The past continuous tense (also called past progressive) expresses:
-
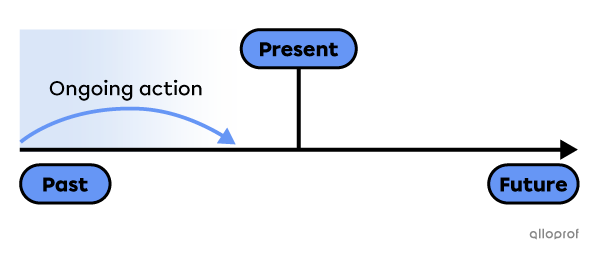
An ongoing action at a specific time in the past.
-
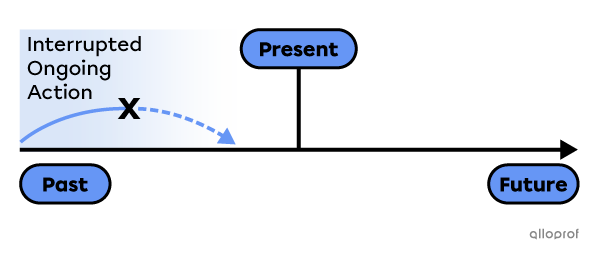
An ongoing action interrupted by another action in the past.
-
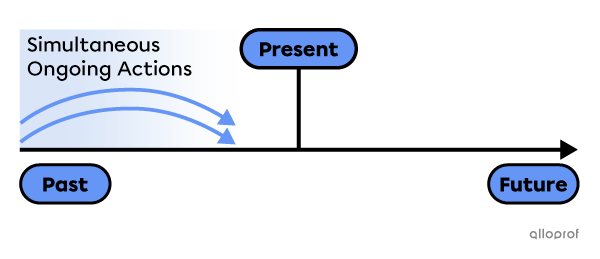
Ongoing simultaneous actions in the past.
-
An ongoing action at a specific time in the past

Yesterday at 8:00 am, Tom was walking to his favourite spot.
-
An ongoing action interrupted by another action in the past

He was sleeping when a loud noise woke him up.
-
Ongoing simultaneous actions in the past
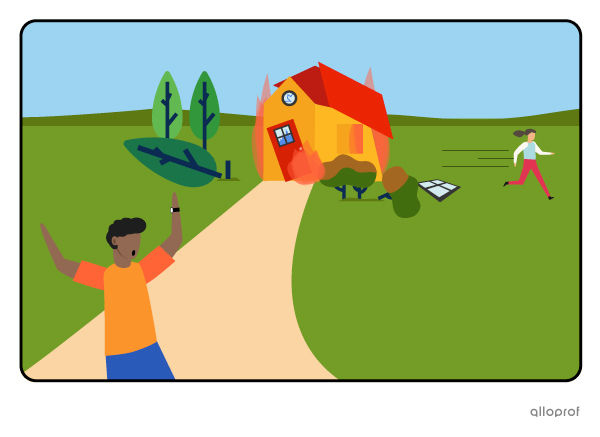

Nadia was running away while Tom was panicking in front of the destroyed house.
-
Setting the Tone
The past continuous can also be used to set the tone in descriptions.
For example:
Tom was running for his life. It was pouring rain. The street lights were flickering and his steps were echoing on the road’s hard surface. Nobody else was walking in the street.
Suddenly, a telephone in a booth at the corner of the street started to ring...
The narration will usually continue in the simple past.
-
Irritating Past Habits*
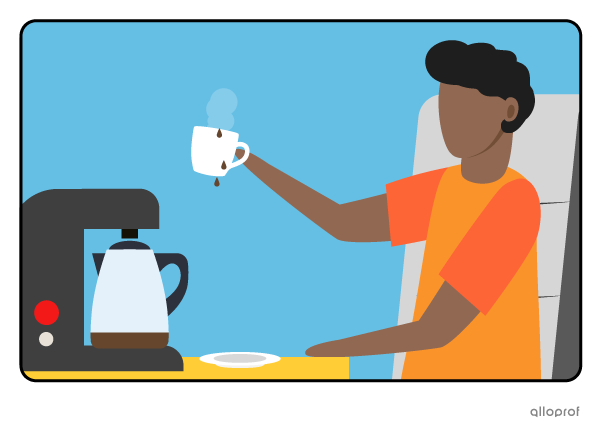

When Tom was younger, he was always drinking coffee in our living room.
*Past habits are used with keywords like always, constantly, forever.
-
Temporary Situations
The past continuous can describe situations in the past that were temporary or unusual.
For example:

This morning, unlike other mornings, Tom was sprinting to catch his train.
Last night, Tom was constantly losing every game he played. He usually played much better.
Points to remember when forming past continuous affirmative sentences:
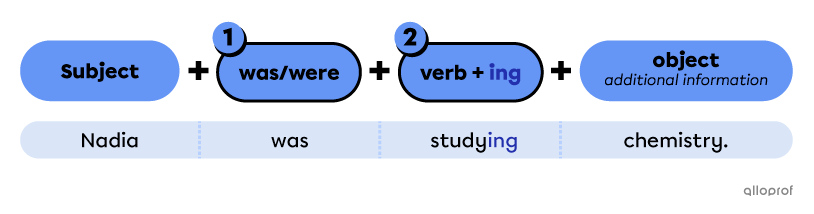

In 2003, Tom was studying chemistry in university.
They were researching new chemical elements.
When vs While
The words when and while are often used in past continuous sentences.
Use when for interrupted actions
Use while for simultaneous actions

He was pouring a liquid into a beaker when it exploded.

