Questions are interrogative sentences. They are used to ask for information.
Most common question types:
Yes/no questions
-
answered by yes or no
-
begin with an auxiliary verb or the verb to be
Information questions
-
cannot be answered by yes or no
-
ask for a more complete answer
-
begin with question words
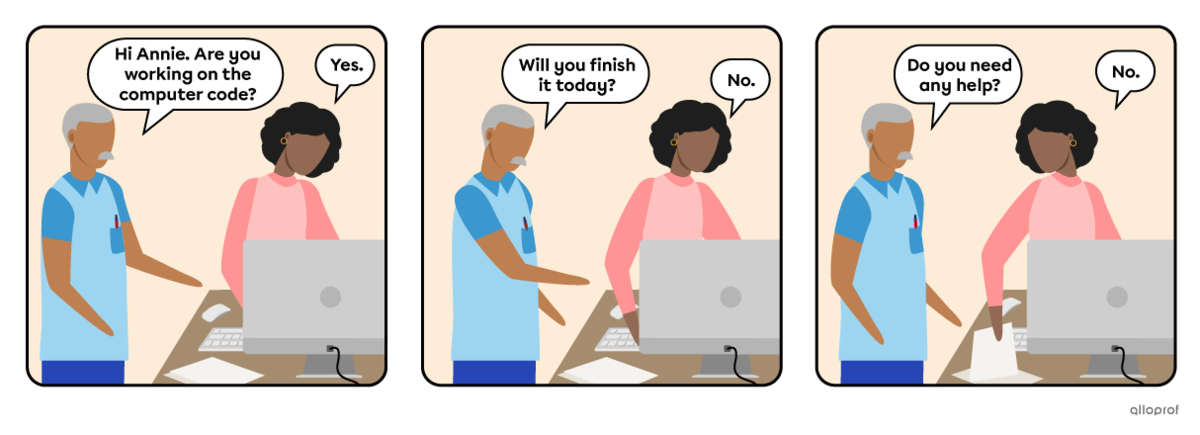
The 4 elements of a yes/no question:
-
The auxiliary verb indicates the verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The verb is the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
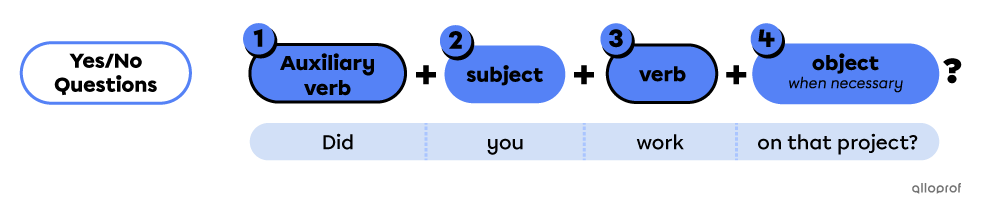

| Auxiliary verb |
Subject | Verb | Object |
| Are | you | working | on the computer code? |
| Will | you | finish | it today? |
| Do | you | need | any help? |
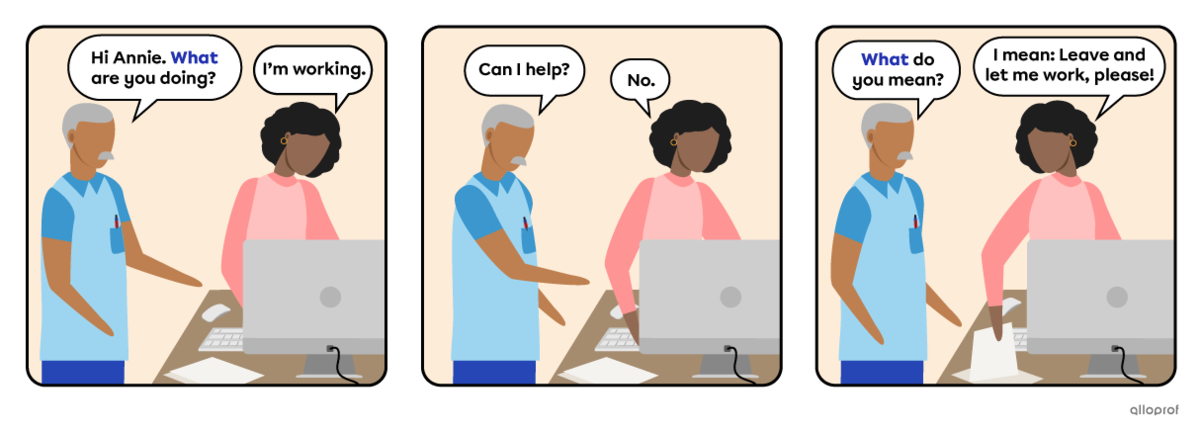
Information questions use almost the same structure as yes/no questions, but they start with:
- A question word indicating what the question is about.
