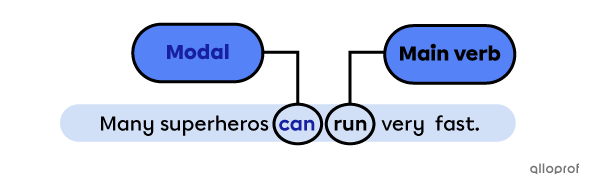
A modal is an auxiliary verb used with a main verb. Modals affect the main verb's meaning and tense.
Modals can be organized into types. These types indicate the meaning added to a verb.
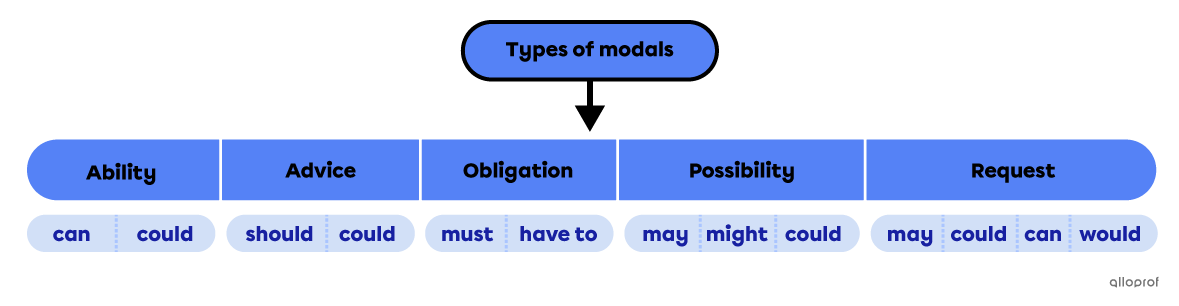
Can is used to express:
-
present abilities and skills
Could is used to express:
-
past abilities and skills
-
conditional abilities and skills
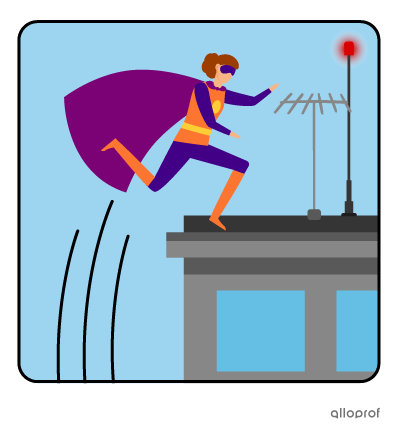

Present ability: She can jump very high.
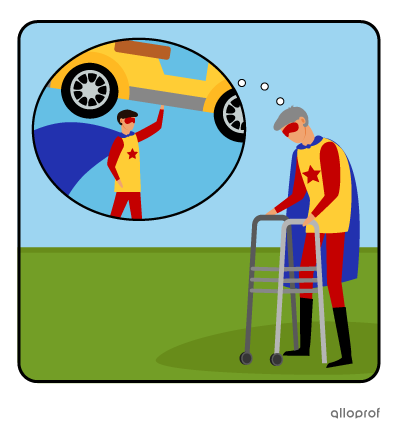

Past ability: “When I was younger, I could lift a car with only one hand.”
Conditional ability: “Maybe I could still lift a car, if I trained very hard.”
Should is used to:
-
give advice
-
make a recommendation
Could is used to:
-
give advice
-
suggest a solution to a problem
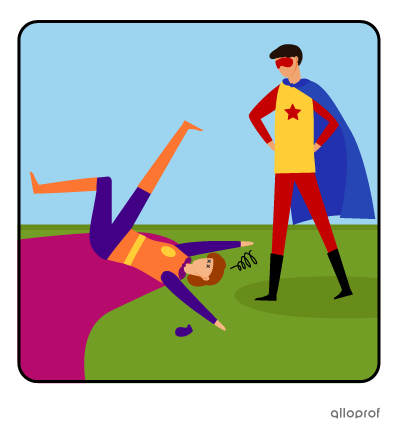

“You should practice your superhero landings.”

“The cape could be shorter.”
Must is used:
-
to express an obligation in the present
Have to is used:
-
to express an obligation
-
to express present, past and future tenses
-
with other modals

“I must defend my city!”

