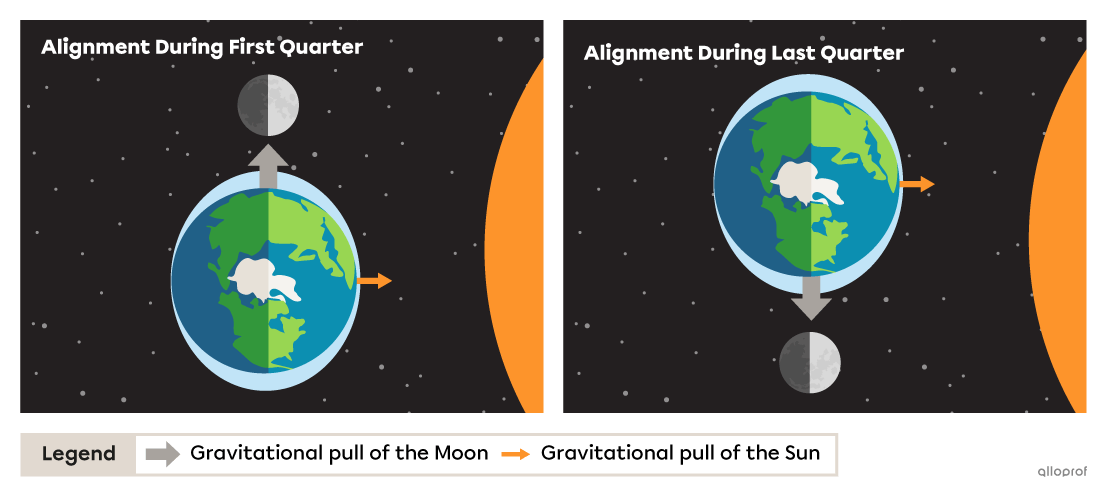
When the Moon’s and the Sun’s alignments with the Earth are perpendicular, the effect of the Moon’s gravitational pull on the water masses is reduced.
Under these conditions, high tides reach lower-than-average levels and low tides reach higher-than-average levels. These tides are called neap tides.
This alignment occurs during the first and last quarter of the moon.
The tidal range increases when the Moon is at its closest point from Earth. This point is called the perigee.
When the Moon is at perigee during a spring tide, there are rare tides with ranges of up to 16 m. They are called king tides.
The highest extreme tides recorded were observed in the Bay of Fundy, on Canada's southeast coast between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia.
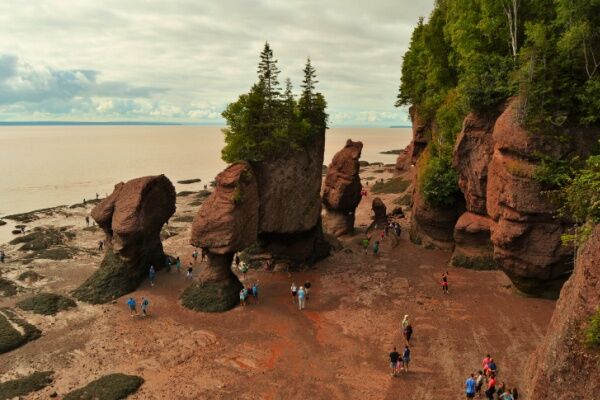

Hopewell Rocks Provincial Park in New Brunswick during an extreme low tide.
Vintagepix, Shutterstock.com
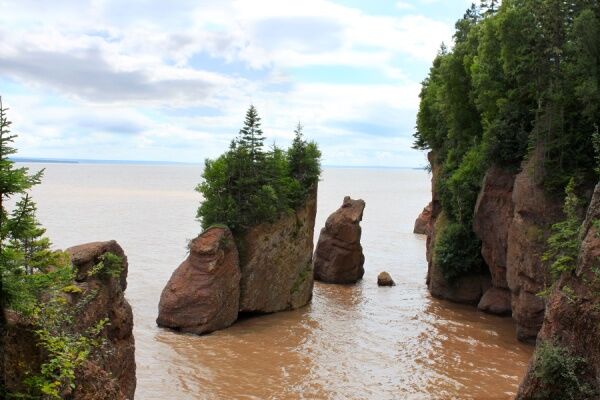

Hopewell Rocks Provincial Park in New Brunswick during an extreme high tide.
gvictoria, Shutterstock.com
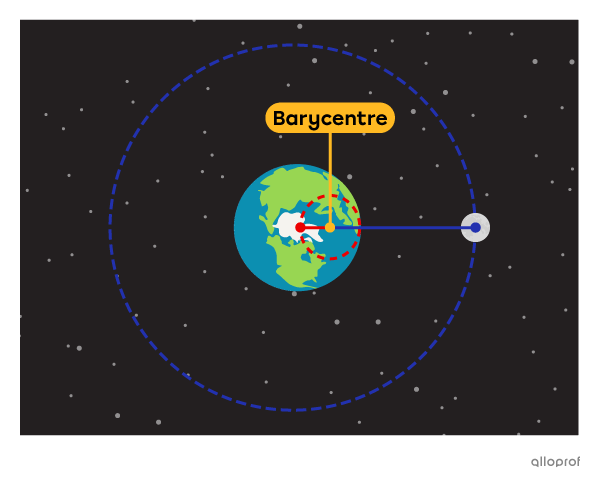
You might think the Moon only revolves around Earth. In fact, both the Moon and the Earth revolve around a point called the barycentre.
If the Earth and Moon had the same mass, the barycentre would lie halfway between them. However, because the Earth is much heavier than the Moon, the barycentre is very close to the Earth’s centre.
The revolution of the Earth and Moon around the barycentre forms the Earth-Moon system.
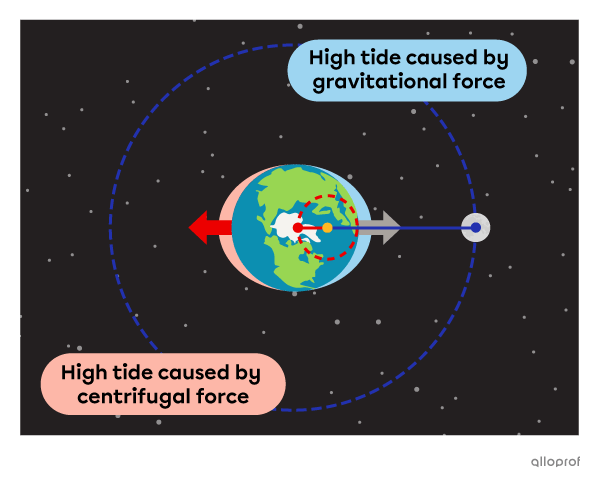
The Earth’s revolution around the barycentre creates a centrifugal force that causes water levels to rise on the side of the Earth facing away from the Moon.
This means that there are always two high tides occurring at the same time on Earth: one facing the Moon and one facing away from the Moon.
Note: English image coming soon!