Next, use the same yes/no questions form for the rest:
-
The auxiliary verb indicates the verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The verb is the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
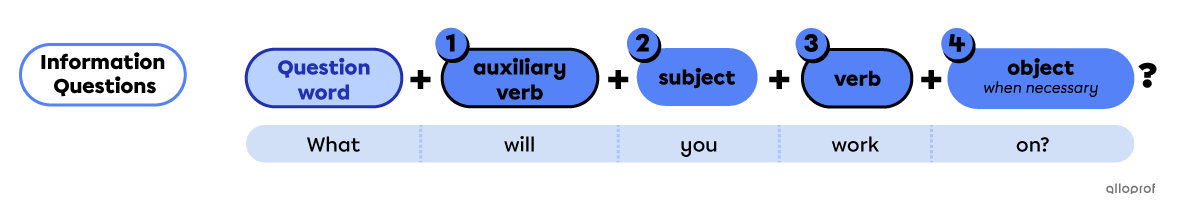

| Question word |
Auxiliary verb |
Subject | Verb | Object |
| What | are* | you | working | on? |
| When | will | you | finish | it? |
| Why | does | it | take | so long? |
*In this example, to be is an auxiliary verb, not the main verb. The verb in the example is to work, conjugated in the present continuous.

| Question word |
Auxiliary verb |
Subject | Verb | Object |
| What | are | you | doing? | No object necessary |
| Can | I | help? | ||
| What | do | you | mean? |
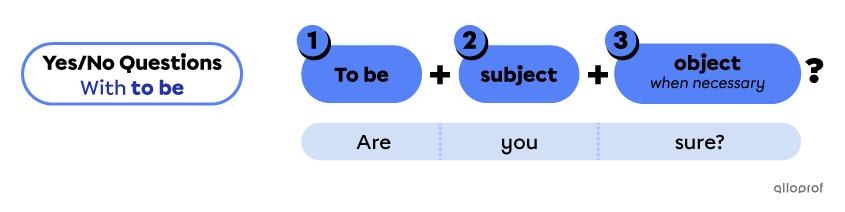
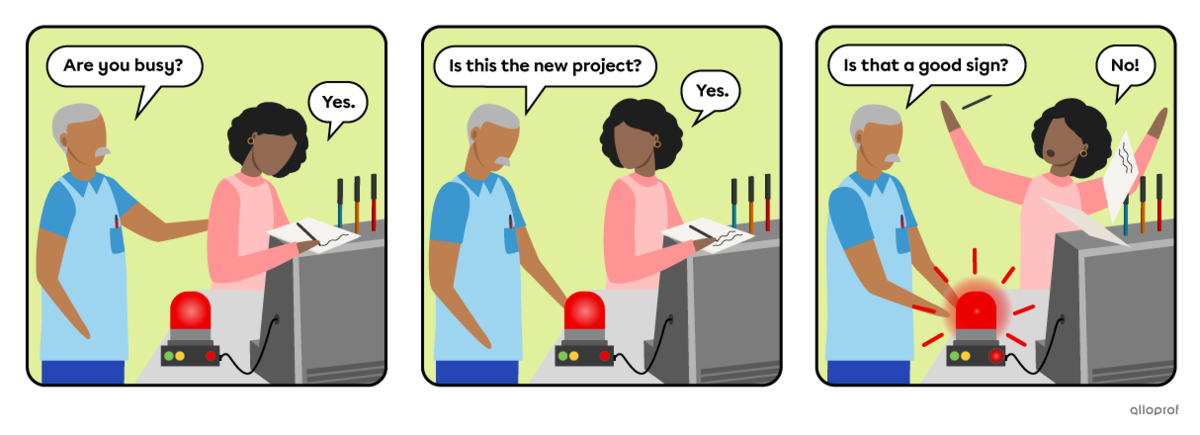
Questions with the verb to be do not use auxiliary verbs when they are in the simple present or simple past verb tenses.
The 3 elements of a yes/no question with to be are the following:
-
The verb to be is conjugated according to the subject and verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.