While Tom was cleaning the mess after the explosion, Nadia was beginning a new experiment.
The verb after when is usually in the simple past. It represents the action that interrupts the one in progress.
The verbs after while are in the past continuous. While shows the action is in progress.

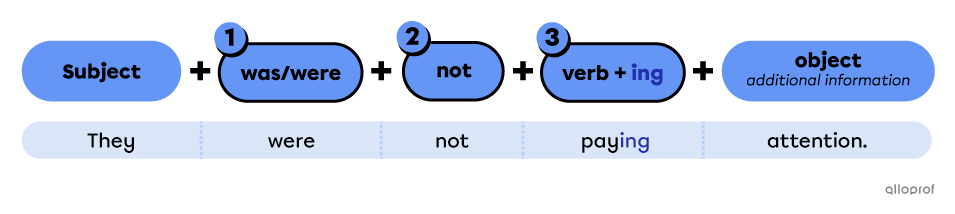
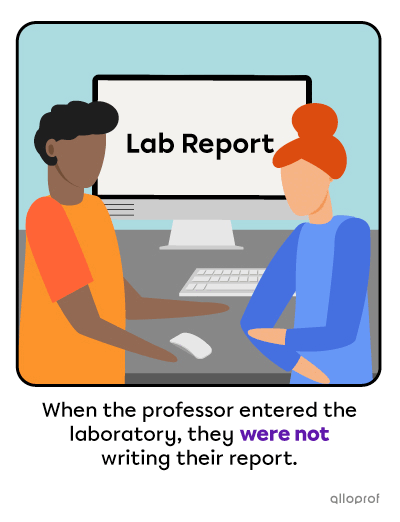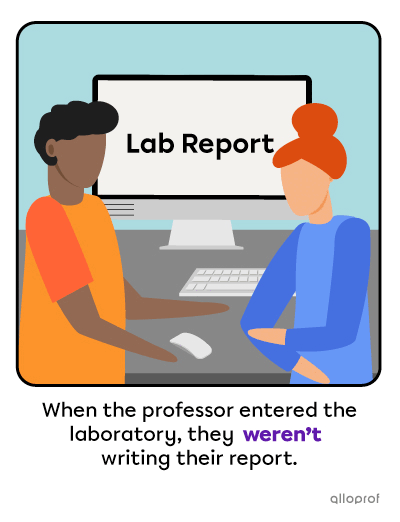
They were not joking anymore after the accident.

Tom was not paying attention when Nadia clapped her hands.
Contractions are often used in the negative form.

-
answered by yes or no
-
answered with information
-
never answered by yes or no
-
use question words
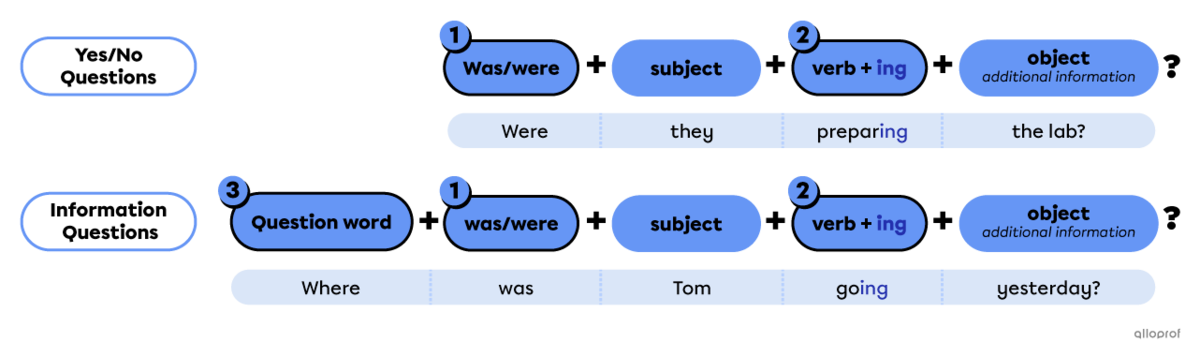
Points to remember when forming questions in the past continuous:
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be (was/were) before the subject.
-
Use the base form of the verb + ing.
For information questions only: -
Place a question word at the beginning
-
Yes/no questions
| Was/were | subject | verb + ing | object*? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Was | Tom | studying | chemistry? |
| Were | they | causing | explosions? |
-
Information questions
| Question word | was/were | subject | verb + ing | object*? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | was | Nadia | testing? | |
| Why | were | they | mixing | chemicals? |
*The object is used only when necessary.