Present: “You have to be more careful.”
Past: “You had to land on your feet, not your face!”
Future: “You will have to take it easy for a few days.”
The modal have to is different:
-
it can be used in several verb tenses and change forms
-
it can be used with other modals
Other modals (can, could, should, etc.):
-
never change forms
-
always use a single modal with the main verb
|
Have to uses: |
Examples: | |
|---|---|---|
|
Present |
have to |
We have to team up against that supervillain. |
|
has to |
She has to practice her superhero landing. |
|
|
Past |
had to |
They had to run away because their enemy was too strong. |
|
Future |
will have to |
I will have to wash my costume after my fight with Skunk-Man. |
|
Conditional |
would have to |
We would have to build a new secret base if you hadn’t defended it. |
|
Possible Obligation |
may have to |
You may have to fight that bad guy again: he escaped last night. |
-
Shall indicates obligation. Less common in American English and more common in British English.
Example: You shall use your power with great responsibility. -
Ought to indicates a moral obligation according to laws, directives, expectations and duties. It can replace should in a context reflecting these situations.
Example: As a superhero, you ought to save the city from evil.
May is used to express:
-
a good probability the action will happen or is true
Might is used to express:
-
a fair probability (not as probable as may)
-
a possibility in the past (past form of may)
Could is used to express:
-
a possibility the action will happen or is true

It may take a long time to learn to fly properly.

Present: He might accidentally get super powers.
Past: It might have worked, if there had not been any problems.

“I think this plan could work.”
Modals of request (also called modals of permission) are used in the interrogative form. They begin a question.
Can is used to:
-
ask permission with very familiar people
-
make a request with very familiar people
-
offer your help
→ Use it moderately.
May is used to:
-
ask permission in a formal situation or with someone you’re a little less familiar with (like your teacher!)
→ Use in most cases.
Could is used to:
-
make formal or informal requests
-
ask permission
Would is used to:
-
make formal requests

“Can I help you with your cat?”

“May I borrow your utility belt?”

“Could you hold this for me?”

“Would you please save me?”
Some modals only affect the tense but not the meaning of the verb.
-
Will indicates the future tense.
Example: They will fight the villain tomorrow. -
Would may indicate conditional.
Example: If she knew how to fly, she would be the best.
Points to remember when forming affirmative sentences with a modal:
-
The modal is an auxiliary verb that is placed before the main verb.
-
Use the base form of the main verb.


“I can grow new arms!”

“You must wear something else.”

“I should get a plane.”
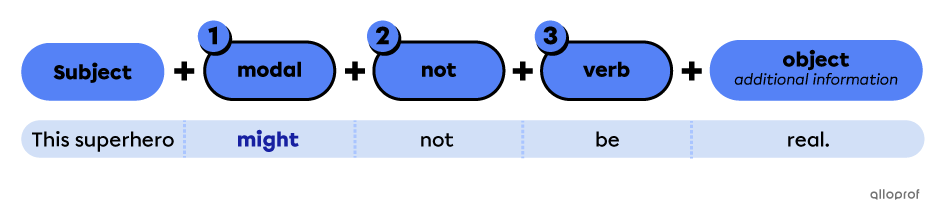
Points to remember when forming negative sentences with a modal:
-
Place the modal (auxiliary verb) before the function word not.
-
Place the function word not between the modal and the verb.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
Modals can be used in their long form or their contracted form.
| Long form | Contracted form |
|
could not |
couldn't |
|
should not |
shouldn't |
|
would not |
wouldn't |
|
cannot |
can't |
|
will not |
won't |
|
must not |
mustn't* |
|
might not |
mightn't* |
|
shall not |
shan't* |
*rarely used (old)
The negative form of can is an exception and is written in one word: cannot.