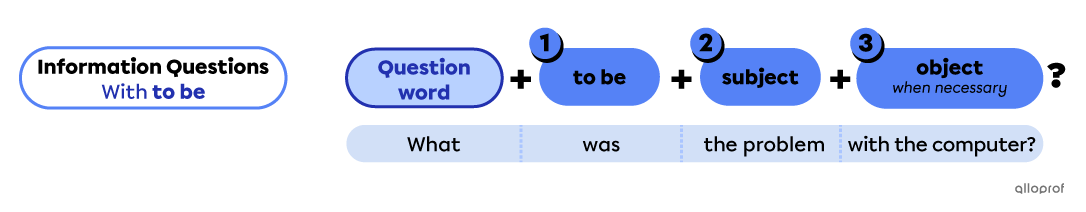
Start with:
-
A question word indicating what the question is about.
Next, use the same yes/no questions form for the rest:
-
The verb to be, conjugated according to the subject and verb tense.
-
The subject is the person, people or thing(s) doing the action.
-
The object is additional information, added when necessary.

| To be | Subject | Object |
| Are | you | busy? |
| Is | this | the new project? |
| Is | that | a good sign? |
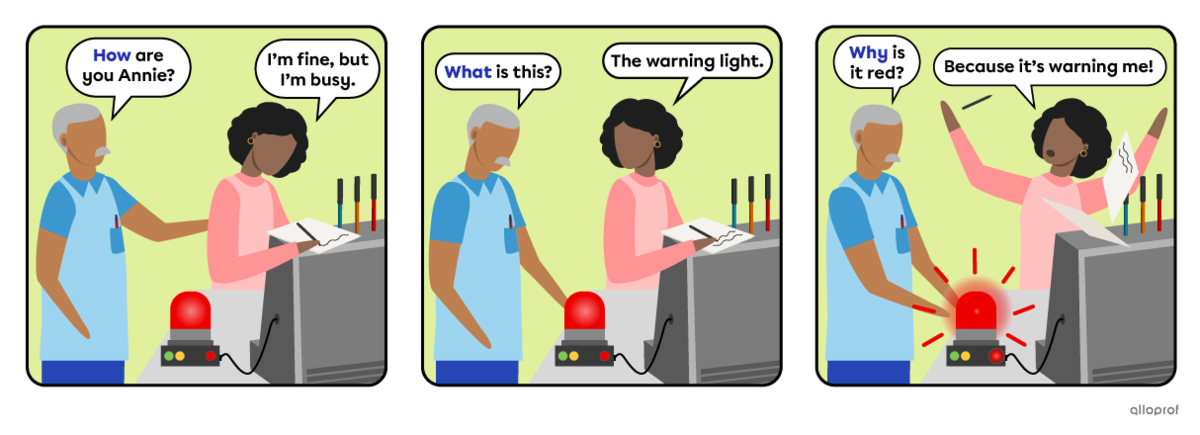
| Question word |
To be | Subject | Object |
| How | are | you | Annie? |
| What | is | this? | * |
| Why | is | it | red? |
*object not necessary
Question words, also known as Wh- words, are used to ask information questions. They indicate what the question is about.
The most commonly used ones are:
| Question word | Asking information about |
| What | things & actions |
| Who | people |
| Where | places |
| When | time |
| Why | reasons & explanations |
| Which | choice |
| Whose | possession |
| How | in what way |
| How many | countable quantity |
| How much | uncountable quantity |
It is 4:00, time for Annie’s coffee break.
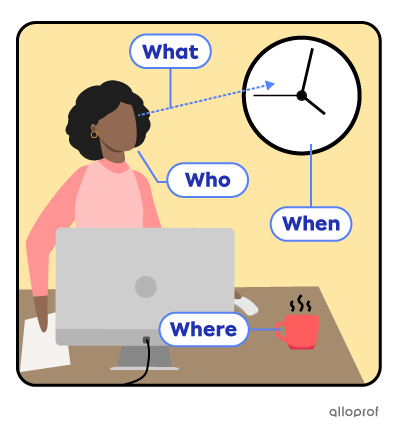
| What | things & actions | |
| What is Annie looking at? | She is looking at the clock. | |
| Who | people | |
| Who is looking at the clock? | Annie is looking at the clock. | |
| When | time | |
| When is the coffee break? | It is at 4 o’clock. | |
| Where | places | |
| Where is Annie’s coffee mug? | It is on her desk. | |
She walks to the coffee machine; Terry is already there.
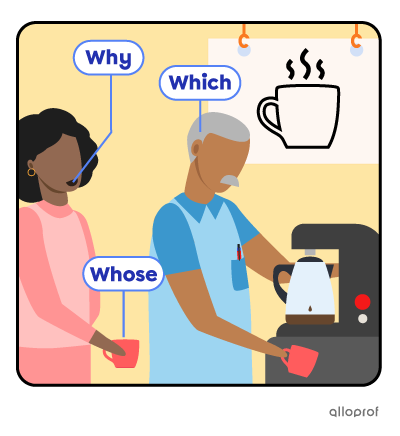

| Why | reasons | |
| Why is Annie smiling? | Because she’s going to get the delicious coffee she loves so much! | |
| Which | choice | |
| Which one of you was there first? | Terry was there first. | |
| Whose | possession | |
| Whose mug is Annie holding? | It’s her own coffee mug (it’s Annie’s mug). | |
Annie is upset because Terry spilled all the coffee on his shirt, again.
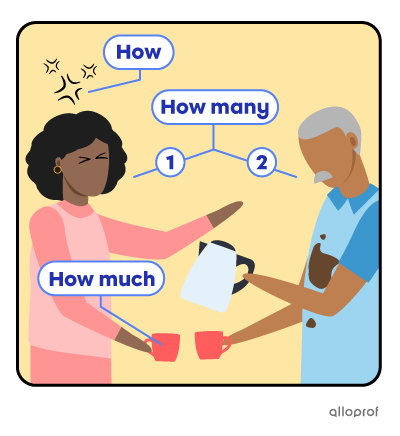
| How | in what way | |
| How is Annie feeling at the moment? | She is upset. | |
| How many | countable quantity | |
| How many people are standing by the coffee machine? | There are two people. | |
| How much | uncountable quantity | |
| How much coffee is Annie going to drink? | None at all, because Terry spilled all of it. | |
Words can be added to question words for more precision.
Nouns can be added to what, which and whose.
| What |
+ |
noun |
| Which | ||
| Whose |
Adjectives or adverbs can be added to how.
| How |
+ |
adjective |
| adverb |
Adding a noun
| What | colour | is this? |
| What | difference | does it make? |
| Which | one | did you watch first? |
| Which | problem | are we fixing? |
| Whose | mug | did you break? |
| Whose | car | are you driving? |
Adding an adjective
| How | big | is the rocket’s fuel tank? |
| How | different | is the new computer system? |
| How | crazy | are you really? |
Adding an adverb
| How | often | do you spill coffee on yourself? |
| How | quickly | can you fix the problem? |
| How | soon | is the rocket launch? |