Have to is not a regular modal. Follow these rules to form a negative sentence:
-
Use an auxiliary verb (do/does, did or will).
-
Place the function word not between the auxiliary and have to.
-
Use the base form have to.
-
Use the base form of the main verb after have to.
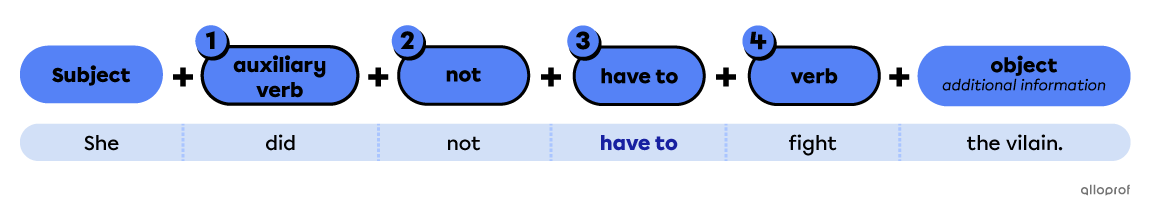
Examples:
|
Subject |
auxiliary |
not |
have to |
verb |
object |
|
She |
does |
not |
have to |
clean |
her room. |
|
You |
didn't |
have to |
take |
a plane. |
|
Points to remember when forming questions with a modal:
-
For a yes/no question, start with the modal.
-
Place the verb after its subject.
For information questions only:
-
Place a question word at the beginning.
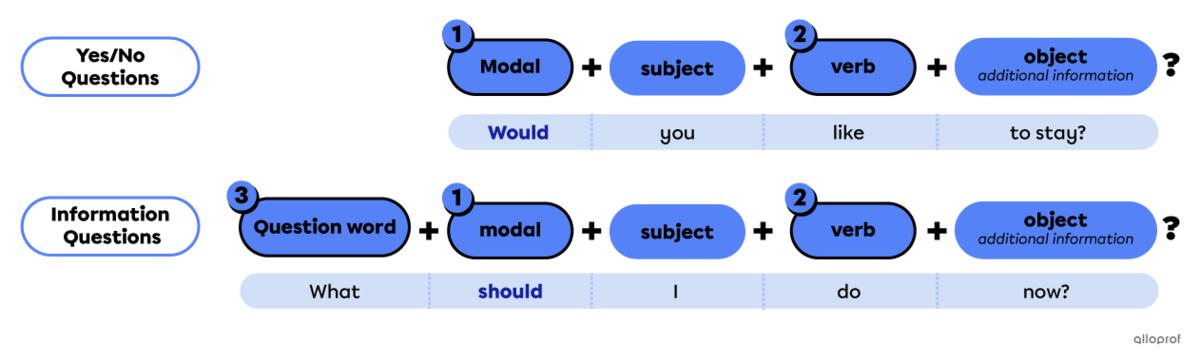
Examples:
-
Yes/no questions with modals:
|
Modal |
subject |
verb |
object |
|
Can |
it |
shoot |
flames? |
|
Should |
we |
open |
this cage? |
-
Information questions with modals:
|
Question word |
modal |
subject |
verb |
object* |
|
Where |
could |
my partner |
be? |
|
|
What |
would |
you |
do |
in my situation? |
*The object is not always necessary.
Have to is not a regular modal. Follow these rules to form a question:
-
Place an auxiliary verb (do/does, did or will) before the subject.
-
Place have to after the subject.
-
Use the base form of the main verb after have to.
For information questions only:
-
Place a question word at the beginning for information questions.
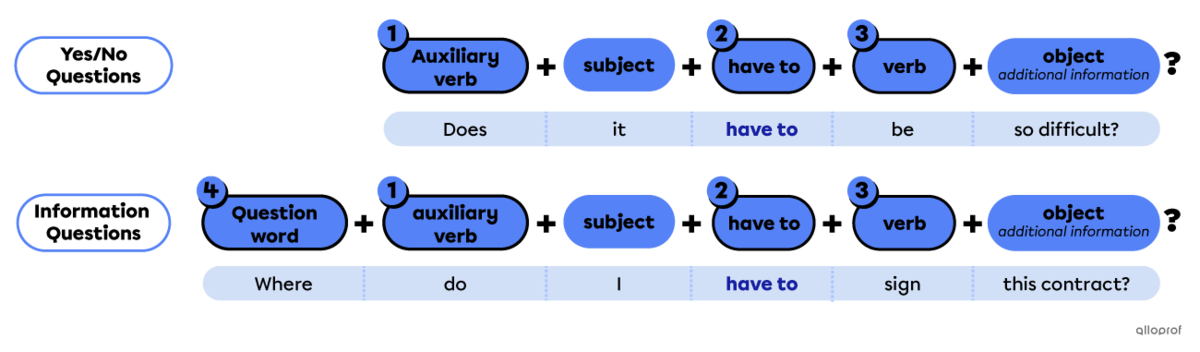
Examples:
|
Question word |
auxiliary |
subject |
have to |
verb |
object* |
|
|
Will |
we |
have to |
pay |
for our ticket? |
|
Why |
do |
you |
have to |
go? |
*The object is not always necessary.