Questions can be used in a negative form. They are used to:
-
confirm information
-
express an opinion
-
make an offer or a request
-
ask about what did not happen or was not the case.
Negative questions use similar forms to regular affirmative questions. The difference is the addition of the function word not after the verb to be or the auxiliary verb used. The contraction form of not — n’t — is generally used when asking negative questions.
Confirming Information
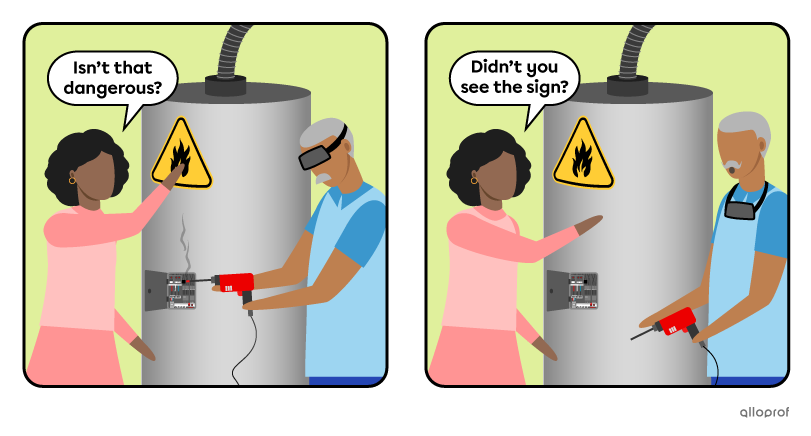
Expressing an Opinion
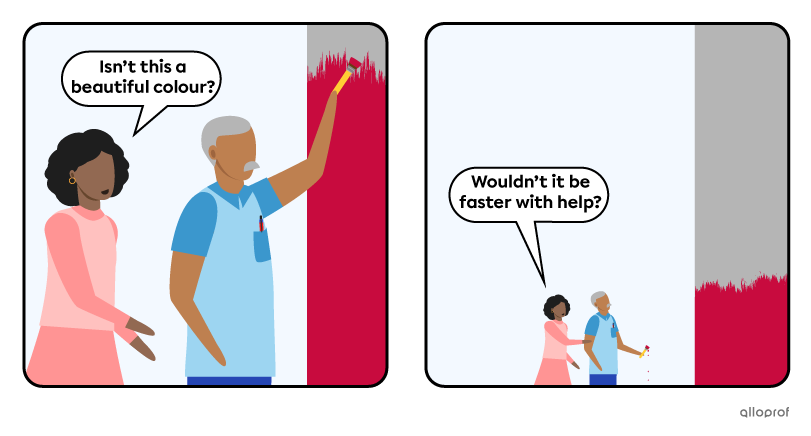

Making an Offer or a Request
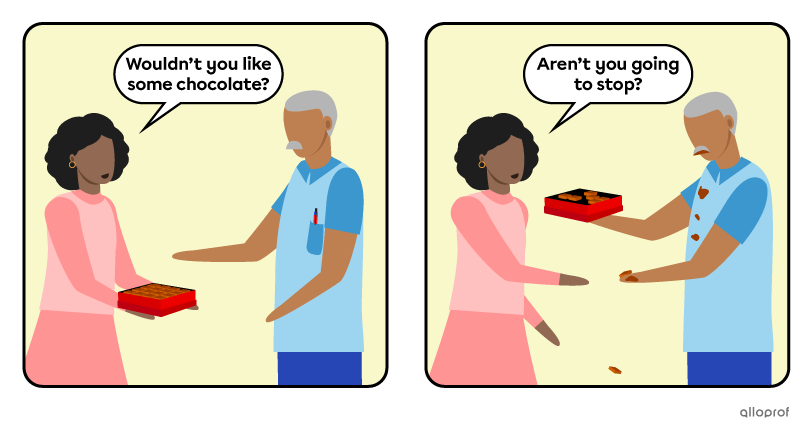

Asking about what did not happen or was not the case
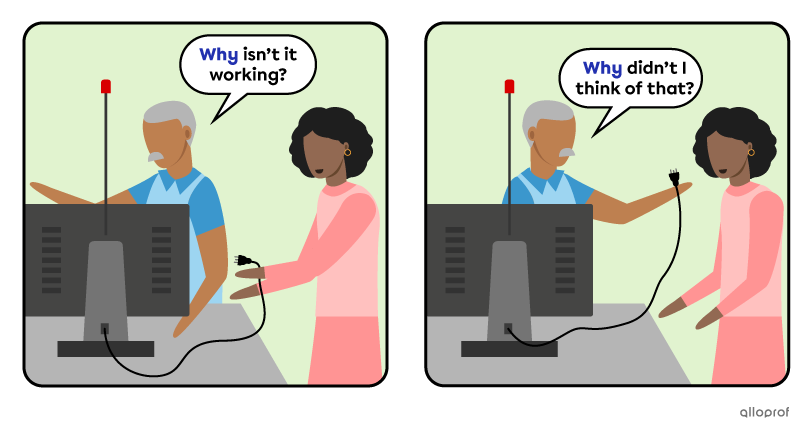

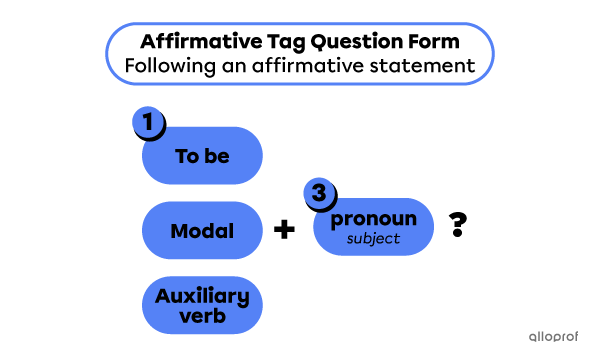
Tag questions are short questions placed at the end of statements. Their purpose is to check if the listener agrees with the statement.
Affirmative statements are followed by negative tag questions.
| Affirmative statement | Negative tag question |
| Annie is a scientist, | isn’t she? |
| You can fix the rocket, | can’t you? |
Negative statements are followed by affirmative tag questions.
| Negative statement | Affirmative tag question |
| Annie isn’t a scientist, | is she? |
| You can’t fix the rocket, | can you? |
Tag questions are formed with 3 elements:
-
the verb to be, a modal or an auxiliary verb to indicate the verb tense
-
the function word not in negative tag questions
-
a pronoun indicating the verb subject.
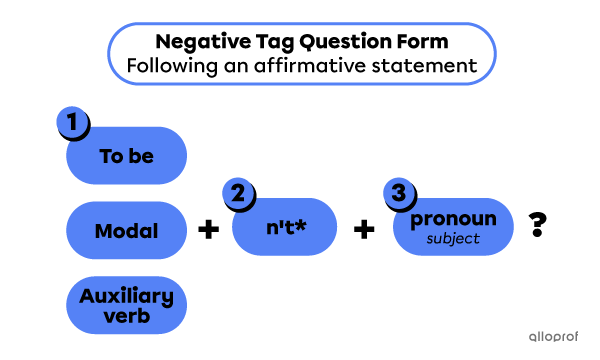
*The contracted form for not is always used in negative tag questions.
| Tag questions using to be | |
| The project is a lot of work, isn’t it? | The project isn’t a lot of work, is it? |
| We are on duty tonight, aren’t we? | We aren’t on duty tonight, are we? |
| This was a good idea, wasn’t it? | This wasn’t a good idea, was it? |
| Tag questions using modals | |
| The system should turn on, shouldn’t it? | The system shouldn’t turn on, should it? |
| Annie can help us fix it, can’t she? | Annie cannot help us fix it, can she? |
| A new computer would help, wouldn’t it? | A new computer wouldn’t help, would it? |
| Tag questions using auxiliary verbs | |
| Annie has fixed the problem, hasn’t she? | Annie hasn’t fixed the problem, has she? |
| You are panicking, aren’t you? | You are not panicking, are you? |
| We have been working efficiently, haven’t we? | We haven’t been working efficiently, have we? |
| Tag questions using no auxiliary verbs in the affirmative statement |
| You write computer code, don't you? |
| We solved the problem, didn’t we? |
| Annie has a lot to finish, doesn’t she? |
Subject questions ask about who or what is doing the action. In subject questions, the question word is used as the subject of the verb.
The 3 elements to form subject questions are:
-
A question word is acting as the subject.
-
The verb is the action.
-
The object* is additional information, added when necessary.
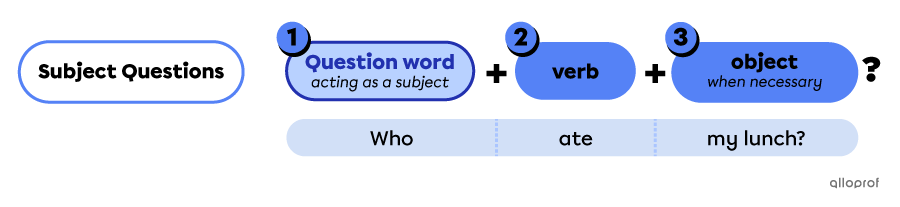
*The object is used only when necessary.
The question words used in subject questions are:
| Question word |
Asking about | |
| Who | people | |
| What | things & actions | Can be combined with a noun. |
| Which | choice | |
| Whose | possession |
| Question word |
verb | object |
| Who | said | that? |
| Who | is working | tonight? |
| What | happened? | * |
| What | is going | on? |
| Question word |
noun add-on |
verb | object |
| What | colours | match | my eyes? |
| Which | computer | works | better? |
| Whose | idea | helps | the most? |
*Object unnecessary for the question.
Rhetorical questions are questions not looking for answers. They are used for effect to emphasise something, make a point, open a conversation, get a reaction, etc.
Rhetorical questions follow the same rules and forms as regular questions.
| Common rhetorical questions | Meaning |
| Who knows? | The speaker doesn’t know and is implying no one else does. |
| Who knew? | The speaker didn’t know and is implying no one else knew at the time. |
| Am I right? | Emphasises what was done or said was correct or right. |
| Are you kidding? | Expresses surprise or disbelief. |
| Who’s to say? | No one knows or on whose authority. |
| Can you blame me? | Justifies a choice or action the speaker did. |
| Who cares? | Expresses it is not important. |
| Why not? | Expresses agreement. |
| Why don’t you? | Suggests or commands. |
The character of Annie used in the examples is inspired by Annie Easley, an American mathematician, a computer scientist and a rocket scientist. To learn more about her life and accomplishments, visit the NASA website.